In This Article
What is Dynamic Disk?
A dynamic disk refers to a logical or physical disk. These disks are designed to use several hard disks in a computer and are technically initialized to offer dynamic storage.
These disks provide mirroring and disk redundancy and use the LDM or Logical Disk Manager database to manage its volume.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The dynamic disks are native to different variants of Windows operating systems such as Windows 2000, Vista, XP, Server 2008 and other later versions.
- These physical disks allow integrating disks with each other, duplicating and dividing data over multiple disks.
- The dynamic disks allow creating different types of volumes on them such as simple volume, striped volume, spanned volume, mirrored volume and RAID 5 volume.
- The working process of the dynamic disks is very much similar to the basic disks but they also allow adding new folders anytime to them to store information as well as spread it among all available folders.
- Using a dynamic disk allows performing specific tasks such as volume and disk management without restarting Windows but there can be some compatibility issues with other services or devices such as USB, ISCSI and FireWire.
Understanding Dynamic Disk
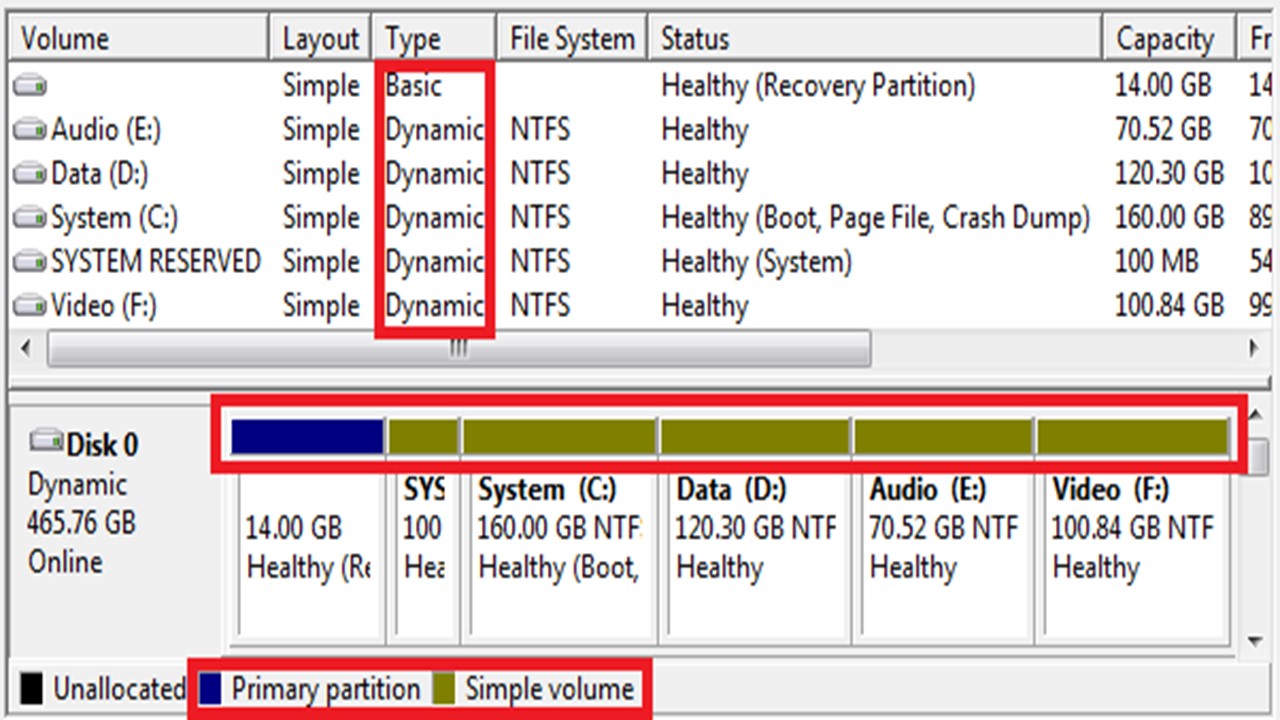
A dynamic disk refers to that disk that has been designed for dynamic storage.
Typically, only one single dynamic disk group can be created by a computer at one time.
The dynamic disks typically come with the capability of holding and managing volumes by using a database.
A lot of different types of dynamic volumes can be created but without the dynamic disks nothing would be possible.
These volumes are usually storage units. These are normally created from the free space available on one or many disks.
You can also format it with a file system as well as assign a drive letter.
The different types of volumes that can be created on the dynamic disks are:
- Simple Volume – These volumes use the available free space of one particular disk. It can be created in one specific region on a disk or it can even be made up of several regions in succession. The simple volumes can be extended onto an additional disk and even within the same disk.
- Spanned Volume – These volumes are created by using the available free space in a disk that is linked together with multiple disks. Also, when a simple volume is extended across several disks it becomes a spanned volume. The spanned volumes can be extended onto as many as 32 disks but these are not fault tolerant and cannot be mirrored as well.
- Striped Volume – These volumes refer to those in which the data stored is concatenated with two or more physical disks. Also, the data on these volumes is divided evenly and alternately to every physical disk. You cannot mirror or extend a striped volume and these volumes are also not fault tolerant. Striping is also identified as RAID 0.
- Mirrored Volume – These volumes are fault tolerant and in them the data is typically duplicated on two different physical disks. This means that the data that is available on one disk is duplicated on the other physical disk for storage purposes. This ensures that the data is still available and accessible on one disk even if the other disk fails. Mirroring is as signified as RAID 1 but you cannot extend a mirrored volume.
- RAID 5 Volume – The RAID 5 volumes are fault tolerant and the data in this case is striped between a group of three or more disks. Across this disk arrangement a premeditated value called parity is also striped and used for reconstructing the data in case there is a failure. This means that when a physical disk fails, the parity and the remaining data can be used to recreate the part of the RAID 5 volume that was on the failed disk.
There are different system volumes that contain files that are specific to the hardware.
These files are usually needed and frequently used to load Windows.
The system volumes can be the same as the boot volume, but that does not have to be always.
A few examples of system volumes are:
- Boot.ini
- Ntldr and
- Ntdetect.com.
The boot volume, on the other hand, holds the Windows operating system files.
These files are typically found in specific folders such as the %Systemroot%\System32 and the %Systemroot% folders.
Once again, the boot volume can be a system volume but does not have to be always.
Now, the dynamic disks are typically created and managed in two particular ways such as:
- By using a Logical Disk Manager or LDM and
- By using a Virtual Disk Service or VDS.
Any given or mentioned information can be stored in a dynamic disk out of all of the dynamic disks your computer may have.
This means that there is a distinct interrelation between these disks.
It is this interrelation between or relevance of every dynamic disk of the computer that will let you see if there is any disk missing when you remove one from the computer.
You can view this in the Windows Disk Management.
Everything that you do will be stored safely in the database of the LDM.
This makes the Logical Disk Manager as important as the partition table of the basic disk.
You can create these volumes by using MBR or Master Boot Record based or GPT or Globally Unique Identifier Partition Table based partition methods.
These will use a specific database to deal with the volumes created on one or many disks.
There can be as many as 2000 volumes and each of these volumes acts as a partition or a separate drive.
You will be able to see a distinct region at the beginning of the dynamic disk.
This area denotes the MBR. The main objective of the MBR is to save the information related to the partition table on the dynamic disk.
This partition table of a dynamic disk however, is not the same as the partition table of the basic disk.
This specific area simply lets the other disk managers and the Windows know that the particular disk is actually a dynamic disk and is not an empty disk.
There is also a specific region marked at the last part of the dynamic disk which indicates the LDM database.
Working Process:
You can think of a dynamic disk, as well as a basic disk, as empty cabinets that can be filled up with information.
Therefore, the function of both is the same and involves:
- Storing information
- Collecting information from several folders and
- Displaying the information to the users.
However, the working process of the dynamic disks is a bit different from the basic disks.
Ideally, in a basic disk, there are a fixed number of folders that it can access.
Also, a basic disk can use only those things that have been setup by the user at the time of formatting the disk.
On the contrary, the working process of the dynamic disks, however, is different because it allows adding new folders to them at any point of time.
The disks can store information in these folders and can also spread it across all available folders in a lot of different ways.
Features of the Dynamic Disk Storage:
Now, take a look at the different features of the dynamic disk storage that make it so useful.
The storage types are usually distinct from the type of the file system.
A dynamic disk, just like a basic disk, may come in different combinations such as:
- File Allocation Table 16 or FAT16
- File allocation Table or FAT32 and
- New Technology File System or NTFS partitions or volumes.
A disk system can have any storage type combination but it is necessary that all of the volumes on that particular disk use the similar type of storage.
Usually, a dynamic disk is not compatible with any portable computer.
They do not even support computers that are based on Windows XP Home Edition.
You will also be unable to create RAID 5 or mirrored volumes if your system belongs to any one of these following categories namely:
- A Windows XP Home Edition based computer
- A Windows XP Professional based computer and
- A Windows XP 64-Bit Edition based computer.
However, in the case of remote computers you can use the dynamic disks to create a RAID 5 or mirrored volume even if the computers are Windows XP Professional based.
The only requirement is that these computers should run on any of the following servers namely:
- The Windows 2000 Server
- The Windows 2000 Datacenter Server and
- The Windows 2000 Advanced Server.
A Windows XP Professional based remote computer may also be used to create a mirrored or RAID 5 volume if it runs on the Windows Server 2003 irrespective of its version being any one of the following:
- Standard
- Enterprise and
- Data Center.
That is not all. It can also run and be used to create a mirrored or RAID 5 volume on remote computers running on Windows Vista.
The versions of the operating system do not matter in that case. It can be any one of the following:
- Starter
- Basic
- Business
- Enterprise
- Home Premium and
- Ultimate.
You will certainly need to convert or manage dynamic disks if you want to use them on a Windows computer.
Tips to Create Volumes on and to Convert Dynamic Disks
Creating volumes on the dynamic disks as well as converting a dynamic disk into a basic disk and vice versa can be done by you in a few simple steps.
In order to create a volume of the dynamic disk you will need to take help of the Windows Disk Management tool and follow these simple steps:
- Go to ‘This PC’
- Click on ‘Manage’
- Click on ‘Disk Management’
- Right-click the free space on the dynamic disk
- Choose ‘New Simple Volume’
- Follow the instructions displayed on the screen to complete the remaining process.
These are the basic steps to create a volume on a dynamic disk. However, based on the type of new volume that you want to create on it, the ways of creation may be a bit different.
Now, if you want to convert a basic disk into a dynamic disk, the process for it involves:
- Going to ‘This PC’
- Clicking on ‘Manage’
- Opening ‘Disk Management’
- Right-clicking on basic disk
- Choosing ‘Convert to Dynamic Disk’
- Clicking ‘OK’
- Clicking ‘Convert’ and
- Confirming your operation when the windows come up.
When all these processes are completed, you will have converted the basic disk into a dynamic disk successfully.
However, if you want to go the other way around, that is to convert the dynamic disk into a basic disk, you can do it in two different methods.
- By using the Windows Disk Management tool and
- By using a command line.
Though most people think that the Windows Disk Management tool only allows converting a basic disk into dynamic disk, it is much to the contrary.
You will find a lot of information in the official site of Microsoft regarding the process to follow to change a dynamic disk into a basic disk back again.
The steps needed to follow for it include:
- Creating a back up of all of the volumes on the dynamic disk that you want to convert into a basic disk
- Going to the taskbar
- Typing Computer Management in the search box
- Right clicking on or selecting and holding Computer Management
- Selecting Run as administrator
- Clicking on Yes to open Computer Management
- Going to Storage
- Clicking on Disk Management
- Opening Disk Management with Administrator permissions
- Right clicking on or selecting and holding every volume on the dynamic disk that you want to convert into a basic disk and
- Clicking on Delete Volume.
When all of the selected volumes are deleted from the dynamic disk, you will now need to right-click on it and then click on ‘Convert to Basic Disk.’
Now, if you want to change the dynamic disk into a basic disk by using a command line the steps needed to follow are:
- Creating a backup of all the volumes in the dynamic disk first
- Opening the command prompt and
- Typing diskpart.
Now, when the DISKPART prompt opens, you will need to type different things that will show different data and info which you will need to take note of. These are:
- Typing ‘list disk’ that displays whether the disk is basic or dynamic along with the size, amount of free space available, MBR or GPT partition style, and an asterisk on the disk that has focus and note the dynamic disk number that you want to convert into a basic disk
- Typing ‘select disk <disk number>’ to select the specific disk with its number and an asterisk mark for focus
- Typing ‘detail disk’ that displays the properties and volumes of the chosen disk
- Typing ‘select volume = <volume number>’ for every volume on the selected disk to select the specific volume with the volume number that can be denoted by simply a number, a drive letter, or the mount point path
- Typing ‘delete volume’ to delete the selected volume
- Typing ‘select disk <disk number>’ this time with the specific disk number that you want to convert and finally
- Typing ‘convert basic’ to convert the selected and empty dynamic disk into a basic disk.
Also, in order to convert a dynamic disk to a basic disk you may use a third-party tool.
There are lots of different third-party tools available for it. Just make sure that you choose a good and professional one.
Typically, the tool to convert a dynamic disk into basic disk should come with specific features that will allow you to do specific tasks on the volumes on the dynamic disk such as:
- Resizing
- Moving
- Cloning
- Checking
- Creating
- Formatting
- Deleting and
- Exploring.
If you choose such tools, you will also be able to manage the disks in a much better and more productive way.
Easy! However, the most important thing to remember when you want to convert a dynamic disk back into a basic disk is to create a backup of all the data that you may need later on before proceeding.
You may also move it to another different volume.
This is important because you will need to delete all the volumes from the disk for such conversion permanently.
Another vital aspect that you should keep in mind is that when you convert a dynamic disk back into a basic disk, you will only be able to create logical drives and partitions on it.
Restoring Lost Data:
Sometimes data can be lost on a dynamic disk just like any other kind of device.
In such situations, you should not fret because there are easy ways to recover lost data from a dynamic disk.
You will simply need powerful hard drive recovery software for that. Most of these software programs will work on Windows 10, Windows 8 or Windows 7 computers and there are only a few steps to follow.
Though different software may have one or two additional steps required for it, typically the basic steps to recover lost data from a dynamic disk include:
- Launching the file recovery software on your computer
- Choosing the location where the files were lost exactly
- Clicking on the ‘Scan’ button.
This will start the scanning process by the software immediately.
Here, the deleted files will be displayed. During the scanning process, if you find the files that are necessary, you may stop the scanning process.
You can also find the target file pretty fast as well.
For that, you will simply need to use the file format filter. You can select all types of files such as:
- Word files
- PDF or Portable Document Format files
- Excel files
- Video files
- Image or photo files and
- Emails.
When you are done with the file selection process, finally, you will have to click on the ‘Recover’ button.
You can store the recovered file in a different location as well. All you have to do for that is browse for that particular location.
Advantages of Dynamic Disks
Finally, take a look at the several advantages of the dynamic disks.
Typically, when you use a dynamic disk you can perform specific tasks such as disk management and volume management and for that you do not need to restart Windows.
In addition to that, you can also create different volumes that are mentioned before.
These volumes will offer a certain level of data protection by allowing you to store the information in a much more varied manner.
These will not be offered by a basic disk.
In terms of functionality, the dynamic disks will offer much more in comparison to the basic disks.
Disadvantages of Dynamic Disks
However, a dynamic disk will offer much more significant advantages when it is used in combination with the basic disks, which is ideally done in most of the cases.
This is because the dynamic disks are usually not considered anything superior. It only creates a more secure environment.
In addition to that, the dynamic disks can also be some sort of a nuisance due to their compatibility issues with other devices and services such as:
- USB or Universal Serial Bus
- ISCSI or Internet Small Computer System Interface and
- Firewire.
It may not also be read by a variety of Windows operating systems.
At this point it is essential to note that Redundant Array of Independent Disks or RAID and other hardware based systems will offer much better in comparison to the dynamic disks that are typically based on software.
It is for this particular reason, several users choose not to use dynamic disks in combination and isolate them to use for any particular purpose.
A few users would rather not use the dynamic disks at all.
Now, since you know a fair bit about the dynamic disks, take a look at the few common questions that you may already have in your mind as well.
What Does a Dynamic Disk Do?
The main objective of the dynamic disks is to offer mirroring and redundancy of disks.
In addition to that, these dynamic disks play a significant role in boosting up the reliability and performance of the system overall.
The dynamic or logical disks are physical disks that typically help in managing its volume by utilizing an LDM or a Logical Disk Manager database.
This LDM database is a hidden database of 1 MB size only and is usually located at the end of the dynamic disk.
This hidden database hold a lot of useful information related to each dynamic disk such as:
- The volume label
- The drive letter
- The volume size
- The beginning sector of the volume
- The file system of the volume
- The current dynamic disk and lots more.
In short, all information related to the volumes on one particular task is recorded in this database.
Should You Use a Dynamic Disk?
This depends on your personal preference. If you want to have more flexibility and enhanced performance and better tracking of volumes, then it is good to use a dynamic disk instead of a basic disk.
On the other hand, if you do not have a Windows system and if this is not good software that will offer you very huge benefits, it is better to use a basic disk and leave everything to it.
What Happens If You Convert to a Dynamic Disk?
The worst that can happen if you convert a basic disk into a dynamic disk is that you will only be left with the current boot volume.
You will not be able to initiate an operating system that you may have set up from whichever volume available on the disk.
Does Converting to Dynamic Disk Delete Data?
The simple answer to this question is, no.
You can convert the basic disk into a dynamic disk directly by using the Windows Disk Management tool and that will not result in any data loss.
However, if you want to convert a dynamic disk into a basic disk, all data and volumes in it should be deleted with the help of the Disk Management tool.
Can You Install Windows 10 on a Dynamic Disk?
Typically, when you want to install Windows 10 on a dynamic disk you will encounter an error message stating that it cannot be installed.
This is because this hard disk space contains several partitions with one or many dynamic volumes. These do not support installation.
You will typically have to convert the dynamic disk into a basic disk in order to install Windows 10 in it and boot from it effectively.
Can a Dynamic Disk be Converted Back to a Basic?
Yes, you can do that by using the Windows Disk Management tool or by using a command line.
You can also convert a dynamic disk back to a basic disk by using a good and powerful third-party tool.
You will need to follow different steps in each of these processes as already mentioned above.
Can Dynamic Disk Boot?
Yes, it can.
However, whether you want to make a system partition or dynamic disk boot, for that, you will need to include the particular disk that has the system partition and the basic active boot in a dynamic disk group.
It is only then that the system partition and the boot will be upgraded automatically to a dynamic, simple, and active volume and your system will boot from it.
Can You Convert My C Drive to a Dynamic Disk?
Yes, you can and it is ok to do so. This is because when you do so, this will not affect the booting of the system disk.
However, if the disk has dual boot then it is recommended that you do not convert it.
Can You Dual Boot With a Dynamic Disk?
Usually, that is not possible.
This is because a dynamic disk is entirely a Microsoft product and the Boot loader of Microsoft will not boot anything other than Windows.
Can You Install Windows 11 on a Dynamic Disk?
Yes, you can but you cannot install Windows directly on a dynamic disk without changing it from a basic disk.
However, to install Windows 11 on a dynamic disk you can use the Windows Disk Management tool, the command line prompt, and even with the help of a third-party tool.
The steps are however different and therefore make sure you are aware of them.
Can You Move a Dynamic Disk to Another Computer?
Yes, you can but there are a few specific requirements.
First, you will have to be a member of the Administrators group, at least, or the Backup Operators in order to follow the necessary steps.
The steps to follow include verifying the volume health, uninstalling the dynamic disk, removing them and installing them into another computer.
What is a Limitation of Dynamic Disks?
Apart from the disadvantages of the dynamic disks mentioned above, one of the most significant limitations of them is that you will have a very hard time fixing the disks if there are any corrupt sectors in it.
This is because there are hardly any tools available as of now that may help in fixing these issues.
Also, you will not be able to use these dynamic disks with any removable medium or on any portable computer.
Is Dynamic Disk Bad?
No, you cannot say that the dynamic disks are bad outright, in spite of the fact that they come with a few limitations and demerits.
These disks will help you to create software RAIDs.
These disks will also give more flexibility to your system to offer a much better performance.
Conclusion
Therefore, you are now aware of the different advantages of using the dynamic disks and, most importantly, what these are, in the first place.
Now you can easily decide whether or not you will go for the dynamic disks or simply stick to the ‘Basics.’