In This Article
What is CPU Fan?
A CPU fan is located on top of the processor that pulls hot air off it to keep it cool. This is a hardware device that can be axial or centrifugal in design.
The CPU fans can come in different sizes and usually in a 3-pin or 4-pin fan connector variant.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A CPU fan follows the thermodynamic principle of convection while pulling off the hot air from the CPU and to cool down the heat sink and the graphics card as well.
- The CPU fans can be classified into three major groups according to the connectors such as the Molex fans, Pulse Width Modulation fans and DC fans.
- These fans can be further classified according to their design and bearings such as static pressure, airflow and hybrid fans and fluid bearing, ball bearing and Maglev bearing fans, respectively.
- By removing the hot air, the CPU fans play a significant role in preventing damages to the internal components, lower and slower performance and system crashes or hang-ups.
Understanding CPU Fan
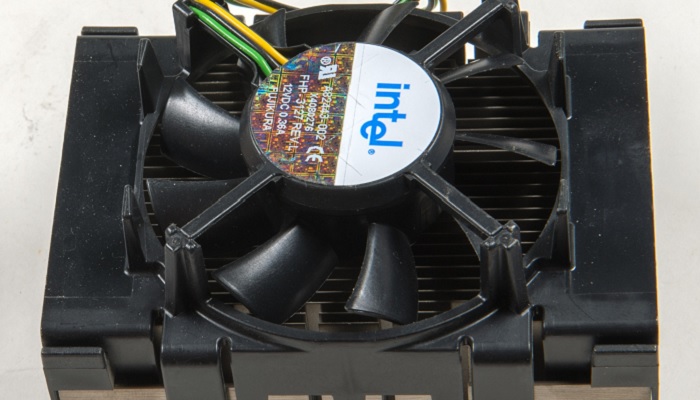

If you ever open up the computer casing and look at the motherboard, (Though it is not recommended, especially if you are technically challenged), you will see a big box inside.
This is actually a fan that is attached to the CPU. That is why it is called the CPU cooling fan.
Just as the name signifies, the primary purpose of the CPU fan is to keep the CPU cool by blowing the hot air away.
Therefore, a CPU fan does what all other fans do – it blows air.
Design
The design of the modern fans also helps in more efficient cooling.
There are heat pipes at the base of the fan that connect to the fins. Most of the modern CPU fans also come with variable speed control features.
There are sensors in the motherboard that monitors the temperature of the CPU when the computer runs.
These sensors direct the CPU fan to speed up when the temperature is high and slow down when it is at low level.
All these happen according to the load and type of activities performed on the computer.
Whether the cooling system is liquid-based or air-based, a part of it consists of one or several fans.
The design of a cooling system includes:
- A heat sink that drains the heat away from the internal components
- A radiator to which this heat goes and
- A fan to disperse the heat away from the computer.
Depending on the fan design as well as the CPU, it may stop when the CPU is idle and start spinning when it performs intensive operations such as running graphics-intensive programs.
Ideally, the CPU is designed to operate silently even at high speeds.
However, if you hear some noise from it even when it runs at a low speed while you perform less intensive tasks on your computer, it indicates an issue or a rogue malware running.
Working Process
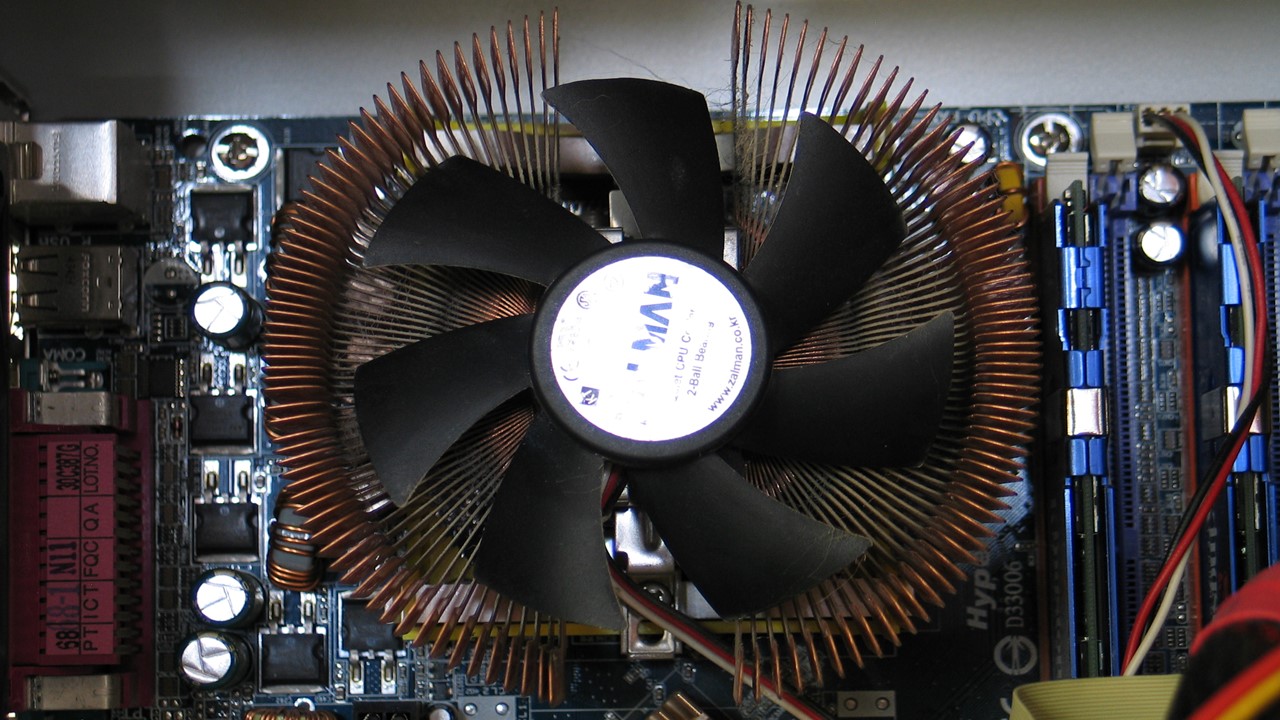
A CPU cooling fan works on the basic thermodynamic principle, convection.
This is the principle that states that any hot object will transfer the heat to the air molecules near its surface in order to cool it a bit.
These hot air molecules keep floating and if these are blown away, the surrounding will be cool since the cooler air will replace them.
These molecules will then absorb the heat and this process goes on and on, provided there is a fan to blow the hot molecules away continuously.
If the stream of cool air is constant, the rate of cooling will be significantly increased.
However, simple convection and a fan will not be enough to keep the CPU cool since the temperature inside can really reach a very high level.
That is why there are heat sinks that conduct heat.
Maximum contact is provided by the greater surface area of the flat bottom of the heat sinks in contact with the CPU.
Also, the upper surface comes with a series of narrow fins.
Between these fins there are air channels that also help in connective cooling due to enhanced surface area.
This increases the amount of hot air for the CPU fan to dissipate.
Functions
The main function of the CPU fan is to blow the hot air from the inside of the computer case out in order to keep the internal components cool.
It also helps in cooling down the heat sink of the CPU and even the graphics card.
Therefore, indirectly, the CPU fans prevent the system from shutting down or crashing due to the hot circuitry inside.
It pulls air through any opening and vent available in the computer including the keyboard if you are using a laptop.
Types
Usually, a CPU fan is sold along with a heat sink and may come in different sizes and types.
The specification may also differ based on different parameters.
Though the purpose of all these fans is the same, the CPU fan can come in a few different types.
The best way to know what type of a CPU fan is installed in your computer is by checking the connector of the fan.
Based on the connectors, there can be three major types of CPU fans which are explained as under.
- Molex Fans – These fans use flat 4-pin connectors and are connected directly to the power supply. However, these fans bypass the motherboard and therefore are not possible to adjust manually.
- PWM Fans – These fans are called Pulse Width Modulation fans. You can adjust these fans manually. These fans use a small, rectangular, 4-pin connector that plugs into the motherboard directly.
- DC fans – These fans are more or less the same as the PWM fans. However, there is one exception. These fans typically come with a 3-pin connector. The one less pin however makes these fans a bit less power efficient. It also lowers its performance level.
More often than not, the manufacturers of the CPU fans also categorize their products based on their design aspects such as the size, blades, and the bearing technology.
Based on these particular factors, you can also have a few other options.
Blade Design
The design of the blade of the CPU fan will determine the volume of the airflow and its effectiveness.
Based on the design of the blades, the CPU fan can be categorized into these three main varieties:
- Static Pressure – These fans are good for heat sinks and cooling radiators since the blades are flat and thicker, which leaves a very small gap between them. This gives more force to the air entering inside the case and while passing through a thick filter. The thicker blades reduce splash back of air where the air slips back into the opposite direction if the blades are thinner after hitting an obstacle while leaving out the case.
- Air Flow – These fans have larger gaps between the blades which allow a larger volume of air to pass through. However, these fans are not a very good option for heat sinks and cooling radiators because the air is pushed out with less force and the larger gaps also result in more splash back.
- Hybrid – These fans will give you the best of both worlds such as swept blades for more efficiency in air scooping and increased velocity. The larger gaps will also ensure that the airflow is excellent within. The blades have lower density and are less flat which reduces noise and turbulence allowing the fans to run more quietly.
Diameter
As a rule of thumb, the static pressure of a fan will be more if it is smaller in size, even if it has a lower RPM or Rotations per Minute.
The smaller size reduces the torque required to rotate the blades, which, in turn, puts less pressure on the fan motor.
That is why smaller CPU fans are the best option.
Based on the diameter, the CPU fans come in three major types such as:
- 120 mm – These fans have a very high RPM but are quite noisy at the same time.
- 140 mm – These fans will produce adequate volume of air.
- 200 mm – Due to the large size, the RPM of these fans will be lower, power consumption will be higher just as the noise, and lifespan will be shorter. However, covering a much larger area, the airflow will be unmatched when compared with the smaller CPU fans.
Bearings
The lifespan of a fan is usually determined by the bearing technology.
Typically, the blades of the fan are attached to a shaft which is inside a cylinder and rotates them.
This cylinder is called the bearing which comes with a mechanism to trim down friction to allow smooth rotation of the blades.
The type of bearings depends on the method used to lubricate the shaft but the main ones are:
- Fluid Bearing – These types of fans are quite cheap but are quite prone to leaks and dust which reduces their lifespan significantly. Leaks result in a rattling noise and dust buildup prevents the blades from rotating for more than a couple of seconds.
- Ball Bearing – These types of fans are expensive but are very durable. There is a ring of balls instead of fluid to reduce friction within the shaft. These fans are not prone to dust or leaks and can tolerate higher temperatures. The problem with them is that these are quite noisy and, if placed vertically, performance is affected due to gravity.
- Maglev Bearing – A short for magnetic levitation bearing, there are magnets used in these fans. It levitates the shaft preventing any contact with the hub while spinning. Though quite expensive, these fans are highly durable and efficient but it is a very new technology for CPU fans.
Remember, a CPU fan, which is located at the top of the CPU, is not the same as the case fan, which is located inside and at the side of a computer case or a power supply fan, which is placed inside the power supply unit or a dedicated video card fan.
The CPU fan is usually much more flexible in comparison to the other fans inside the computer case.
Why is the CPU Fan Important?
In simple words, a CPU fan is needed whether you overclock or not because it will prevent a thermal shutdown.
It will move the hot air through the computer case.
Typically, when you work on your computer, the processor and other components inside the computer casing, such as the RAM and GPU, will produce a huge amount of heat.
This is a common by-product which cannot be avoided but it can surely be dispersed and that is why you need a CPU fan.
If this heat is not dissipated, it will increase the core temperature of the internal components, all of which have a specific temperature tolerance level.
These components will start to falter as and when that particular temperature threshold is crossed.
This will result in a lot of issues such as:
- Damaging the internal components
- Slowing down of the computer
- A lower performance
- System hang-ups and even crashes.
And, these may not happen in that particular order. In order to avoid this disaster, your computer, just like any other computer, comes with a cooling system.
Therefore, the fan plays a very important role in maintaining the core temperature and is a very important part of the cooling system.
Can a Computer Run without a CPU Fan?
Ideally, the CPU fans do not have any direct involvement in the internal mechanism or processing of the processor.
Therefore, technically speaking, it is possible to run a computer without a CPU fan but it is highly not recommended.
However, the CPU typically cannot work without a fan for a long time.
The high temperature produced and quick heat buildup will fry the internal components pretty quickly beyond repair.
That is why even a liquid-cooled computer system needs to use fans.
Even if your computer is powered by a high-end CPU, running it without a fan will not allow it to run more than a minute or two.
And, if you are using a low-end CPU, running your computer without a fan is not worth it considering the drastic aftereffects.
The CPU fan, along with the heat sink manages the temperature of the CPU preventing damage even when you overclock which will produce an even greater amount of heat.
When the CPU overheats, you will experience symptoms such as:
- Freezing of computer
- Computer becoming unresponsive
- System crashes
- Computer restarting without warning
- Computer showing Blue Screen of Death or BSoD and
- Other unexpected error and warning messages shown on the screen.
All these are least desired by any computer user and therefore you should not use your computer without the fan.
Where Does a CPU Fan Get Power from?
Since it is called a CPU fan, it is quite natural to think that the fan runs on the power of the CPU, which however is not true.
Believe it or not, the CPU fan typically draws the power necessary for it to operate from the motherboard.
This power is drawn through the connector or fan wire which is attached to the dedicated header for the CPU fan located on the motherboard.
How Do You Know If Your CPU Fan is Working?
It is very easy. When the CPU fan does not work, you will observe a few specific things.
You should keep an eye on these to know whether or not the CPU fan in your computer has failed or has started to show signs of failing soon and act accordingly. These are:
- Noise – Typically, as said earlier, the CPU fans are designed to run silently. Therefore, a humming or rattling sound is a sure sign of failure.
- Overheating – Overheating of the components of a computer is a sure sign of CPU fan failure. A fall in the performance level by more than 10%, repeated freezing, and BSoD are some signs of CPU fan failure.
- Alerts – Some computers may send alerts to the users using dedicated software when the CPU fan fails.
However, CPU fan failure does not signify the end of the world. There are some easy solutions that can mend the issue quickly, and even permanently.
You can do it yourself if you are tech savvy, or else, take the help of a pro. The solutions are:
- Check the wires whether or not these are connected properly to the motherboard and connect them properly if they are not
- Check if the fan is installed properly or not on the motherboard and install it properly if it is not
- Check for dust buildup clogging the fan and clean it if it has to make it easier for the blades to spin and
- Check the bearing and tighten the screws if it has come loose or get it serviced if you see signs of abrasion in it.
Once you are done with these checks and mending, further overheating should be prevented. For that, you will need to follow these specific steps:
- Move your computer if it is set up in a hot room or near to any hot object
- Ensure it does not get direct sunlight
- Stop overclocking
- Use additional cooling system if you live in a hot region
- Keep the air vents and the CPU fan clean and
- Enable Fan Duct with Fan and Active Heat Sink in the Advanced Setting in the BIOS or Basic Input Output System.
If none of the above steps work, something in the CPU fan may be broken or damaged. In that case you will have to replace it.
Does CPU Fan Affect Performance?
To be very precise, the answer to this question is both yes, and no.
Ideally, the CPU fan will not have any direct influence on the performance of the computer.
However, it does affect it indirectly since it prevents lowering of the performance of the system by managing the temperature inside the computer case.
Typically, a better CPU fan will prevent overheating much more efficiently.
You can overclock for a speedy performance since the CPU fan will not allow the CPU to throttle under pressure.
However, in short, the CPU fan will not increase the performance as such.
How Long Does a Computer Fan Last?
It is quite difficult to answer this question because the general range may vary according to the usage of the computer system on the whole.
It will also depend on the quality of the CPU fan itself as well as on how well you maintain it.
If you use a stock fan of Intel and run it 24/7, it will run quite efficiently for about 8 years before you experience a drop in its performance by about 10%.
However, you will hardly use a computer 24/7 if you are not into cryptocurrency mining.
However, any type of good CPU fan would last anywhere between a couple of years to 10 years.
On the other hand, the standard CPU fans may last for up to 5 to 6 years if you maintain them on a regular basis.
If you allow dust particles to build up on the CPU fan, it will however lower the lifespan as well as the integrity and performance of the fan.
Also, frequent overclocking will reduce the lifespan of the CPU fan because it will consume much more power and generate a lot of heat in the process than usual.
This will make the CPU fan work harder which will increase the probability of failures and damages, thereby lowering its life.
Is it Safe to Increase CPU Fan Speed?
Well, pushing anything to the limit will come with its characteristic consequences, and this applies to the CPU fans as well.
Ideally, if you increase the speed of the CPU fan and make it run at its maximum capacity, a few good and bad things will happen at the same time. For example:
- The increased speed will move the air more quickly from one place to another. However, you should make sure that the air is not obstructed here or else it would result in a splash back.
- The higher speed of the CPU fan may emit some noise. However, this is a matter of personal choice. If the noise does not distract you and make you uncomfortable, this should not be a big issue to you.
- The increased speed of the fan will surely reduce the life expectancy of the CPU fan. This is because the faster the fan blades run, the more will be the wear and tear because it will have to endure a much higher resistance while overcoming the friction. It will also put additional stress on the fan motor and bearing.
- When there is an increased airflow, there will also be a higher chance of dust accumulating on the CPU fan, which is bad. Any dust buildup on the bearing will trash the fan slowly but surely. This means that you will have to clean and maintain the fan more frequently. If you have that much time and are okay with such hassles, it should not be an issue to you. once again.
- The CPU fans are designed to consume less power during operation but that is when you run them within a reasonable speed. Higher speed means more consumption of energy. This will cost you more electricity and a higher monthly bill. If you are okay with that, this also should not be a major issue as well.
Therefore, you can see that increasing the speed of a CPU fan is a personal thing.
However, with all that said, now the question is why on earth would you want to increase the speed of the CPU fan when especially the manufacturers do not want anyone to do it since it will shorten its life.
Moreover, you really do not need to do anything by yourself since most modern CPU fans are driven by the BIOS.
This means that the speed is regulated automatically according to the need and load on the computer, or the CPU in particular.
Therefore, it will spin faster when there is more heat and slower when the temperature is within the desired level.
So, unless you are used to buying a PC on a regular basis or if you do not have any serious heat issues or if it is not the last resort, you should not increase the speed of the CPU fan. It is not safe.
Instead, the best thing to do is to ensure that the CPU fan speed is set to auto.
If you really need more cooling, it is prudent to invest in additional fans or air conditioning.
Conclusion
Now you surely know why the CPU fans are considered to be an integral part of the computer.
This article tells how it helps the system to work properly and also ensures its long life and how it may damage your computer if you do not use them while using your computer.