What is Parallel Processing?
Parallel processing refers to the technique of distributing the computer processes evenly between two or more processors or cores of the CPU.
In this technique, a single activity is divided into several smaller parts and assigned to different processors or cores in the computer to work concurrently, while being in sync with the help of software.
Understanding Parallel Processing
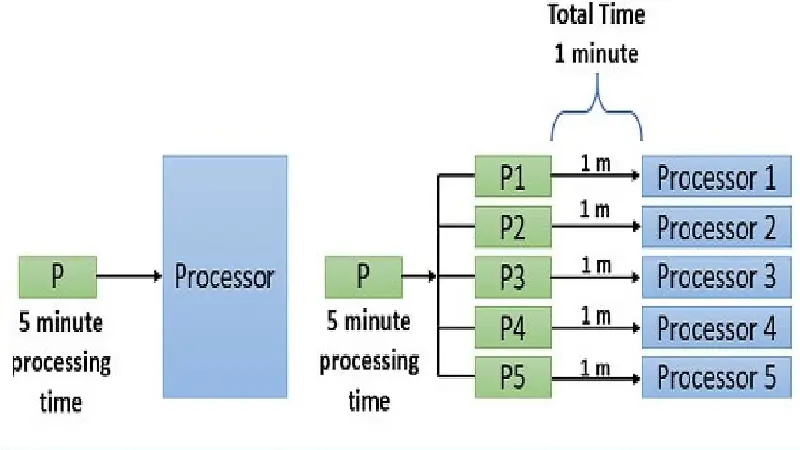
Parallel processing in computers is a specific technique of computing where several streams of data processing or calculation tasks occur in parallel.
There are quite a few CPUs or Central Processing Units working at the same time to make this happen.
However, this indirectly means that there are two specific requirements in the first place for parallel processing to happen. These are:
- The computer should be equipped with a processor with multiple cores
- The operating system must be able to support parallel processing or the software should be written specifically to allow executing instructions in parallel.
At the most basic level of parallel processing, the registers are used in a much better way in this technique than in sequential processing. It processes each bit simultaneously.
When an array of functional components performs simultaneously for the same or different related activities, it helps in removing the higher level of complexities in data processing.
This specific process of data processing can be used to solve problems using a regular desktop or laptop computer that would have needed a supercomputer otherwise.
Also, the operating systems of today determine the number of processors that may work together. This makes parallel processing even more cost-effective as compared to serial processing in most cases.
The principal purpose of parallel processing is to:
- Improve the processing capability of a computer
- Enhance the throughput or the amount of data processed per unit time.
Simultaneous processing helps the expert network and data center managers and is integral to process and supply more real-time data to micro service rollout, Internet of Things or IoT sensors, Graphics Processing Units, cloud services, and different endpoints.
In parallel processing, each of the processor or core performs operations in parallel as instructed in the following ways:
- Pulling data from the memory of the computer and
- Using software to communicate with each other to stay in sync when data values change.
When the processing is complete, the software will fit all the data from the different parts of the task together to produce the result of the single task.
What are the Characteristics of Parallel Processing?
Parallel processing can be characterized as either fine-grained or coarse-grained. In fine-grained parallelism, the tasks communicate with each other several times in a second to produce the results in real time, or close to it.
The other is a bit slower process due to the infrequent communication with the tasks.
Basically, it splits a complete task into two or more synchronized task segments and works on them simultaneously using multiple cores or processors.
Each processor performs concurrently, and the nodes share disks, data, and other resources.
Parallel processing can also be characterized by its processing architecture, which can be as follows:
- Multiple and separate processing core, which can be either homogeneous, having identical cores, or heterogeneous, having non-identical cores
- Symmetric, with two or more homogeneous and independent processors managed by one single operating system that treats each equally
- Distributed, where processors can be located on different devices in a network with their communications and actions coordinated through message queues or Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Massively parallel, where a large number of processors execute a set of computations simultaneously
- Loosely coupled, where individual CPUs have their own memory and can carry out a few operating system and user instructions independently.
Read Also: What is Golden Cove Processor? (Explained)
Ideally, all the processors in parallel processing are tightly coupled, run on the same operating system and they share the same user terminal and secondary storage.
Types of Parallel Processing
Parallel processing can be categorized into several other types based on the method of processing the instructions.
Different types of parallel processing include MPP, SIMD, MISD, SISD, SPMD, and MIMD. Each of these has different features and works differently, which is why some are more popular than the others.
SIMD or Single Instruction, Multiple Data:
- Processing is done by two or more processors
- Follows the same instruction set
- Each CPU handles the data differently
- Instructions are supplied by each of the processors with their distinctive set of data
- Helps in analyzing large data sets with similar benchmarks
- Same algorithm is applied to different data sets sent by several processing components
- All units are supervised by a single control unit
- Same instructions are sent by the control unit to each processor while processing different pieces of data
- Several modules in the shared subsystem help in communicate with every processor at the same time
- Divided further into organizations that use word-slice and bit-slice modes.
MIMD or Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data:
- Processing is done by two or more processors
- Data is supplied from different streams
- Each processor accepts instruction streams separately
- Can run multiple tasks simultaneously
- Uses a more sophisticated algorithm
- Interacts between the CPUs because all memory flows are altered from the shared data region that is sent out by all processors.
MISD or Multiple Instruction, Single Data:
- Each processor receives similar data input
- Uses different algorithms to process the data received
- Number of operations is influenced by the number of available processors
- Uses several processing units
- Each operates according to the instruction and on an analogous data flow
- The output of one processor is the input of the following processor.
SISD or Single Instruction, Single Data:
- Uses a single processor
- May or may not be able to process in parallel, depending on the configuration
- There can be more than one functional unit but the only control unit is in charge of all of them
- Manages a single data source and algorithm
- Instructions are executed sequentially and across all the execution phases
- Uses several functional units and pipeline processing to accomplish parallel processing.
SPMD or Single Program, Multiple Data:
- It is an MIMD variant
- All processors execute similar instructions
- Used as a message passing program by computer systems with distributed memory to a set of separate computers, collectively known as nodes
- Every node interacts with other nodes by launching its application and using send/receive routines
- These messages can also be used for barrier synchronization
- Transfer of messages follows specific communication methods, such as TCP/IP or Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol over Ethernet and dedicated high-speed interconnects, such as Myrinet and the Supercomputer Interconnect.
MPP or Massively Parallel Processing:
- Used to manage and coordinate the execution of program operations
- Uses multiple processors
- Each CPU uses its own memory and operating system
- Can handle different program sections and a large amount of data
- Processors use a messaging interface to communicate
- Message transmission is enabled between processes with a set of related data links for it to function.
Parallel Processing Examples
Examples of parallel processing include computer simulations made by the supercomputers used in astronomy and astrophysics, geoprocessing, agriculture, banking and cryptocurrencies, medical imaging, video-post production and others.
- Astronomy and astrophysics – This helps in studying star collisions, black holes, galaxy mergers, and more.
- Agriculture – It helps in making predictions regarding supply and demand ratios of different essential crops to help the policymakers to stabilize markets and the farmers to manage their budgets.
- Cryptocurrencies and banking – It helps in risk calculation, credit scoring, fraud detection, formulating financial regulations, and more.
- Video post-production – This helps the high-budget movies and films with special effects with state-of-the-art rendering.
Some other examples of parallel processing include several computers, super and otherwise, used for studying, analyzing, or developing:
- Energy usage
- Weather patterns and climate changes
- Earthquakes
- Seismic surveying
- Quantum chromodynamics
- Genetics
- The physics of new materials
- Medical imaging such as MRI, X-rays, CT, optical tomography and more
- Processors used in high-power desktop and laptop computers
- Investment industry
- Entertainment
- Vehicle engineering and Computational Fluid Dynamics
- Drug research and discovery.
Read Also: What is Program Counter? Example, Uses & More
Parallel processing also plays a significant role in developing machine learning algorithms and implementing them in several AI programs.
This is because it allows faster processing of more data points and produces more precise and useful insights.
What is Parallel Processing in Operating System
Typically, the operating system used in parallel processing is the same for all the processors. Since these are packed tightly in one casing, they can run on the same OS.
However, the operating system used in the process in particular can be of different types. It can be a separate, symmetric or master/slave operating system.
Separate operating system:
In this type of arrangement, each of the processors will have a separate copy of the operating system along with the file system, memory and I/O devices.
This is typical for a hypercube architecture where every node is like a separate computer. However, this type of parallel processing needs a lot of memory and execution time.
Symmetric operating system:
In this type of environment, every processor of the system is the same in every possible aspect. All data structures of the operating system are located in the global memory, which is accessible by every processor.
There is a microkernel in each processor that helps them work in parallel and when one or two of them fails, it may slow down the system but prevent it from coming to a standstill.
However, it is quite complex and difficult to build or debug.
Master/Slave operating system:
In this arrangement, there is one master processor. This executes the operating system. The other processors are considered slave processors and are used as resources such as memory or I/O devices.
The master processor knows the capabilities of each slave processor and accordingly assigns them tasks and resources.
This means that the master processor is in control of everything, and if it fails, the entire system comes to a halt.
Ideally, an operating system running on a multicore processor can be considered a parallel operating system, such as Windows 7, 8, 10, all of which do parallel processing. In short, most modern operating systems support parallel processing.
What are the Key Elements of Parallel Processing?
The key elements of parallel processing are speedup and scaleup, synchronization, locking and messaging.
Speedup and Scaleup:
These elements help in measuring the goals of parallel processing in the following ways:
- Speedup – This shows the extent to which the hardware can execute the same task in less time as compared to the original system.
- Scale-up – This expresses the additional amount of work done by a smaller system in the same time period as compared to a larger system.
Synchronization:
This is an important success factor that signifies proper management of concurrent tasks to ensure correctness. The less synchronization needed, the better will be the speedup and scale-up.
Dividing a task needs little synchronization and its amount depends on the number of users, amount of available resources and type of tasks sharing them.
Little synchronization is required for a smaller number of tasks but a lot of it is needed for coordinating a large number of concurrent tasks.
Locking:
This is one way of synchronizing the tasks. Several different locking mechanisms are required for synchronizing tasks in parallel processing and one such internal locking facility is the Integrated Distributed Lock Manager or IDLM.
This helps in:
- Coordinating resource sharing between the running nodes
- Communicating with each other
- Coordinating database resource modification
- Keeping track of the current resource ownership
- Accepting lock requests from application processes for resources
- Notifying the requesting process about the availability of a lock on a resource
- Getting access to a resource for a particular process.
Messaging
And finally, parallel processing needs to communicate between the nodes in operation and therefore it needs a fast and efficient messaging system with very low latency and high bandwidth. This is facilitated by the IDLM.
Does Google Use Parallel Processing?
Yes, Google uses parallel processing which helps it run a distributed network involving thousands of low-cost computers. The technology speeds up the data processing process significantly.
Ideally, there are three discrete parts in Google. These are:
- Googlebot – This is the web crawler that fetches web pages.
- An Indexer – This searches each word on a page and stores the resultant index in a large database.
- A query processor – This compares a search query of the user to the stored index and advocates the most relevant documents.
Read Also: What is Out-of-Order Execution? (Explained)
Parallel processing helps these three parts to perform their functions most precisely in the following ways:
- The web server sends the user query to the index server to look for a word in it that matches a particular word in the query
- The query moves to the doc server which retrieves the stored document
- The search result is returned to the user.
All these actions are performed in just a fraction of a nanosecond, thanks to parallel processing.
Advantages
- Higher fault tolerance since processes can be rescheduled to another processor to get completed if one processor fails in the system
- It uses multiple processors which increases the throughput of the system
- The number of processors can be increased and the system configured according to the need
- Cost of build-up and maintenance is low
- Improved response time
- More resources are used to decrease execution time
- Solves larger problems in quick time
- Larger application in the real world
- Benefits of using non-local resources when local resources are limited
- Minimal waste of potential computing power
- Effective use of hardware
Disadvantages
- Tasks need to be structured properly to be executed in parallel
- The sequences of tasks need to be preserved
- Difficult to achieve the desired parallel architecture
- Needs better cooling technologies in the case of clusters
- Needs managed algorithms
- High power consumption
- Difficult to create the required high cohesion and low coupling
- May affect control algorithms and conjunction of the system
- Data transfer and thread creation cost may be more than the gains due to synchronization
- Needs code tweaking for special target architectures
Parallel Processing Vs Sequential Processing
- In parallel processing, a task is divided into several smaller tasks and each of it is carried out on a separate node, but in sequential processing, it is executed as one single large task.
- Parallel processing uses two or more processors to complete a task, but, in comparison, sequential processing uses one to do the same.
- Parallel processing is relatively faster in comparison to sequential processing because it completes only one task at a time.
- In parallel processing, more CPU power is allotted to the tasks so that it can execute it instantly on its own processor without having to wait, but in sequential processing, since there is a single resource, the following tasks need to wait for the previous ones to get completed.
- Parallel processing can solve larger problems in quick time as compared to sequential processing.
- Parallel processing is more suitable for modeling, simulating, and understanding complicated real-world phenomena than sequential processing.
- In parallel processing the hardware and resources are used more effectively in comparison to sequential processing, where a considerable part of these are left idle.
- In parallel processing the workload on a processor is not as high as it is in the case of sequential processing. That is why in sequential processing, the processor heats up quickly.
- In parallel processing data is transferred in bytes or chunks of 8 bits, but in sequential processing, it is transferred in bit by bit form.
- In parallel processing, messages defined in the service operation are processed by the subscribing system in parallel and in no specific order, but in sequential processing it is the inbound service messages that are processed in the order received.
- The registers are used more effectively and productively in parallel processing than is sequential processing.
Which Generation Uses Parallel Processing?
Typically, parallel processing is a feature of the 5th generation computers and major electronic components that are based on multicore processors and Artificial Intelligence or using ULSI or Ultra Large Scale Integration technology.
Conclusion
Parallel processing is very useful to expedite data processing and has been around for a while.
It has varied applications, being able to process large amounts of data in a quick time.
It helps in financial risk management, big data analysis, medical imaging, video color correction, just to name a few of its uses.