In This Article
What is Computer File Manager?
Generally, a file manager refers to a software program that enables the users to view the files on their computer storage, edit, copy, or delete them as and when required.
In plain and simple words, a computer file manager allows the users to manage and organize their files.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A file manager or file browser allows the users to perform necessary operations on a file or a set of files. Every operating system has one.
- It can be used to create a new file or open and rename, edit or print an existing file. You can also copy a file, move a file, search files, delete files and even modify the file properties and permissions using the file manager.
- It comes with useful features such as different view modes, editors, drag-n-drop, file sorting, built-in control feature, and multi-language support, audio and video players.
Understanding a Computer File Manager
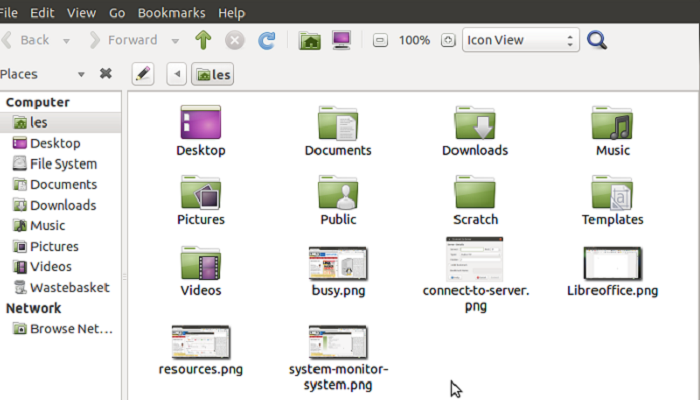
A file manager, also referred to as the file browser, offers a user interface that allows the users to perform some of the most common yet necessary set of operations on a file or a group of files. Some of these operations include:
- Creating a new file
- Opening an existing file to view, edit or print
- Renaming an existing file
- Copying or moving the entire file
- Searching for specific files
- Deleting unnecessary files from the folder and
- Modifying the attributes and properties of the files along with file permissions.
Usually, the files and folders are displayed by the file manager in a stratified tree based on the structure of the directory which makes it easier for the users to browse them.
Though the file manager allows the users to view and organize their files, it is the operating system that actually allows the users to store and access the files on a storage device.
As Microsoft Windows improved in the newer versions, Windows Explorer became the default file manager.
On the other hand, in the case of Apple computers, Finder is the default file manager.
The file manager window typically has two panes where the left pane shows the most commonly used folders, displays the network and devices.
On the other hand, the right pane of the file browser displays all the contents of the folder that a user selects in the left pane.
You can also view the files on the storage of your computer in different ways. These include:
- Icon View: This is basically the default view of the files and folders in the file manager.
- List View: In this option you can see the files and folders as a list which also includes all relevant information in detail regarding the files such as their name, type, size, time and date of creation or when the files was last modified.
Both theoretically and practically, a file manager is very useful for the users to the extent that it would be impossible to manage the files without this specific feature of a computer.
Features
Computer users all over the world use a ton of information every day.
Most of the files and folders created by them are stored on the computer but a significant amount of files may also be stored in the cloud.
Therefore, they need a more competent file manager to work on all the files irrespective of where they are stored.
They need much more advanced features than simply being allowed to edit, move, copy, and delete files or folders as is offered by a standard JavaScript file managing application.
However, users who like the old school way imagine that Windows File Explorer is the only file manager and is the simplest one at it as well.
Well, it does have adequate features and functionality to be sufficient for users using a home laptop but when you need to deal with multiple documents at the same time the features of it may turn out to be inadequate.
In such situations you will need to use something from the ‘Generation next’ that comes with enhanced features to suffice modern file management systems based on JavaScript. Some of these features include:
- Various view mode such as dual-panel view, cards view, table view, as well as customization options and a preview panel
- Text and image editors that will allow making quick changes in the text of a document or crop an image
- Drag-n-drop feature that will allow quick moving of files from one location to another
- Sorting and searching feature to quick search from a lot of different files based on specific parameters such as size, name, date of creation and more
- Support different sources so that the data of the file system can be taken from any sources such as physical stores, cloud storage or any other
- Built-in audio and video players so that the AV files can be played in the preview panel
- Built-in access control feature that will assign access rights to restrict access to files and folders and allow the users to hide internal information when required from the customers and
- Multi-language support so that it allows translating the context menu of the file system into any supported language.
Considering all these features, you should choose a file manager based on your requirements and that of the particular project.
Here are a few specific types of file managers along with their respective features that you can choose from.
The features of the file manager can be different which may vary according to the type of file manager concerned.
It also depends on the different attributes of the files browser itself such as its type of file transfer support, networking and user interface.
For example, when you are using a graphical file manager, it will allow you to copy or move files using the ‘copy and paste’ and ‘cut and paste’ options respectively.
You can also drag and drop the files as well as select a different menu for the target path.
The file manager will show both the source as well as the destination directories when you transfer files.
Along with that, it will also show other different things related to the file transfer such as:
- The transfer process or progress as a percentage along with the size of the file
- The progress bar
- The name of the file that is being transferred
- The total number of files and/or the remaining number of files
- The numerical and graphical transfer rate.
It will also allow you to pause the process of file transfer which will allow access by other software for a full sequential read temporarily.
You can resume the file transfer process later on and for that you will not have to restart the file transfer.
There are a few specific types of file managers that may allow moving multiple files.
You can copy and delete each of the selected files individually from the source.
On the other hand, there may be a few specific types of file managers that may copy all of the selected files first and then delete them from the source later on.
The features of the file managers may also vary depending on the user interface.
For example, there are file managers that come with features that are similar to the features of the web browsers. These features include:
- An address bar
- Forward and backward navigation buttons
- Tabs
- A bookmark sidebar and more.
The features of the file managers may also vary according to the networking.
For example, there are a few particular file managers that provide network connectivity through different networking protocols such as:
- HTTP
- FTP
- SMB
- NFS
- WebDAV.
This is attained by letting the users browse for a file server by connecting and accessing the local file system of the server or by offering the full client implementations of it for file server protocols.
As said earlier, the features of the file manager will vary according to the type of it. Here are some of them for your knowledge.
File-List File Managers:
These file managers are older and are lesser known than the orthodox file managers.
The Neptune File Manager is one example of a File-list file manager that operated on Xerox Alto and was used extensively in between 1973 and 1974. It had some features that are typically found in the orthodox file managers.
Another good example of this type of file manager is flist. This was introduced on the Conversational Monitor System sometime before 1980.
This file manager is considered to be a variation of FULIST, according to its author Theo Alkema, which was introduced before late 1978.
Typically, the flist file manager came with a list of files that existed in the minidisk of the user.
Users can sort the files by any file attribute and it also allows passing the file attributes to scripts or function-key definitions.
This made it pretty simple to use this particular file manager as a part of different script types such as:
- XEDIT
- CMS EXEC and
- EXEC 2.
This particular software program supported only IBM VM/SP CMS.
However, it provided inspiration to other programs including file-list as well as others that ran on different other operating systems including flist that functioned OpenVMS and FULIST that operates on Unix.
Orthodox File Managers:
Orthodox File Managers, which is also referred to as OFM sometimes, are text menu based or command based file managers.
These file managers are considered to be one of the longest running families prior to the GUI or Graphical User Interface based types.
The OFMs typically come with three windows which include one command line window and two panels.
The command line is an essentially minimized shell or command window that you can expand to full screen.
The two panels, on the other hand, are situated symmetrically at the top of the screen.
These panels can be hidden or even resized with normally the last line of the command line in the terminal window visible only.
Only one of these two panels is active at any given point of time. This active panel comes with a file cursor.
This panel shows the information related to the directory that is being worked on currently as well as the files that are contained in it.
The active panel contains the files that serve as a source of files on which the file manager performs the specific operations such as copying or moving files from this panel to a destination that is represented in the other passive panel.
This method is most effective for system arrangements where the keyboard is the sole or main input device.
On the other hand, the passive or inactive panel contains the contents of the same directory or any other which is considered to be the default target for the file operations.
The display can be customized which appears in the columns that contain the relevant information of the files.
The users are also allowed to switch between the active panel and passive panel easily when desired by simply pressing the tab key.
These allow a closer and more effective integration with the operating system shell underlying through the command line.
It uses the terminal window related to it, which allows viewing the output of the shell commands entered and executed on the command line.
These file managers allow the users to use a lot of keyboard shortcuts which free them from using the mouse.
The users are also allowed to create their own scripts and file associations that appeal to a specific type of files and organize them in a hierarchical tree like user menu or user script library.
In addition to that, the users can also expand the functionality of the file manager by using the Start menu, User menu or the Extensions menu.
Some other common and useful features of the orthodox file managers include:
- Information is displayed on the active and passive panels to use them to build commands such as current file, path to left or right panel and others on the command line
- A built-in viewer for the fundamental file types
- A built-in editor to import specific components of the panels into the text that is currently being edited
- Virtual File Systems or VFS support to view compressed archives or to work with files using an FTP or File Transfer Protocol connection
- A word commander in the name
- A path that shows the source and destination of a directory that is being used and
- Details of the size of the directory along with disk name and usage usually at the base of the panels.
The GUI file managers also come with an additional tabbed interface where the Function keys from 1 to 10 can be used and it is the same for all orthodox file managers.
For example, F5 will copy a file from the active panel to the passive panel and F6 will move the file.
There are some file managers that also come with tabbed panels, such as Total Commander, which allows the users to manipulate several active and passive directories at the same time.
Portability is one exceptional feature of the orthodox file managers which are available in most of the platforms with both graphical and command-line interfaces which deviates from the norm.
This allows users to work with it on different platforms without having to do much of relearning about the interface and these file managers are also actively supported by the developers.
Navigational File Managers:
In spite of being a newer type, the navigational file manager has dominated the file management field for desktop computers, especially after the introduction of Graphic User Interfaces.
Typically, this particular type of file manager also comes with two panes.
However, these two panes are asymmetrical, unlike the two panes of the orthodox file managers, both in their use and contents.
The left pane shows the file system tree and the right pane contains the contents of the same.
However, the theme of this specific file manager is quite different in the macOS where it offers a Miller columns view in the Finder.
The navigational file manager is designed on the following concepts:
- To display the location that is viewed currently on the window
- To allow changing the location of the current directory being viewed
- To represent files, directories and programs with the help of icons and
- To change the location of the open directories by typing a different location or by pressing the back button or by using the supplementary pane with part or whole of the file system being represented by the navigation tree.
The interface of the navigational file manager also looks pretty much the same as the web browser complete with forward, backward, and reload buttons.
In most of the navigational file managers there is also an address bar where the users can type the path of a file or a directory or a URL.
When you select a directory in the navigation pane located on the left side it will be designated as the current directory.
This means that it will display the contents of it in the Contents pane which is located on the right.
However, when you expand (press the + sign) or collapse (press the – sign) a part of the tree, it will not change the contents displayed on the right pane even if you do not select a directory.
But, it may not be the same when you collapse a parent of the existing directory.
In such cases, the selection will be realigned on the current parent directory that you have collapsed which will, in turn, change the list displayed in the Contents pane.
The good thing about the navigational file manager is that while moving from one location to another you will not need to open a new window.
You can easily open the file manager and communicate by using the clipboard or drag-and-drop operations.
This means that you can see more than a few directories at the same time and carry out cut and paste activities between instances.
The file operations in this case are based on drag-and-drop as well as the editor metaphors.
This means that you can select a file or a directory and then copy it on the clipboard and paste it further in a different location in the file system as well as in a diverse occurrence of the file manager.
Spatial File Manager:
File managers that have a spatial mode, such as Nautilus, are called spatial file managers.
However, it was removed with the advent of GNOME 3.x version where each of the windows displays the directory that is open.
These file managers use a spatial metaphor in order to signify directories and files just any physical object.
This means that the spatial file managers emulate the ways in which people typically interact with physical objects.
The spatial file managers follow specific concepts such as:
- Each open directory is represented by a single window and
- Each of these windows is unmistakably and irreversibly linked to a specific directory.
Spatial file managers offer stability. That is to say that the directories, files and windows go where the users move and put them and they stay there.
This means that they maintain their spatial state. The files and directories also retain their other specific physical attributes such as:
- Their size
- Their shape
- There color and
- Their location.
Also, the users can view the same item in one window at a given point of time.
3D File Managers:
The 3D file managers are a specific scheme that has been attempted by a few projects to implement in displaying the structures of files and directories.
However, these types of file managers have not become popular since there are no specific standards followed in this type of system.
Also, the precise implementation seems to differ from one project to another.
Web-Based File Managers:
The web-based file managers typically represent the scripts written in different languages. These can be Ajax, Perl, PHP, ASP or any other server-side language.
These file managers use a web browser without a FTP or File Transfer Protocol Access while managing and editing files and directories located on a remote server or a local server when installed there.
The web-based file scripts are quite advanced and normally are commercially distributed for administering and managing files and to construct more secure user accounts with respective permissions for each account.
This means only those people will be allowed to access any document who are authorized to, whether these files are stored on the user directories of the individuals or on the server. They can access these files by using any web browser from anywhere and anytime.
For any organization, the web-based file manager may act as the digital repository of the company.
Here the organization can store different documents, publishing layouts, digital media and presentations.
They can store, manage and share these files internally or even externally with customers, remote workers and suppliers.
The use of these web-based file managers are growing increasingly.
The main reason for their popularity is due to the rise in the popularity and demand of more dynamic web Content Management Systems or CMS.
It also helps in managing media on the websites according to the needs of the non-technical website moderators.
How to Use?
There are several use cases of this software program and it varies according to the app used or the person using it.
Some of the most significant uses of it are as follows:
- The file manager allows the corporate apps to use it to store all of their documentation related to HR such as Corporate Values, Employee Handbook and more.
- As for the app of an insurance company, the file manager can be used by the field agents of the company to upload claim photos and process.
- And, in the field of education, this useful feature can be used to provide the students with relevant and important documents related to their studies. The students can also use it to submit their completed projects.
Every operating system has a file manager whether it is Windows, macOs or Linux and for different operating systems the uses of the file managers are different.
But before knowing the uses of them, you should know how to access the file manager in each different operating system separately. Check out alternative file managers.
In Windows 10:
The default file manager of Windows 10 is File Explorer. It is easy to access it because the icon of the File Explorer app in the form of a folder is pinned to the taskbar. This is the easiest and fastest way to access it.
Some other options to access it include:
- From the Start Menu – Select Start, type File Explorer in the search bar, and click on the File Explorer desktop app.
- Via Run Command – Select Start Menu, type or go to Run, type Explorer, click OK.
- By Right clicking on Start Menu – Right click on Start Menu, click on File Explorer.
When open, this file manager will prove to be one of the more functional apps of Microsoft when you use it to browse folders, manage files, and preview the contents of the files.
In macOS:
Named Finder, the file manager in Mac is always running and it is the app the system will start up with provided you have not messed up with the default behavior of Mac.
In Linux:
Linux, as it is, is known to be a complicated operating system to use but the recent versions of it are quite intuitive.
There are several default file managers incorporated in some of the popular Linux distros such as Nautilus, Nemo, Dolphin, PCManFM, Caja, Thunar, and Pantheon Files.
Accessing and using these file managers may vary from one operating system to another but to keep things simpler the Linux developers ensure that you can access the file managers in the pseudo Start menu on the taskbar or a desktop icon.
In Android:
If you are using an Android OS higher than 5.0, the file manager can be found by default. In order to open it all you have to do is tap on the file manager app icon in the apps list.
This file manager is very simple to use due to the simplistic design of it. It will satisfy the needs of simple browsing, copying, moving, or opening files.
In iPhone:
Though the initial iPhones did not have a file manager app in them, it was introduced by Apple with the iOS 11 with the inclusion of a Files app in the home screen. This is able to access and manage files stored on the local device.
It is also very basic in nature, just as the default Android file manager and supports basic file management operations such as opening, copying and moving files quite well.
The primary use of the file manager, as stated earlier, is to download, upload, and manage files within the app. However, the uses may vary depending on where you use it.
For example, when you are using it in the dashboard of the app itself, you will see that there are two parts in it namely, files and folders.
If you want to organize your files by using the Folders option, you are advised to create those files first and then upload them to the folders.
On the other hand, if you do not want to use the folders option, you can upload the files to the file manager’s home screen.
If you want to add a new file or folder, the first step to follow is to click on the ‘Add New’ green button in the lower right hand side corner under the Files section. After clicking on it, you will find two options – one, to create a new folder and two, to upload a new file.
If you want to upload a file, the File Explorer will come up on your computer.
Here you can find the file that you wish to upload. From here you can upload the file to the home screen of the file manager.
You can also upload more than one file at the same time after the initial file that you wanted to upload has been uploaded.
You will have to select the ‘Add More Files’ option from the prompt for that.
If you want to upload files to folders, you will have to create a new folder first by selecting the ‘New Folder’ option and then name the folder and click on ‘Create.’
The created folder will be seen in the ‘Folders’ section.
When you see the folder, click on it to enter and upload files to it. You may also include subfolders to it by using the ‘Add New’ button.
You can create as many subfolders as you like.
If you want to steer back to the home screen of the file manager you will simply need to click on the ‘Home’ button.
This is located at the top left-hand corner of the dashboard of the file manager app.
You can use the navigation area to move to folders of higher level.
You can delete or rename a file after you have created it at a later point in time by clicking on the three dots located next to the folder.
You can also delete the files you have uploaded to the file manager and will also have an extra option to download it.
Users can use the file manager app to interact with its features in different ways as well.
For example, if you want to create a new folder or upload a file in the file manager app, you simply have to tap on the + button.
This is located at the right hand corner at the bottom of the screen.
You will get a prompt asking you whether you want to create a new folder or want to upload a file.
If you click on Folder, you will get an option to tap on ‘Create’ to create it and rename it.
One the other hand, if you click on File, you will get a prompt where you will have to click on ‘Add More Files’ so that you can access the files in the storage device to upload them.
If you are doing this for the first time, you may additionally be asked to allow the app to access the files on your device. You will need to accept it.
For deleting, renaming, and downloading a file, the same process of clicking on the three dots next to the File or Folder is to be followed.
That is all you have to do in order to manage your files via the file manager and interact with the features of the app.
Conclusion
Sometimes you may not need all the functions of the file manager when you work on a certain project since few features can be too specific.
Thanks to this article, now you know what added features to look for and how to scale up while using the most suitable file manager for your computing needs.