What are the differences between DIMM and SODIMM? Both the DIMM and the SODIMM are used to provide SDRAM or Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory to a computer.
The difference in the respective terminology may be a bit confusing to the unaware and may even seem to be meaningless since both are used for the same purpose but in different devices.
In This Article
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The larger size of the Dual In-line Memory Module enables it to be used in a desktop computer but the Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Modules are used in laptop computers mainly.
- In spite of a fewer number of pins, the SODIMMs offer similar functionality as the DIMMs.
- The DIMMs cannot be used horizontally onto the motherboard as the SODIMMs because they are thicker.
The 8 Differences Between DIMM and SODIMM
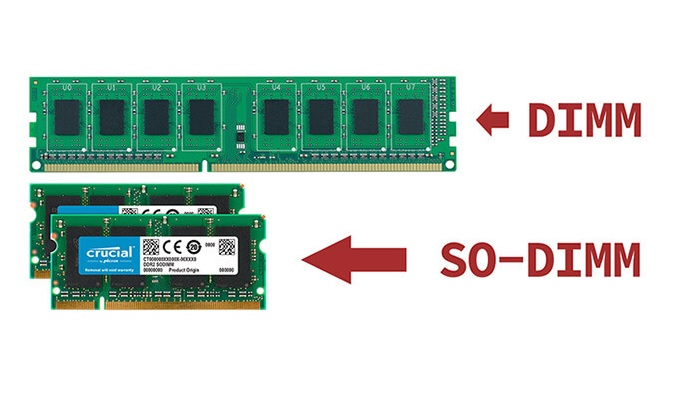
1. Full Forms
While DIMM is the short for Dual Inline Memory Module, SODIMM, on the other hand, is the short for Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module.
2. Used in
Typically, a DIMM is used in desktop computers mainly because it is larger in size and comes with more pins.
On the other hand, the smaller SODIMMs are typically used as the laptop RAM and in the ultra-small form factor computer systems such as netbooks or notebooks.
3. Size
The DIMM is ‘full size’ as compared to the SODIMMs which are comparatively smaller in size typically due to their ‘Small Outline’ format.
4. Number of Pins
The DIMM RAM usually comes with a higher number of pins, which can be 168, 184, or 240 in total, depending on the type of DIMM.
On the other hand, the SODIMM has a fewer number of pins of either 144 or 200 in total, depending on the model but offers almost the same functionality as the DIMMs.
5. Power Consumption
The DIMMs seem to beat the SODIMMs in power consumption because it consumes much less power.
On the other hand, in spite of their smaller size, the SODIMMs relatively consume more power.
6. Memory Density
It is due to the wider area of the DIMMs that allows them to have a relatively higher memory density.
On the other hand, the narrower and smaller size of the SODIMMs does not allow them to have as high a memory density as the DIMMs.
7. Overclocking Ability
The larger number of contacts due to the larger number of pins in the DIMMs offers higher overclocking ability comparatively.
On the other hand, the lower number of pins and contacts do not allow the SODIMMs to offer such benefits.
8. Installation Methods
You cannot install a DIMM onto the motherboard horizontally because these memory modules are thicker and larger.
However, this is not an issue in this case because the desktop computer cases usually have a lot of space inside them to accommodate a range of components all installed differently.
On the other hand, the SODIMMs being narrower and smaller in size allows installing them horizontally onto the motherboard, if possible, and therefore make the most out of the space limitations of the laptop computer cases.
Which is More Useful – DIMM or SODIMM?

Both the DIMM and SODIMM are useful because these will allow easy access by the processor to the necessary data for its operations.
Still, under a few specific contexts, a DIMM is a slightly better option due to its larger size and higher data flow.
In addition to the list of differences mentioned above, which is truly not much in number, knowing a few other relevant and important facts about the DIMM and SODIMM will surely help you in making a decision.
Since these memory modules are used in different computing devices, it cannot be said that the computing world could do with any one of them. Moreover, none of them are interchangeable.
Typically, the DIMMs were created because a better memory module was required to meet the multitasking demands of computing these days.
These specific types of memory modules quickly replaced the SIMM being able to support larger amounts of data transfer with their higher data flow.
In short, the DIMMs provided more options to the end users. But, that was mainly restricted to the larger commercial desktop computers.
As for the laptop computer users, they required something with a much smaller outline to fit on the motherboard inside the smaller space of the casing.
Hence, the Small Outline DIMM was created to fulfill the requirement of RAM for them.
The form factors of both the memory modules are nearly the same in terms of performance.
For example, take a DDR3 DIMM and a DDR3 SODIMM.
Here the former will be double as wide and contain 240 pins than the latter with only 204 pins in it.
However, the DDR3 SODIMM will have only two Chip Select lines for each memory channel, but in comparison, the DDR3 DIMM will have double that.
On the other hand, the DDR3 SODIMM will have 14 address lines in each memory channel as opposed to 16 of them in a DDR3 DIMM, which allows using wider Integrated Circuits in the SODIMM.
Moreover, none of the SODIMM form factors support for parity or Error Correction Code or ECC and there are only 8 bits of Data Queue Strobe in them as opposed to 9 bits available in the DIMMs.
Different generations of the memory modules will come with different numbers of pins, as said earlier.
The following table shows the differences of it very clearly:
- As for the SDR memory type, a DIMM will have 168 pins but, in comparison, a SODIMM will have 100 or 144 pins
- As for the DDR memory type, a DIMM will have 184 pins but, in comparison, a SODIMM will have 200 pins
- As for the DDR2 memory type, a DIMM will have 240 pins but, in comparison, a SODIMM will have 200 pins
- As for the DDR3 memory type, a DIMM will have 240 pins but, in comparison, a SO DIMM will have 204 pins and
- As for the DDR4 memory type, a DIMM will have 288 pins but, in comparison, a SODIMM will have 260 pins.
This shows that the DIMMs always have a higher number of contacts in comparison to the SODIMMs, irrespective of their types.
This particular difference offers the DIMMs an advantage along with their considerably longer size that allows them to have a much higher margin for overclocking than the SODIMMs even if they have the similar technical specifications.
This typically allows the DIMM modules to have higher memory densities as well.
Though most of these differences may not have any significant impact on the consumer hardware, considering the speed and capacity of an 8 bit and a 16 bit DRAM Integrated Circuit, the SODIMMs tend to be more expensive in comparison to the DIMMs.
Likewise, there are several different aspects in these memory modules that make both of them important in today’s computing world.
So, now you may ask, why do manufacturers not make laptop computers with DIMM memory then?
Well, the simple and basic reason behind this is the shortage of space that does not allow using anything large.
It may occupy the space of another vital hardware component and prevent using it.
Apart from that, DIMMs cannot be installed horizontally in a laptop computer without installing an additional sister board along with the motherboard.
Once again, due to space crunch, this is something that is not quite viable in the case of a laptop computer.
And finally, if you are looking for a performance difference between SODIMM and DIMM RAM, there will not be any when you use them as they are intended to be.
This means that, there may be a significant effect in the performance if you are using an adapter, especially in terms of video performance.
This is because the signal integrity will be compromised when it has to go through the connector and the Printed Circuit Board or PCB, even though the pins may be mapped correctly from the SODIMM to the DIMM.
In short, the DIMMs are carefully designed to offer stable performance due to its specific trace or wire lengths and circuit capacitance.
All you have to do is dial down the speed. This will result in a performance increment favoring the increased RAM over speed.
Therefore, with all that said and explained, going for a DIMM is quite worth a try.
If you are planning to buy an additional memory, the cost difference is simply not a good and strong enough point that may validate purchasing a SODIMM memory, unless you are buying it for your laptop computer.
Conclusion
So, with the differences between a Dual Inline Memory Module and Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module clearly explained along with a few other relevant and important facts about them, you now surely know which a better option to go for is.