What is Disk Management?
Disk Management refers to the Microsoft Windows utility in Windows XP. This allows the users to view the disk drives in their computer and manage them along with the partitions related to those drives.
Understanding Disk Management
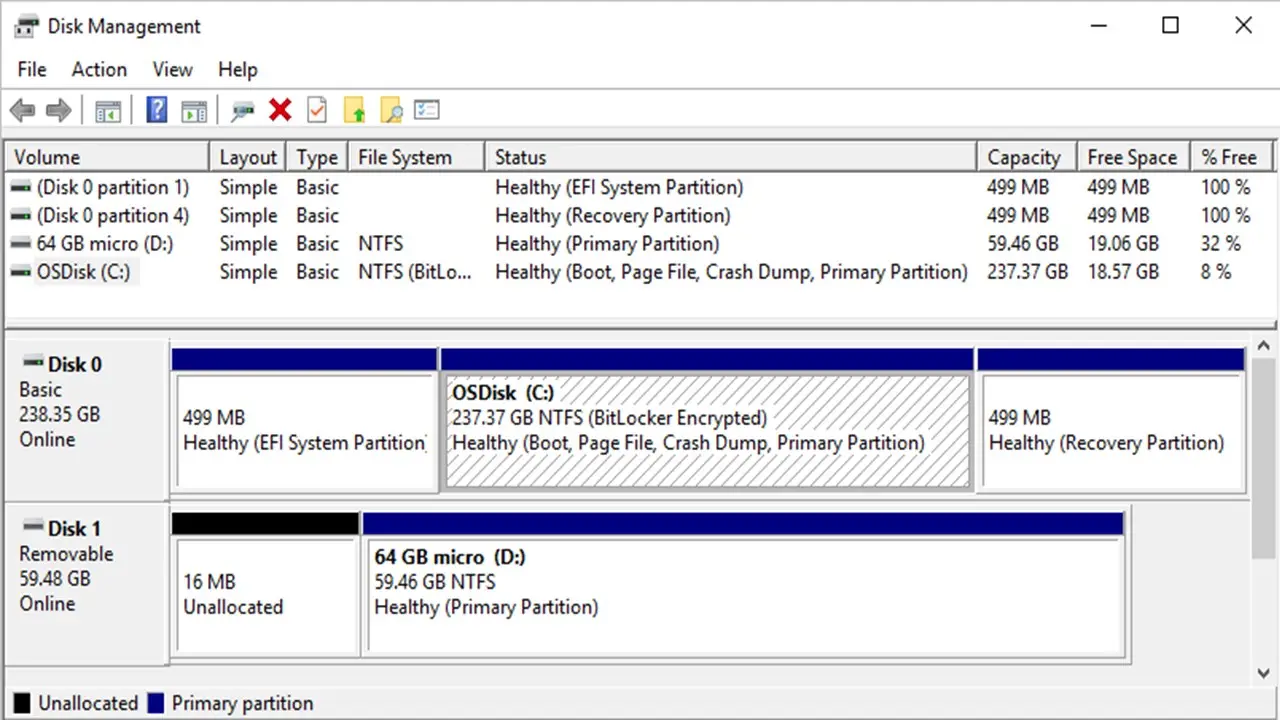
Disk Management is a utility program introduced with Windows XP for the first time.
This tool does not only allow the users to have a look at the different disk drives installed in their computer system, but also allows them to manage the partitions respective to each of the drives.
Disk Management is supposed to be the replacement for the earlier fdisk command. This tool displays each drive along with several other related elements of it such as:
- The file system
- The type
- The layout
- The capacity
- The status
- The free space on the disk and its percentage
- The fault tolerance
Accessing the tool
Typically, you can open this utility program by accessing the Run option. You can do this in any of the two following processes:
- Open it right from the Start menu straightaway or
- By pressing the Windows and R leys at the same time on your keyboard.
Once the Run option is open, you will have to type diskmgmt.msc in the box and hit Enter.
However, if you are using a Windows 8 system, you can type it directly on the Start screen and access the Windows Disk Management utility program.
Another way to open the utility program is:
- To go to the Control Panel
- Select Classic View
- Double-click on the Administrative Tools
- (If in Category view you will have to click Administrative Tools under Performance and Maintenance)
- Double-click on Computer Management in the Administrative Tools window
- Go to Storage section
- Click on Disk Management
You must note here that this utility is not available without administrator rights to your computer.
As for other Windows operating systems, the processes to follow are almost the same and are explained in the later sections of this article.
In the Linux operating system, you can use different commands to view the disk space and check disk partitions such as:
- fdisk
- sfdisk
- cfdisk
- parted
- df
On the other hand, in the Mac operating system, you can use the Launchpad in the following way:
- Click on the Launchpad icon.
- Type Disk Utility.
- Click on the Disk Utility icon.
Disk Management Tools
The Disk Management tools, also known as disk utility, are utility software.
These tools include disk cleaners, disk checkers, and disk analyzers and they help in performing the disk management functions including partitioning and formatting devices.
Here are some of the basic disk management tools with their respective functions in brief.
Disk Cleanup tools:
These tools help in getting rid of the unwanted and unnecessary files on the drive, therefore creating additional free space by clearing clutter that may include the following:
- Web caches
- Temporary files
- Old backups
The tool also helps in protecting the privacy of the information of files while using HTTP cookies, log files, and others.
A few examples of Disk Cleanup tools are as follows:
- Piriform CCleaner
- Razer Cortex
Disk Compression tools:
These tools are especially useful for increasing the amount of storage space on a drive. It is typically done by reducing the size of the information when it is stored on the disk. While reading the information, it is decompressed.
A few examples of Disk Compression tools are as follows:
- DriveSpace for Microsoft Windows
- DiskDoubler for Mac
Disk Checker tools:
These are typically checking tools that scan the whole hard drive or the logical structures of the files only and remove the corrupted areas or the files that are not saved properly. It helps in increasing the efficiency of the hard disk.
A few examples of Disk Checker tools are as follows:
Disk Formatters:
These tools help in preparing a hard disk, USB flash drive or any other data storage device for initial use. These tools can format a drive at three different levels such as:
- Low-level formatting
- High-level formatting
- Partitioning
You can also use these tools to erase a drive permanently.
A few examples of the Disk Formatters are as follows:
- EaseUS partition master format tool
- HP USB disk storage format tool
Disk Partitioning tools:
These tools actually split the disk into different regions, called partitions, to allow managing each area separately and more efficiently.
The information about each partition, such as its size and location, is maintained in a partition table.
A few examples of the Disk Partitioning tools are as follows:
- GParted
- GNU Parted
- Diskpart
Disk Space Analyzers:
These specific tools specify the usage of space on a disk by analyzing the size and other criteria of each file, folder, and even the subfolders. The information is displayed via graphical charts.
A few examples of the Disk Space Analyzers are as follows:
- DiskReport
- GNOME Disk Usage Analyzer
- KDE Filelight
Disk Defragmenter:
This particular utility software is used to reduce fragmentation of files by rearranging them and storing them in contiguous memory areas.
Since there are no file fragments, the accessing time is reduced and so is the time to read from and write to these files.
A few examples of Disk Defragmenters are as follows:
- Perfect disk
- Deflaggler
Backup software:
This specific software helps in keeping a backup copy of all the information on the disk. This helps in restoring the file whenever a file is deleted accidentally or in the event of disk failure.
A few examples of Backup software are as follows:
- Veeam
- Unitrends Backup and Recovery
What is a Disk Management Example?
A few common examples of Disk Management would include disk formatting, bad block recovery and booting from the disk in the case of the operating system.
Disk Format:
Disk formatting can be of low-level format or physical format, where the disc is divided into several sectors before storing data on it. This helps the disk controller to read and write very easily.
Here, the sectors actually retain 512 bytes of the following:
- Data
- Information
- Error Correction Code (ECC)
The optional disks, however, preserve the files by using the data structure of the operating system.
Typically, the entire process is conducted in two phases such as:
- Dividing the disk into several cylinder groups that are treated as individual logical disk
- Logical formatting or creating a file system
The data structure of the first file system is stored on the disk by the operating system, which contains both allocated and free space.
In order to increase the efficiency, the blocks are grouped by most file systems into clusters where the disk I/O runs in blocks and the file I/O runs in a cluster.
Boot block:
When you switch on a computer system or restart it, the location of the operating system kernel is searched by the programs held in the bootstrap Read Only Memory (ROM).
The system starts when the kernel is loaded into the memory and the operating system starts.
There is only a small bootstrap loader program stored in the ROM and to change the code, you will need to change both the hardware chip and the ROM. Ideally, the whole bootstrap code is retained in the disk boot block.
Such a disk that comes with a boot partition is usually known as a system disk or a boot disk.
Bad blocks:
Typically, the Hard Disk Drives are vulnerable to errors due to the moving parts inside them that typically have a very small tolerance. There are bad blocks in them bloated from the factory. The blocks can be handled in a number of ways.
The list of these bad blocks is maintained by the disk controller, which can instruct each bad sector to be replaced logically with one of the additional sectors. This structure is referred to as sector transfer or sparing.
The data recovery process is set off when there is a soft error. Sometimes, manual intervention may be required to prevent loss of data due to irrecoverable hard errors.
How to Get to Disk Management in CMD?
You can get to and start using the Disk Management utility program in a couple of seconds in CMD by using different commands such as diskpart, list disk, select disk, list partition, select partition and more.
There are three different and easy ways to get to the Disk Management utility in Command Prompt.
You can access the utility through the following steps:
- Go to the Start menu
- Open Run (you can also open it from the Apps screen)
- Type diskmgmt.msc
- Press Enter
Alternatively, you can access Disk Management by:
- Pressing Windows and X keys together on your keyboard
- Selecting Disk Management
You may also access the program in the following ways:
- Opening the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys
- Going to File
- Running new task
- Entering diskmgmt.msc
- Selecting OK
Once the Command Prompt is open, the next steps to follow to use the utility program for different purposes are mentioned hereunder.
If you want to delete a partition, the steps to follow and the commands to give are:
- Typing “diskpart.exe” in the Run box and pressing Enter to open the DiskPart command window
- Typing “list disk” and pressing Enter
- Typing “select disk [disk number]” and pressing Enter
- Typing “list partition” and pressing Enter
- Typing “select partition [partition number]” and pressing Enter
- Typing “delete” and pressing Enter
If you want to extend a partition, you will need to open the DiskPart window and then type the following:
- “list disk” and press Enter
- “select disk [disk number]” and press Enter
- “list partition” and press Enter
- “select partition [partition number]” and press Enter
- “extend size=n” and press Enter
If you want to create a new partition from the command prompt, the commands to give are as follows:
- “list disk” and press Enter
- “select disk [number]” and press Enter
- “create partition primary [size=n]” or “create partition logical [size=n]’ and press Enter
- “assign letter=H” and press Enter
If you want to convert the Globally Unique Identifier Partition Table (GPT) or Master Boot Record (MBR) during Windows installation the commands to give are as follows:
- “diskpart” and press Enter
- “list disk” and press Enter
- “select disk [disk number]” and press Enter
- “clean” and press Enter
- “convert mbr” and press Enter
You may also convert the FAT32 file system to NTFS from the command prompt. The command to give is “convert [drive letter:] /fs:ntfs” and press Enter.
Is Disk Management in Windows 10?
Yes, Disk Management is in Windows 10 and is available as a built-in utility. It will allow you to view and manage the internal and external hard drives in your computer.
You can use it to format and reformat or create partitions in the hard drives, rename them by assigning particular disk letters and even change the size of the partitions.
You can get to the utility in several ways. Here are the most commonly used methods.
Way 1: Via This PC
- Go to This PC
- Right click on the icon
- Choose Manage from the content menu
- Go to the Computer Management window
- Select Disk management
Read Also: What is Spindle? (Explained)
Way 2: Via Run option
- Press Windows and R keys simultaneously on your keyboard
- Type “Diskmgmt.msc” in the Run box
- Press Enter
Way 3: Via Search
- Click Search
- Type “disk management” in the box
- Select Disk Management from the list
You may also access it directly from Search by typing “disk management” in the box and choosing “Create and format hard disk partitions” from the result.
To use this utility program, follow these steps:
- Select the disk or partition
- Right click on it
- Select the operation that you want to perform
- Follow the step-by-step instructions
Where is Disk Management in Windows 7?
The Disk Management utility program in Windows 7 is in the Computer Management segment.
If you want to access it, you can do so by following these easy steps:
- Click on Start
- Right-click Computer
- Click on Manage
- Click on Disk Management from the two panes displayed in the Computer Management window.
This new window will display all the drives installed in your computer that have been detected by Windows.
What is Disk Management Used for?
Ideally, the Disk Management utility in Windows will help you to perform a lot of advanced storage tasks such as initializing, shrinking, or extending drive volumes, changing the drive letter and lots more that are necessary for disk management.
With the help of this utility program, you will find performing advanced storage tasks much easier. Such tasks may include:
- Initializing a new drive
- Extending the basic volume of an existing drive
- Shrinking the basic volume of the same
- Changing a drive letter
You will also find it very easy to create a new logical drive or a partition on a basic disk by using the Disk Management tool.
All you have to do is first decide whether you want to create a new partition or a new logical drive in an extended partition.
If you want to create a new partition, then follow these steps:
- Right-click on the Unallocated space on the Basic disk you want to partition
- Click on New Partition
If you want to create a new logical drive in an extended partition, then follow these steps:
- Select the particular extended partition you want to create the logical drive in
- Right-click on the free space on it
- Click on New Logical Drive
Once you are done with this initial selection, the other steps to follow are the same for both and are as follows:
- Click on Next on the New Partition Wizard
- Click the type of partition you want to create such as primary partition, extended partition, or logical drive
- Click Next
- Specify the size of the partition in the MB box
- Click on Next
- Decide whether or not to assign a drive letter to the new logical drive or partition manually or have the system enumerate it automatically
- Click on Next
- Click on Do not format this partition if you do not want to format it or click on Format this partition with the following settings and fill the fields in the Format dialog box
- Click on Next
- Confirm that the selected options
- Click on Finish
The new drive letter assignment along with the label name of the drive will be displayed against the new drive listed in My Computer.
Conclusion
You can access the Disk Management utility program easily to view and manage the disk drives.
It is a very important management tool available in the Windows operating systems.
You can use it for different disk management functions such as creating, deleting, and formatting the partitions of the disks, just to name a few.