High-level formatting is the third stage of the formatting process, typically following low-level formatting and partitioning. It involves:
- Creating a new file system on a disk partition or logical volume
- Initializing the root directory and file allocation tables
- Preparing the drive for use by the operating system
The High-Level Formatting Process
During high-level formatting, the following actions occur:
- Erasing the path to existing data (without necessarily erasing the data itself)
- Rebuilding data structures like the boot sector
- Creating File Allocation Tables (FATs)
- Establishing the root directory structure
Importantly, high-level formatting doesn't typically erase all data on the drive, making data recovery possible in many cases.
When is High-Level Formatting Used?
Common scenarios for high-level formatting include:
- Installing a new operating system
- Preparing a new disk for use
- Resolving file system errors
- Removing write protection
- Freeing up disk space
High-Level vs. Low-Level Formatting
Key differences include:
- Data Recovery: High-level formatting often allows data recovery, while low-level formatting typically doesn't
- Speed: High-level formatting is generally faster
- Impact: High-level formatting has less impact on drive lifespan
- Accessibility: High-level formatting is more commonly used by everyday users
How to Perform High-Level Formatting
Several methods exist for high-level formatting:
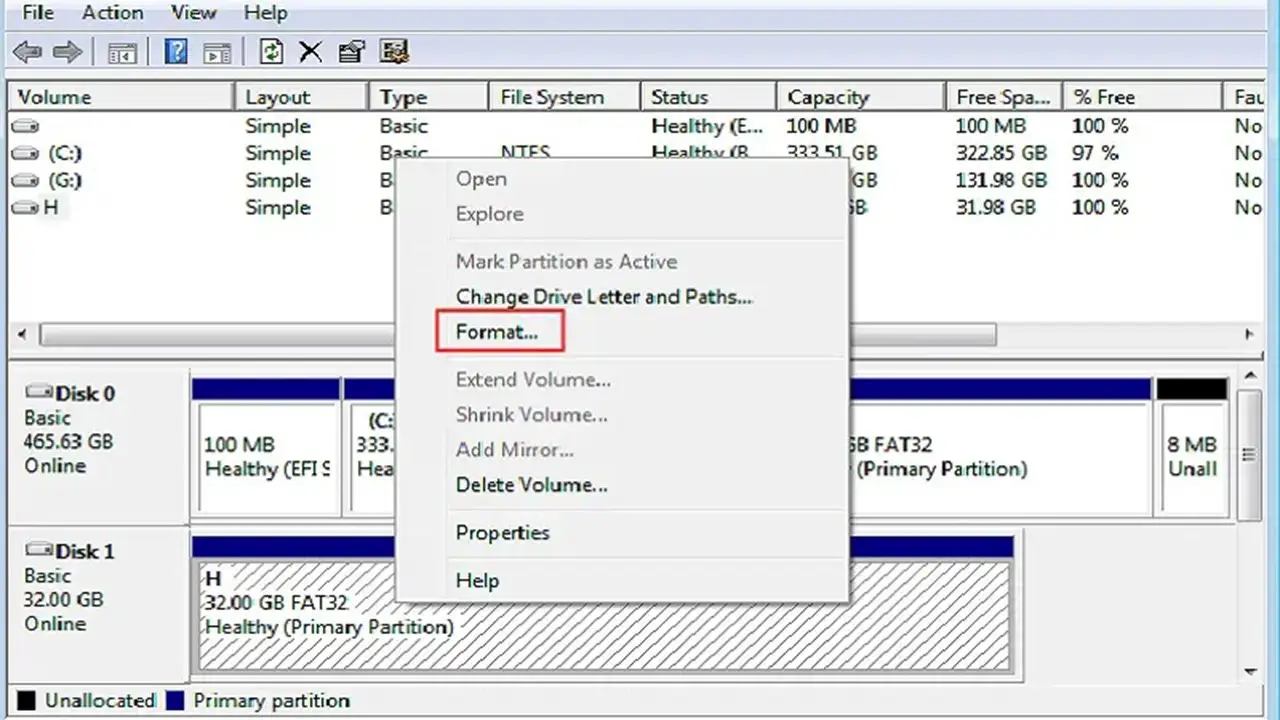
Windows Disk Management:
- Press Windows + R, type "diskmgmt.msc"
- Right-click the desired drive and select "Format"
DiskPart:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator
- Type "diskpart" and follow the prompts
Third-party software: Tools like AOMEI Partition Assistant offer more features and flexibility
Conclusion
High-level formatting is an essential process for managing storage devices. While it doesn't erase all data, it prepares drives for use by creating necessary file systems and structures. Understanding high-level formatting can help you better manage your computer's storage and troubleshoot common issues.
Read Also: What is Disk Management? Tools, Example & More
By mastering high-level formatting, you'll be better equipped to handle various storage-related tasks and maintain your computer's performance.