What is Audio Modem Riser (AMR)?
An Audio Modem Riser or AMR refers to the expansion slot for a short riser on the motherboard. It is usually found in a few Intel computers such as Pentium III and IV as well as in AMD Athlon and AMD Duron computer systems.
In technological terms, the AMR refers to the particular Intel specification which defines a new architectural structure for designing a motherboard.
Understanding Audio Modem Riser (AMR)
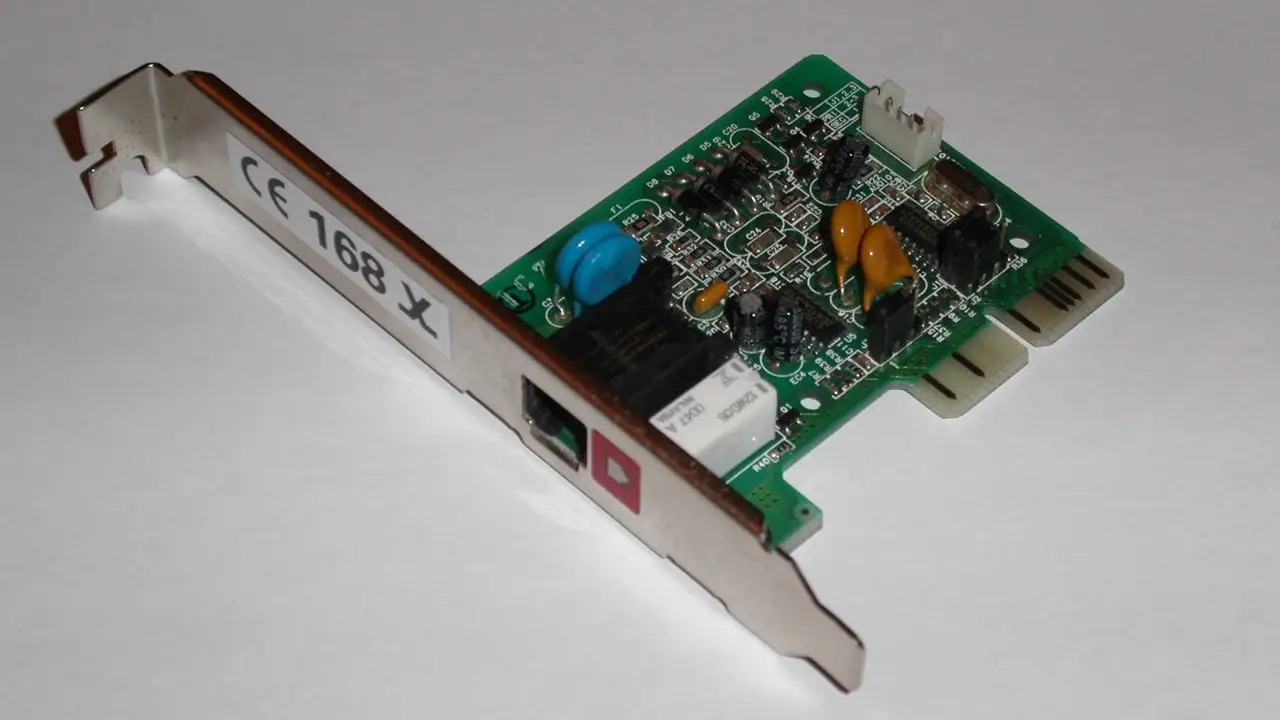

An Audio Modem Riser is called a riser board because it rises above instead of lying flat on the motherboard.
The design of it offers an inexpensive and alternative way to use unique analog I/O systems for modem and sound card functions in a computer.
Read Also: Balanced Technology Extended (BTX) Explained
Apart from providing audio and modem function support to less costly modem riser cards, the AMR offers a much smaller slot which makes it cheaper to make as well.
In addition to that, reusing the card on different motherboards also reduces the cost of Federal Communications Commission or FCC certification.
Earlier, without the AMR specification in place before, the analog I/O functions of the motherboard had to go through a lengthy international telecommunication and FCC certification procedure.
When the analog I/O functions are separated from the motherboards it offers much higher audio quality and lesser delays during production.
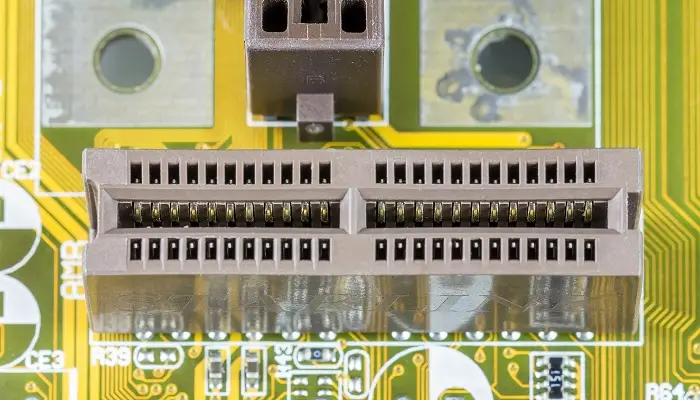
The design specification of the AMR uses two separate rows of 46 pins in total, 23 pins in each.
This tiny riser board fits onto the motherboard directly and uses analog I/O audio functions that need a software driver.
There is also a modem circuitry that consists of a codec chip. This chip helps in translating analog and digital signals.
Though the AMR helped the manufacturers to build custom systems with more advanced audio and modem designs at a low cost, many Original Equipment Manufacturers preferred not to use it.
It is due to its limited capabilities such as lack of Plug and Play feature. The hardware accelerated cards were also not supported by it.
The primary goal of the AMR is to allow installing and using Host Signal Processing or HSP devices in the computers which can be a modem, a sound card, or a network card.
This slot was superseded by the CNR or Communications and Networking Riser and ACR or Advanced Communications Riser though the latter standard is backwards compatible with AMR.
Read Also: Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA) Explained
However, both these became obsolete when the technology moved towards incorporating audio interfaces on the motherboards directly. As for the modems, they continued using the PCI slots.
However, AMR failed to gain popularity and mass adoption over the years due to several good reasons such as:
- Sound cards and modems are now integrated into the motherboards
- There are better technologies such as PCI Express are now available
- AMRs are known to have connection and compatibility issues and
- Most people use broadband now.
One of the most significant drawbacks of the AMR is that it does not have any onboard or own processing power.
It makes use of the power of the CPU or the Central Processing Unit of the computer for all functions performed by it.
In the process, it cuts about 20% of the CPU power from the users.
Therefore, AMRs are usually not found in the modern motherboards even though they replaced the PCI or Peripheral Component Interconnect slots.
Functions of AMR Slot
The AMR slot allows translating between analog and digital signals with the help of the codec chip in it.
It also acts as an interface between the phone line and the motherboard to exchange data helping the users to use the internet and e-mail at a low cost.
Conclusion
This short article surely has been very useful to you to know about the Audio Modem Riser and its features and characteristics.
You now also know the most specific reasons as to why it failed to gain popularity and mass adoption and was superseded by the CNR and ACR slots.