In This Article
What is a Disk Sector?
The disk sector refers to the smallest unit for storing data on, reading data from, or writing data to a hard disk drive. In other words, the disk sector is a precise division on the storage medium of a diskette or a hard disk drive.
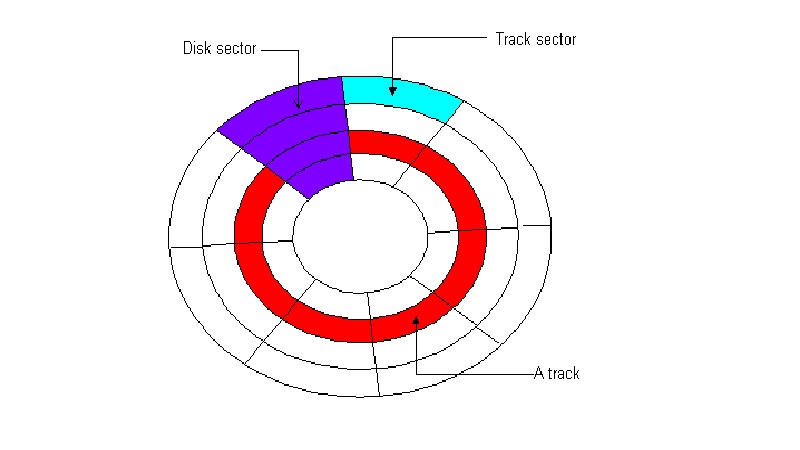
Technically, a sector typically signifies the wedge-shaped slice of a specific circular track. The term sector refers to one whole arc that holds 512 bytes of data. Every sector on a hard drive is typically given a number to help with interleaving.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A disk sector denotes the smallest storage space on the hard drive that can be accessed. Each sector is given a specific name. It helps in interleaving and keeping tabs of the data by the disk drive and the operating system.
- There are usually more disk sectors on the outside and get reduced while moving inwards towards the middle of the disk. This particular variance in the sectors on each track is called the zoned-bit recording.
- The number of sectors on a disk may vary according to the size of the hard drive, but, typically, every sector will be of 512 bytes. However, there are a few modern hard disk drives that come with 4K sectors of 4096 bytes.
- The number of sectors on a hard disk drive can be checked easily by using the System Information tool in Windows and looking at the Bytes/Sector, Sector/Track and Total Sectors sections.
- Large files can consume thousands of these sectors while storing them on a hard drive. In such cases, several groups of sectors, referred to as a cluster, on a disk are used to store them and fit them into a single disk sector.
Understanding a Disk Sector
The smallest storage unit on a hard disk drive that can be used to store data and accessed is called the disk sector, or, less commonly, as a block.
Typically, a disk on a hard drive gets divided into sectors and tracks when these undergo low-level formatting.
Here, the tracks signify the concentric circles all over the disk and the sectors represent the small segments within each of these circles that resemble an arc.
Each of these sectors on the tracks are given a name that helps in interleaving and the disk drive as well as the operating system to keep a tab on where exactly an information is stored on the hard drive with the help of the sector and track number.
Typically, a sector is a specifically sized partition of any kind of storage media such as:
- The hard disk drives
- The optical disc drives
- The floppy disk drives
- The flash drives
Every sector of the hard disk drive stores a definite amount of data that a user can access.
Considering traditional geometry, a disk sector would mean the part of the disk between the disk center, its two radii and the corresponding arc formed by them. This, typically, gives the disk sector the shape of a slice of a pie.
In complex terms, a disk sector is the intersection of the track and geometrical sector.
The circular tracks on each circular disk platter on the hard drives get longer when they move outward from the middle or center of the disc.
This means that you have a larger number of sectors on the outer sides of the disks along the tracks than there are on the inside.

Zoned Bit Recording
The difference in the number of sectors on the outside and inside of the disk of a hard drive results in a variance in the number of sectors on each of these tracks, giving rise to a phenomenon referred to as ‘zoned-bit recording.’
In the modern hard disk drives, this technique is used due to the difference in strength and density of the sectors based on their locations.
Typically, the sectors that are located near the outside of the disk are much stronger in comparison to the sectors that are located near the center of the disk.
However, these sectors, located on the outer region of the disk, tend to have a lower bit density.
With the use of zoned bit recording, the disk of the hard drives is divided into several different zones first, and then each of these zones is further divided into sectors.
The result of this technique is that the zones in the outer section of the disk that have more sectors can be accessed much more quickly than the zones situated in the middle of the disk.
Size
Initially, the size of the disk sectors was either 128 bytes or 256 bytes, but it was later increased to a fixed maximum of 512 bytes.
This is the traditional sector size of a hard disk drive. And as for the CD-ROMs and DVD-ROMs, it is 2048 bytes.
However, as for the modern and larger hard disk drives, this limit was further increased to 4096 bytes, and are often referred to as the Advanced Format size. These are also called the 4K sectors, with respect to 4000 bytes.
You can customize the size of sectors to maximize the available storage area.
For example, if you use your hard drive to store a large number of smaller files, you can fill the storage space with more files when you decrease the size of the disk sectors. This will leave no room leftover.
Typically, depending on the size of the sectors of the disks, storing large files may need a lot of them, often thousands.
This has a significant problem. If one of these sectors gets corrupted, then the entire file will be more likely to be unreadable.
Though the corrupted data can be fixed by means of a disk utility program, the physical damage that may be caused to the disk cannot be repaired. These physically damaged sectors are referred to as the “bad sectors.”
The computer system can identify these bad sectors on the hard disk drive and may even bypass them during operation but these damaged sectors will prevent the storage system from working efficiently and properly.
Usually, the size of the sectors available on the hard disk drives does not matter much. It is actually the number of sectors available that typically determines the storage capacity of a hard disk drive.
Basic Parts
Every physical sector on a modern hard disk drive is typically made up of two fundamental parts. These are:
- The sector header area, which is usually referred to as the ID
- The data storage area
Sector Header Area
Typically, this particular area of the sector of the hard disk holds the information that is necessary and used by the hard disk drive and the controller. The different types of information include:
- The address identification
- The sync bytes
- The flaw flags
- The error detection and correction data
There may be an alternate address contained in the header area as well. This alternate address is usually used when the data area becomes unreliable.
Typically, the address identification is necessary for the hard drive operation because it allows ensuring that the drive mechanics have placed the read and write heads correctly over the desired location of a particular data that is requested for a read or write operation.
Data Storage Area
This specific area on the sector of a hard disk drive is also used to store different types of information and data such as:
- The user data
- The sync bytes
- The Error Correcting Code (ECC)
ECC is usually used to check whether or not there are any errors introduced into the data and also the possibilities of rectifying those errors along with.
How Many Sectors Are There in a Hard Disk?
Typically, the number of sectors on a hard drive will vary from one hard drive to another depending mainly on the size of them because the other parameter, the size of the disk sector, is fixed at 512 bytes.
However, in most cases, a disk cluster will have as many as 4 to 8 sectors in them.
Here are some examples of the number of sectors in hard disk drives with respect to their sizes:
- A 500 GB hard drive will have as many as 976,562,500 sectors.
- A 1 TB hard drive will have as many as 2147483648 sectors.
- A 2 TB hard drive will have as many as 3,906,250,000 sectors.
Therefore, you can see that the number of sectors on a hard disk drive can have a variety of values and there is nothing called an obligatory value.
However, usually, all modern hard disk drives come with as many as 63 sectors per track.
It is not difficult at all to know the number of sectors a hard drive has. You can calculate it if you know the size of your hard disk. All you have to do is divide it by 512, the fixed size of a disk sector.
If you do not like to do the math, then here are some easier ways summarized for you.
You can use the Windows Disk Checking Utility, the Command Prompt, or any reliable third-party software utility.
Using a software utility:
To use a free software utility program, follow these steps:
- Run the software.
- Select the hard disk.
- Go to the Sector or Total Sector parameter.
- Right-click on it and note the number.
You can even find out how many sectors a partition on your hard drive has. All you have to do is select a partition and then see the total sectors.
Using the Command Prompt:
You can also check it from the system information by using the Command Prompt. The steps to follow in this case are:
- Running msinfo32 in the command line
- Looking at the System Information GUI window that pops up
- Selecting System Summary from the left pane
- Clicking on Components
- Selecting Storage
- Choosing Disks
- Look for the desired drive in the right pane
- Check the value for Bytes/Sector
It may be displayed as “Bytes/Sector 4096.”
Conclusion
A disk sector refers to the unit that represents the smallest physical storage area on a hard drive.
As you have come to know from this article, on most of the file systems, the size of one sector is fixed at 512 bytes.
Based on this parameter and the size of the hard drive itself, the number of sectors in it may vary.