In This Article
What is Back Side Bus (BSB)?
The Backside Bus or BSB refers to the computer bus which connects the secondary cache and the CPU. Therefore, it can be considered as a part of the CPU and its operating speed is reliant on the speed of the CPU.
From the technical point of view, the backside bus was designed when the 2nd generation Pentium III processors came with the Level 2 or Advanced Transfer Cache on the die.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Most backside buses connect the CPU with the Level 2 cache but sometimes they may also connect it with the Level 1 cache to enhance the speed and efficiency of the CPU during its operation.
- A Backside Bus connects two chips and is typically faster than the Front Side Bus and much faster than the peripheral buses such as PCI and ISA.
- These buses can be made much wider than the Front Side Buses which help in improving the communication process between the CPU of the computer and the secondary memory since it can carry more data.
- Using the BSB does not only enhance the performance of the system overall but also shortens a lengthy process by eliminating the need for extra signals and protocol overheads by the bus.
- The use of these buses is very rare today because most of the processors come with integrated Level 2 and Level 3 cache into them.
Understanding Back Side Bus (BSB)
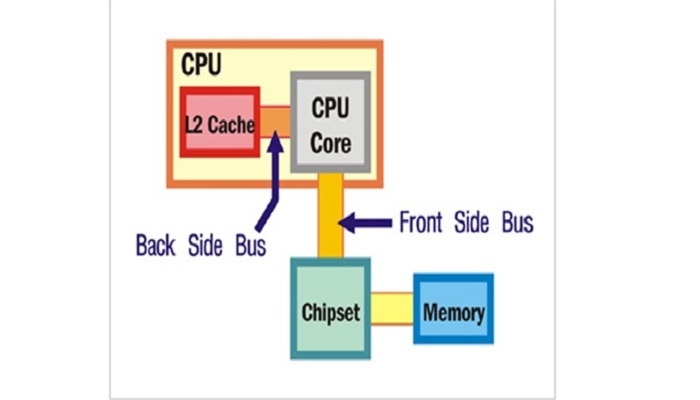
Usually, data is carried to and from the CPU of a computer by two different types of buses or channels such as the Front Side Bus or FSB and the Backside Bus or BSB.
The Backside Bus is the dedicated channel between the Central Processing Unit and the Level 2 or secondary cache.
This cache typically stores all those necessary data and information that are used frequently by the CPU to function as well as other related data.
Being located close to the processor, it allows faster access to the necessary data by the CPU which, in turn increases the overall speed and performance of the computer system.
This is because it allows the CPU to function more efficiently and complete the repetitive processes much faster.
All the required operational information and data from the Level 2 cache is sent through the Backside Bus which is why it needs to be fast to prevent lags in the performance of the CPU.
That is why BSB typically operates at the speed of the CPU and therefore is usually much faster than the Front Side Bus.
It is also much faster in comparison to peripheral buses such as the Peripheral Component Interconnect or PCI and Industry Standard Architecture or ISA bus.
The use of BSB actually removes the severe bottleneck in the speed of operation of the CPU because it increases the speed of the memory and allows faster access to the data stored in it for the processor.
This improvement over the previous practice when only one system bus was used provided a dedicated channel to optimize the communication process between the CPU and the cache.
This actually eliminated the need for additional signals as well as protocol overheads that expedited the process of a general-purpose bus.
The systems that had both FSB and BSB were referred to as systems with Dual Independent Bus (DIB) or dual bus architecture.
Being closer to the CPU, the shorter distance also helps the BSB to operate better and faster at higher clock speeds to increase the performance and throughput of the computer system on the whole.
Initially, cache was connected externally to the microprocessor die with the BSB but now it is typically on-die, and, as said earlier, this increases the clock frequency of the BSB making it equal to that of the processor itself.
The BSB can be designed much wider in comparison to the on-chip or off-chip Front Side Buses up to 256 bits or 512 bits.
This improves CPU communication even more with the cache memory since the need for any additional procedures is eliminated.
In short, cache in a computer being the smallest amount of memory is very fast.
The CPU therefore accesses it first to find the relevant data using the BSB to expedite the process that would have been much lengthier otherwise, provided the data is used recently.
However, today most of the computers come with CPUs with integrated L2 and L3 cache into it. This eliminates the need for a BSB any more, making them pretty obsolete.
What Does BSB Do?

A Backside Bus is typically used to connect two different chips that have the same clock rate as the CPU or the Central Processing Unit. Ideally, it connects the Level 2 cache and the CPU.
The BSB acts as a bridge that helps the cache to move in two separate directions.
It allows the CPU to use it to access the data it has stored previously for accessing it quickly in future when instructed.
For example, there are two chips in a Pentium Pro microprocessor.
One of these chips comes with the primary cache and the CPU and the other with the secondary cache.
It is the Backside Bus that connects these two chips so that both operate at the same speed as the processor.
On the other hand, if you consider the Pentium II processor, there is a bigger secondary cache measuring 512 KB.
However, this operates at half the speed of the processor.
Back Side Bus vs Front Side Bus
Operation
The Backside Bus carries data to and from the Level 2 or secondary cache of the computer but, on the other hand, the Front Side Bus transfers data between the memory and the Central Processing Unit.
Speed
The clock frequency of the BSB is often as fast as the clock frequency of the CPU itself because it cannot afford to lag behind when any request for data access is made by the CPU.
On the other hand, the FSBs are often much slower than the BSBs with their clock frequency being actually half of the latter. However, FSBs are faster than the peripheral buses like PCI and ISA buses.
Connection Type
The BSB is a separate link or a bridge between the bus and the device but, in comparison, the FSB is the physical connection between the devices.
Conclusion
The Backside Bus is an important component of a computer that helps in enhancing the performance of it by allowing the CPU to access the necessary data for its operation quickly from the secondary memory.
It can be made wider to carry as much as 512 bits of data which further adds to the performance.