What is Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)?
Extensible Firmware Interface or EFI in short refers to a firmware standard. It is developed by and introduced by Intel and is designed to improve the features of the Basis Input Output System or BIOS adhering to the UEFI or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface.
Technically, EFI is the division made on a data storage device used by the computers.
Understanding Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)
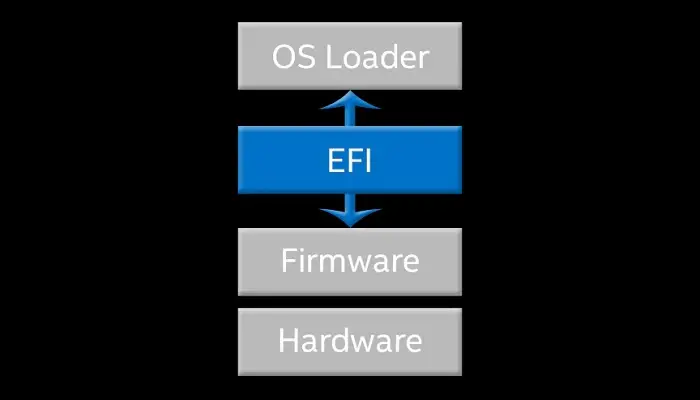
When you look into the configuration of your computer system you may have noticed that there are disk volumes or partitions in it.
In Windows there are usually two partitions, one larger and one smaller.
The smaller partition may range between 100 MB and 600 MB in size and this is called the Extensible Firmware Interface partition, or simply EFI.
It is quite an essential aspect of the computer system to function properly.
The word ‘Extensible’ signifies that the EFI can be changed depending on the situations.
While talking about EFI, most of the time reference to Windows 10 will be made but these partitions have always been a part of its earlier versions and even in other operating systems such as Linux and Mac.
There are a few changes made in the EFI in order to make it a general standard for the specifications of UEFI or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. A few notable changes are:
- Exclusion of the boot loader which allows selecting the operating system by the firmware
- Inclusion of a small shell to run at boot that offers a manageable and small working setting with nothing on the computer and
- Offering an option to create drivers by the vendors which cannot be reverse engineered.
Since EFI adheres to the UEFI or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, the latter loads the files saved in the Extensible System Partition or ESP while booting a computer to start the installation process of the operating systems and other different utilities.
Therefore, for a system to boot properly, the EFI plays a significant role in conjunction with the UEFI and the ESP.
At times, you may see that the EFI Partition is missing or you may even delete it accidentally.
You can fix it by either recovering the EFI partition by using a special recovery tool or by recreating the partition using diskpart in Windows 10.
These days, there is a UEFI BIOS or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface Basic Input Output System in most Windows systems and it is these systems in particular that will come with an EFI partition.
Other systems typically have the boot information included in the primary partition.
Ideally, when a computer starts there are several things that happen in it before Windows starts to function.
At first the BIOS starts which is actually a minimal operating system that is stored on a chip. This wakes up the firmware and hardware.
After that, it looks for the EFI partition for the instructions related to starting Windows and interacting with it.
When it is found successfully the boot process and the Windows starts.
You will not be able to see the EFI partition In Windows 10 in the File Explorer because it is valuable and therefore hidden.
However, it is not very hard to find it. All you have to do is use Disk Management Windows utility by following these steps:
- Select the Start button
- Type disk and
- Select the Create and format hard disk partitions option.
In the Disk Management window, you will be able to see the EFI partition. However, if you want to see what is inside the partition, you will need to use the Command Prompt.
This process is a bit complicated to navigate but a free third-party tool can make it easier. The steps to follow are:
- Downloading and installing the tool
- Running the partition wizard
- Finding the EFI partition
- Right-clicking on it and
- Selecting Explore to see what is in it.
If, in any case, the EPI partition is broken and your computer cannot boot, you can recover data from it by following these particular steps, irrespective of the format it is in.
However, you will need a reliable third-party tool for it and then follow these steps:
- Create a bootable media on another computer that is working fine using an empty CD, DVD or USB flash and selecting the correct option and
- Boot the computer from the bootable media by changing the BIOS boot order to ‘Removable Device’ and use a different external drive to store the files recovered.
You can also use Windows 10 clean installation to recover the lost EFI partition through the Command Prompt.
Extensible Firmware Interface System Partition
The Extensible Firmware Interface System Partition, commonly known as ESP refers to a small division of about 100 MB that is formatted with FAT 32.
This is the place to store the EFI boot loaders and applications that are necessary by the firmware during the startup process.
Usually, ESP is automatically generated after installing the operating system if the hard drive in the computer is in the GPT or Globally Unique Identifier Partition Table style.
It is supported by both Windows and Mac operating systems.
ESP is usually not visible via File Explorer or Finder for Mac OS X because it does not have a drive letter. Also, your system will not be bootable if you delete the ESP.
If your Windows has a GPT disk and you want it to boot normally, it should necessarily contain an EFI system partition along with an MSR or Microsoft Reserved Partition.
Sometimes, when you move the operating system into the hard drive, the ESP may not be generated and in that case the system will face issues during boot up as well.
In such situations, you will need to create an EFI partition and then install the boot loader. This will make the hard drive bootable once again.
The specific steps that you need to follow to create an EFI partition table are:
- Boot the computer system using a Windows installation or recovery disc
- Press Shift + F10 key during the setup process to enter into the command prompt
- Run a few specific commands in order to reduce the partition and free up the allocated space
- Create the EFI partition from the unallocated space by using specific commands
- Use a few other commands to install boot loader and other apps as required after creating the partitions and
- Reboot the computer system.
In the above steps you will need to use different but specific commands. The commands to use in step 3 are:
- Diskpart
- List disk
- Select disk X where X is the number of the disk that needs to be partitioned
- List partition
- Select partition N where N is the number of the partition to be reduced in size
- Shrink desired=500 where the number indicates 500 MB by which the partition is to be shrunk.
The specific commands to use in step 4 are:
- Create partition EFI size=200
- Format quick fs=fat32 label=”System” and
- Create partition msr size =128.
The particular commands to use in step 5 are:
- bootrec /fixboot and
- bcdboot c:\Windows /s b: /f ALL.
However, if it is an EFI-only system, you will not need the last two options and the command would read bcdboot C:\Windows.
Read Also: What is a FireWire Port? Works, Pros, Cons & More
You can delete the EFI system partition if you want in Windows 10 if you have an external hard drive and not an internal one since it will not need it to boot the drive.
Moreover, you may also need to uninstall the original EFI partition to create a new one in a Mac system and want to install Windows operating system in it.
Ideally, in order to delete it, you will need to use a third-party partition manager because the native tools offered by Windows will not let you delete the ESP.
If you use a reliable partition manager, you need not worry about data loss in Windows 7, 8, 10, 11, XP or Vista.
The steps to follow to delete ESP from your system are:
- Install and run the partition manager
- Connect either a CD or a USB drive to the computer
- Click on Make Bootable Media
- Follow the instructions on the wizard to create the bootable disk
- Boot the computer system using the bootable device
- Right click on EFI partition on the main window that you want to delete
- Select Delete Partition
- Click Ok on the pop up window to confirm
- Click on Apply to save the changes and exit.
The EFI partition will now be an unallocated space and you can use it to any current partition by using the Merge Partitions function.
EFI Specifications
The EFI specifications define the standard interface on the platform as well as the APIs used for the interaction with the operating system and the data structures.
The specifications offer varied information about EFI which includes and are not limited to:
- The correct return codes
- Proper typedefs
- Formatting
- Conventional BIOS Specs
- EFI Platform Specs
- Different measurements
- UEFI Secure Boot policy measurements
- NIST Special Publication
- EFI SpecID event and more.
These specifications are updated on a regular basis and therefore you should download the latest updates on it.
What Does EFI Do?
The primary job of the EFI is to connect the operating system to the firmware of the hardware components installed in the computer system.
The EFI partition also functions as the storage space for different files and utilities such as:
- The boot loader that starts the boot process, device drivers and the system utilities and also ensures that they are working together
- The device drivers that tells Windows how to interact with the different hardware components in the system
- The data files that holds all information related to the boot process and corresponding logs
- The system utilities or small programs that help in starting Windows and running it and
- The BitLocker data that stores the secret encryption of a drive and interacts with the Trusted Platform Module or TPM to decrypt or encrypt the drive.
In addition to that, the EFI also offers different types of services that can be categorized into two broad groups namely, boot services and runtime services.
Boot services are offered only when the platform is owned by the firmware before the ExitBootServices() call. These types of services include:
- Text and graphical consoles
- File, bus, and block services.
Runtime services are accessible when the operating system is functioning and include:
- Date and time and
- NVRAM access.
A few other types of services offered by the EFI are:
- Graphics Output Protocol or GOP services
- SMM services
- ACPI services
- UEFI Memory map services
- SMBIOS services
- Device tree services for RISC processors
- Time services that include daylight saving fields, time zone support and other variable services.
In addition to that, EFI also initializes tests of the hardware components of the system such as:
- PCIe link training
- Memory training
- USB link training and more.
After that it boots loader either from a network connection or from a mass storage device.
What are Applications of EFI?
Apart from loading the operating system, the EFI can also run a lot of UEFI applications that can be used by the UEFI Shell and the boot manager of the firmware.
As for the UEFI applications, one such is an OS boot loader. It can be Windows Boot Manager or others such as rEFInd, GRUB and Gummiboot.
Read Also: What is Input Buffering? (Explained)
These help in loading the operating system files into the memory and also provide a user interface for selecting another UEFI application to run.
It can also be applied for defining a few protocols that can be used as a set of software interfaces for interacting between two different binary modules.
EFI also provides an ISA independent device driver apart from regular Instruction Set Architecture device drivers which is especially stored in non-volatile memory as EBC or EFI Byte Code.
The EFI 1.0 specification also supports graphics features by defining a Universal Graphic Adapter or UGA protocol.
UEFI 2.1 helps in managing user input, fonts, local strings and form in HTML by defining Human Interface Infrastructure or HII.
Apart from the above, EFI also helps in UEFI, CSM, and network booting.
EFI also offers a shell environment that can be used to carry out other UEFI applications which includes several UEFI boot loaders.
There are also different types of commands that can be used in this environment to gather a lot of different information about the firmware or the system. Some of the commands used are:
- help
- guid
- dh
- unload
- set
- alias
- map
- mount
- pause
- ls
- mkdir
- cd
- echo
- mode
- cp
- memmap
- type
- dmpstore
- comp
- rm
- load
- ver
- date
- err
- time
- stall
- reset
- cls
- bcfg
- vol
- attrib
- edit
- Edd30
- mm
- mem
- EddDebug
- Dblk and
- Pci.
However, with virtualization and UEFI, the list of applications will be even longer and include different devices and software such as:
- HP Integrity Virtual Machines
- Open Virtual Machine Firmware of Intel SourceForge
- VMware Fusion 3 software for Mac OS X
- VMware Workstation before version 11
- VMware Workstation 14 for Secure Boot
- The vSphere ESXi 5.0 hypervisor
- VirtualBox 3.1
- Open Virtual Machine Firmware of TianoCore
- The VMware ESXi version 5 hypervisor
- Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machine of the 2nd generation and
- Google Cloud Platform that shields VMs support with Secure Boot.
You can even use the extensions of UEFI to add extra functions to the regular firmware stored on the Read Only Memory or ROM of the motherboard.
Where is Boot EFI Located?
Typically, the booth EFI files are typically located in drive C. In the UEFI systems the path to follow to locate the Windows boot loader for EFI is \Windows\System32\Winload and for others it is C:\Windows\Boot\EFI.
Is It Alright to Boot from EFI File?
Yes, it is okay to boot from an EFI file. You can do it by launching the Boot Devices menu option by pressing the F9 key. When you elect an option from there you will be able to see the list of all file system mappings that are available.
Apart from the common ones, you can boot different types of operating systems from EFI file or specification including:
- The Linux kernel
- HP-UX
- OpenVMS
- Intel-based Mac OS
- Windows 2000 Itanium version
- The x64 Windows operating systems with Windows Vista SP1
- FreeBSD kernel and
- Oracle Solaris 11.1 and later.
What will Happen if EFI system Partition is Deleted?
You can delete the EFI partition thinking that you will get an additional 100 MB of space at least but you should not do that.
This is because when you delete it, the BIOS will think that there is no Windows in your computer. In that case the system will not start properly.
It is basically like deleting the operating system of the computer itself.
Conclusion
So, going through this article you now have a thorough understanding about Extensible Firmware Interface including what it means and its uses.
As you can see, the EFI system partition in Windows 7, 8, 10, 11 is very important which ensures that the computer system boots in the normal way.