In This Article
What is Expansion Bus?
An expansion bus actually refers to the set of wires and protocols used for the expansion of computers. Also known as an external bus, this is ideally a tool to communicate between the CPU and other peripherals with the help of an expansion board.
In simple words, it is the input/output conduit to transfer data and information.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The expansion bus allows expansion of the computer system by inserting other expansion boards into the slots and helps the CPU and other devices to communicate with each other.
- There are different types of expansion buses available in the market such as ISA expansion bus, PCI expansion bus, AGP expansion bus, MCA expansion bus, EISA expansion bus, VESA expansion bus, and the most popular Universal Serial Bus.
- The expansion buses are typically used to transfer data between the computer hardware which includes memory, CPU, video cards, sound cards, SCSI controller cards and network interface cards.
Understanding Expansion Bus
Ideally, a bus in a computer is a pathway for the set of signals to travel through and allow carrying and passing information to the internal as well as external components of a computer.
An expansion bus is one specific type of different bus that you get in a computer that allows the Central Processing Unit or CPU to communicate with the other devices in the computer and vice versa.
These expansion buses are also known as external buses because these are outside of the CPU.
For your additional information, the other types of buses that you may find in a computer are:
- Address buses that allow the CPU to select and write to a specific memory address
- Data buses that allow the devices of the computer to send information back to the processor
- FireWire (IEEE 1394) buses that allow connecting high speed devices
- AMR or Audio Modem Risers that can function either as Audio, Modem or both
- CNR or Communication and Network Risers that support USB, audio, modem, and Local Area Networking or LAN interfaces of main logic chipsets
- PCI-X which is a high performance bus that supports Gigabit Ethernet, Fiber Channel, and Ultra3 Small Computer System Interface or SCSI and
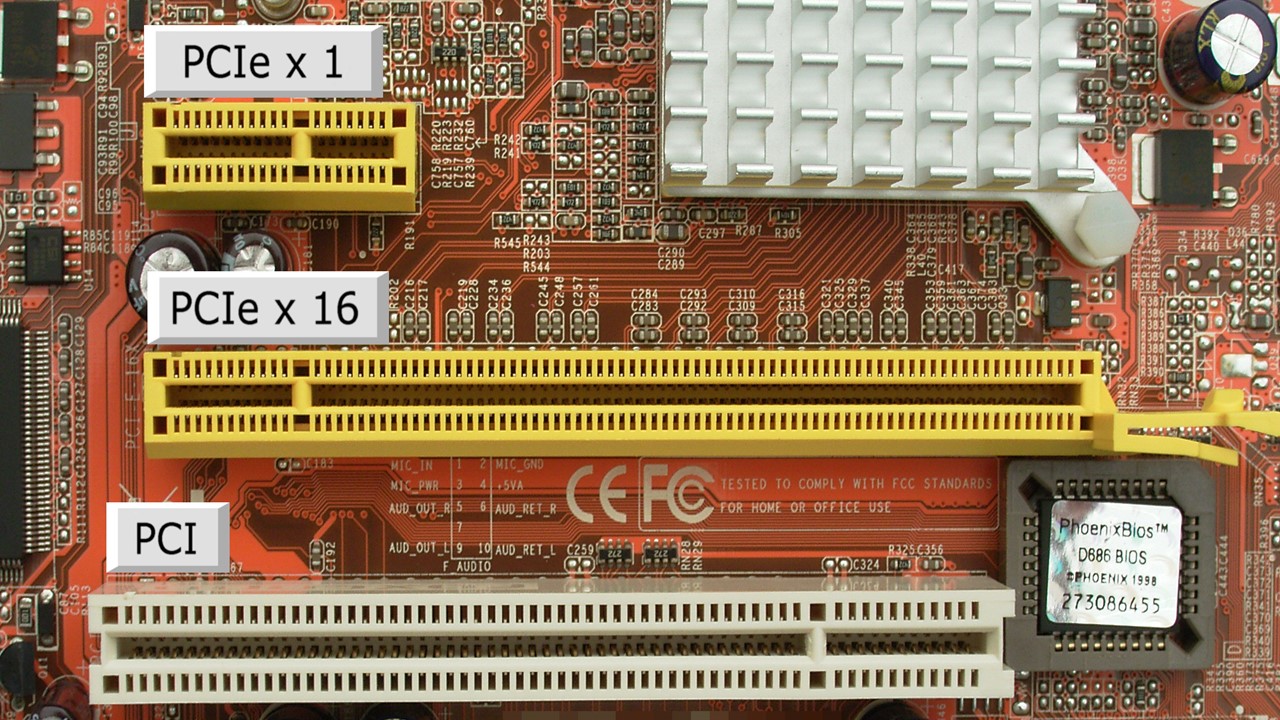
- PCI Express which is a high speed serial I/O interconnect standard that allows high speed connectivity.
You will also get specific laptop buses such as Personal Computer Memory Card International Association or PCMCIA or simply PC Cards.
These are usually available in three types with each having different measurements and usage but all support 16 or 32 bit bus width.
The Express Cards are the latest type of card that is used in the newer laptop computers.
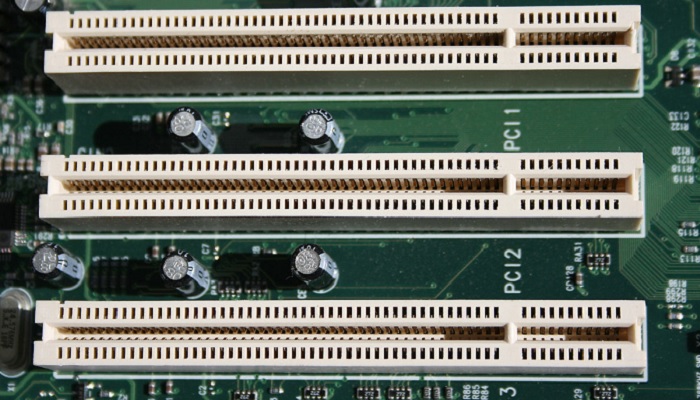
Now, coming back to the expansion bus of a computer, this typically refers to the series of slots that you may see on the motherboard.
Different types of expansion cards are inserted into these slots to carry data and signals from the Central Processing Unit or the CPU of the computer to the different peripheral devices that are attached to it.
The Working Process
The motherboard has specific data bus paths that make data flow possible between the processor of a computer and its other components.
The structure of the motherboard has several data bus paths for different parts and each of them leads to a particular expansion bus.
This is actually a narrow slot in the motherboard and every slot comes with an integrated circuit and every circuit is created differently.
This allows the circuits to talk to the different devices attached to the computer system such as the monitor, printer, CD-ROMs, and others. Typically, it is these slots that are also referred to as cards.
Ideally, in the modern computers you will find all fundamental peripheral devices are already built onto the motherboard.
Therefore, you may not have to use all the expansion slots available in your computer.
However, this does not mean that the expansion buses are not being used in your computer. Usually, the built in ports and controllers still use these I/O buses in order to talk to the CPU.
That is to say that they operate in such a way as if they are simply add-on cards that are plugged into the expansion bus slots of the computer.
Types of Expansion Buses
Here are a few specific types of expansion buses that you will find in a computer system today along with a short description of each along with.
ISA Expansion Bus:
ISA or Industry Standard Architecture bus was introduced by IBM or International Business Machines and was originally an 8-bit bus.
However, later on in 1984 it was extended to a 16-bit bus.
The characteristics of the ISA bus are as follows:
- The 8-bit wide ISA buses come with a clock speed of 4.77 MHz and a data transfer speed of 2.38 MB/s and
- The 16-bit wide ISA buses come with a clock speed of 8.33 MHz and a data transfer speed of 8 MB/s.
It was released originally as a proprietary bus and only IBM could build the peripherals and the genuine interface. Later on, however, other clone manufacturers started creating it in the 1980s.
The ISA bus is still in use simply due to the reason it is cheap and supports backwards compatibility.
PCI Expansion Bus:
The PCI bus was introduced in 1992 by Intel. This specific expansion bus came in a 32-bit and a 64-bit variant.
The characteristics of the PCI bus are as follows:
- The 32-bit wide PCI Client buses come with a clock speed of 33 MHz and a data transfer speed of 133 MB/s and
- The 64-bit wide PCI Server buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 266 MB/s.
The PCI bus is one of the most popular and extensively used expansion buses in computers today.
AGP Expansion Bus:
AGP or Advanced Graphic Port was introduced in 1997 by Intel. This expansion bus is also available in a 32-bit bus and a 64-bit variant.
This particular type of expansion bus is designed specifically for meeting the high demand for 3 dimensional graphics.
The characteristics of the AGP are as follows:
- The 32-bit wide AGP 1x buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 266 MB/s
- The 32-bit wide AGP 2x buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 533 MB/s
- The 32-bit wide AGP 4x buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 1066 MB/s
- The 32-bit wide AGP 8x buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 2133 MB/s and
- The 64-bit wide high end AGP 8x buses come with a clock speed of 66 MHz and a data transfer speed of 4266 MB/s.
These expansion buses typically have a direct line to the memory of the computer.
This allows storing the 3-D elements in the system memory rather than in the video memory.
The AGP is considered to be one of the fastest expansion buses that are used today but only in video or graphics environments.
Apart from these major types, the expansion buses are further divided into several other categories such as:
MCA Expansion Bus:
Ideally, the Micro Channel Architecture or MCA buses were created after the ISA buses and came with a lot of improved features.
One of the most significant properties of the MCA bus is that it can transfer data both in 16-bit chunks as well as in 32-bit chunks.
Another significant innovation that came along with the MCA buses was bus mastering.
This refers to the technology where smaller processors are placed on the expansion card which offered several benefits such as:
- A better control over the data transferring process and
- A better communication between the CPU and the card.
However, the MCA buses were not compatible with the ISA cards and therefore could not become very useful or popular.
They are history now and an alternative to them was developed – the Extended Industry Standard Architecture or the EISA bus.
EISA Expansion Bus:
This replacement of the MCA bus was compatible with the older ISA cards and therefore is still used widely.
These specific buses work on a 32-bit data path but the most unique aspect of them is that these buses also offer a basic disk setup just like the MCA bus.
However, the difference is that they support the ISA technology as well.
The EISA slots are physically twice as thick as the older ISA slot.
This means that the EISA will not fit in place properly in an ISA card and could only reach to the first and top row of the connectors, thereby being unable to use both the rows of connectors.
VESA Expansion Bus:
The Video Electronics Standard Association bus or VESA bus was created with the only intention to enhance the video properties and graphics performance of a computer.
These buses can operate at a speed ranging between 25 MHz and 32 MHz which is often the same speed at which the processor of a computer operates.
However, the VESA buses could not make it to the mainstream because it was very difficult for these buses to keep up with the growing speed of the processors today.
The production of them therefore became too expensive.
Universal Serial Bus:
The USB or Universal Serial Bus is the most popular type of bus used today. This newest addition to the computer bus collection helps in connecting almost all types of external peripheral devices to the computer which includes and are not limited to:
The thin USB port is found in most of the motherboards and you will even find at least two of them in the modern motherboards and placed close to the keyboard. However, these can also be offered through an expansion card.
The good thing about the USB is that it can support both isochronous or time-dependent and guaranteed fixed data delivery rate for more demanding devices and multimedia applications as well as asynchronous or intermittent data transfers.
Depending on the amount of bus width required by a peripheral device, the USB may support the following rates of data transfers:
- 1.5 Megabits per second for devices such as a keyboard, mouse and those that do not have high amount of bandwidth requirement and
- 12 Megabits per second for high bandwidth devices such as scanners, modems, monitors, speakers, and more.
The good thing about the USB devices is that these can be connected to the computer while it is running and the operating system will recognize it easily. If any driver is required, it will be prompted by the operating system.
However, there is a problem with the embedded USB ports.
These are not worth repairing and generally it is better to replace them with a new USB interface card.
Where is an Expansion Bus Found?
Typically, the expansion bus slots are found on the motherboard of a computer.
And, you will usually get the opening for the expansion slot at the back of the computer.
This slot actually provides the required electrical connectivity to the motherboard for the expansion card.
What is an Expansion Bus Used for?
As said earlier, the expansion buses in a computer are normally used to connect different peripheral devices to the motherboard of the system.
It is used for transferring data and information between the internal hardware of the computer system such as:
- The memory
- The CPU
- The sound cards
- The SCSI controller cards
- The video cards and
- The network interface cards.
These buses typically use the data bus of the motherboard itself to transfer data between a specific device and the other devices that are connected to the computer.
In the computers of the early days, data was transferred between a device and the CPU at about the same rate as the CPU.
However, over time, the speed of the processors increased significantly and this created a bottleneck in the movement of data through the buses.
Therefore, the design capability of the buses required to change for the better in order to do away with the bottleneck during data transfer.
And, that is what the expansion buses are used for – to eliminate the bottleneck.
What Does an Expansion Bus Do?
The expansion buses actually act as a medium that lets data flow from one place to another as desired.
The expansion buses typically support any devices added to the computer system with the help of the expansion slots.
It usually runs at a stable rate, which may vary depending on the design of the specific type of bus.
In short, the expansion bus, also known as the Input/output or I/O bus, is that which connects all the different components of a computer to the processor.
The expansion buses ideally perform a lot of important functions to ensure that your computer operates in just the way it is supposed to and offer a high level of performance, constantly.
These buses provide the required electrical connection directly to the main logical circuitry of the computer.
This plays a crucial role in improving the power and performance capabilities of the computer system on the whole.
The expansion buses also help in determining exactly a lot of other things such as:
- What type of peripheral devices can be added to the computer system
- How many add-on cards can be attached to the system
- How much memory there should be on the expansion cards
- What are system components can be added to it and
- How easy it is to set the system up.
While providing the common pathway for the address, data, and the control signals to link different elements of the computer, the design of the expansion buses also ensure that the right type of data reaches from the source to the desired destination.
This is done by sending specific patterns of digital bits via the circuits of the bus of the computer in a particular sequence from one location to another.
Most importantly, the expansion buses provide specific signals so that the working of the add-on cards is perfectly synchronized with the remaining components of the computer system.
What Expansion Bus Uses Lanes?
Ideally, it is the PCI Express buses that use lanes in order to send and receive data.
The number of lanes would however vary depending on the model and it is assumed that higher the number of lanes, the faster and better will be the data transfer.
Which are the Most Commonly Used Expansion Buses?
Typically, the Peripheral Component Interconnect or PCI bus and the PCI Express bus are the most common types of expansion buses used in computers today.
Conclusion
After reading this article now it should be very much clear to you that an expansion bus in a computer typically acts as an input/output pathway that carries data from the processor of the computer to the different peripheral devices connected to it.