In This Article
What is Dual BIOS?
A Dual BIOS in a computer system refers to the main BIOS and backup BIOS on the motherboard. This specific feature helps the motherboard and the system to recover easily with no downtime in the event of any issue during its update.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Dual BIOS is present in the motherboards in the form of two Serial Peripheral Interface or SPI flash chips for redundancy. Some high end graphics cards also support this feature.
- Backup BIOS on the board helps the target overclockers to make a switch easily and quickly when the main one is bricked by using a button or a jumper. Apart from that, it also helps in protecting it from external virus attacks or corruption of data.
- All motherboards do not come with this particular aspect which is particularly an enthusiast feature. Also, random corruption or a BIOS upgrade by the users is very rare.
- Adding this feature increases the complexity, cost of manufacturing, higher retail price, and assembly time of a motherboard. These are often not necessary for a majority of users who look for a cheap computer to buy and have no intention to mess with the BIOS of the motherboard.
- Using this feature allows using Basic Input Output System ROM1 or ROM2 for boot up but it is necessary to set the switch to the target ROM that needs an update and the Dual BIOS switch should not be used while the update is happening because it may corrupt the ROMs.
Understanding Dual BIOS
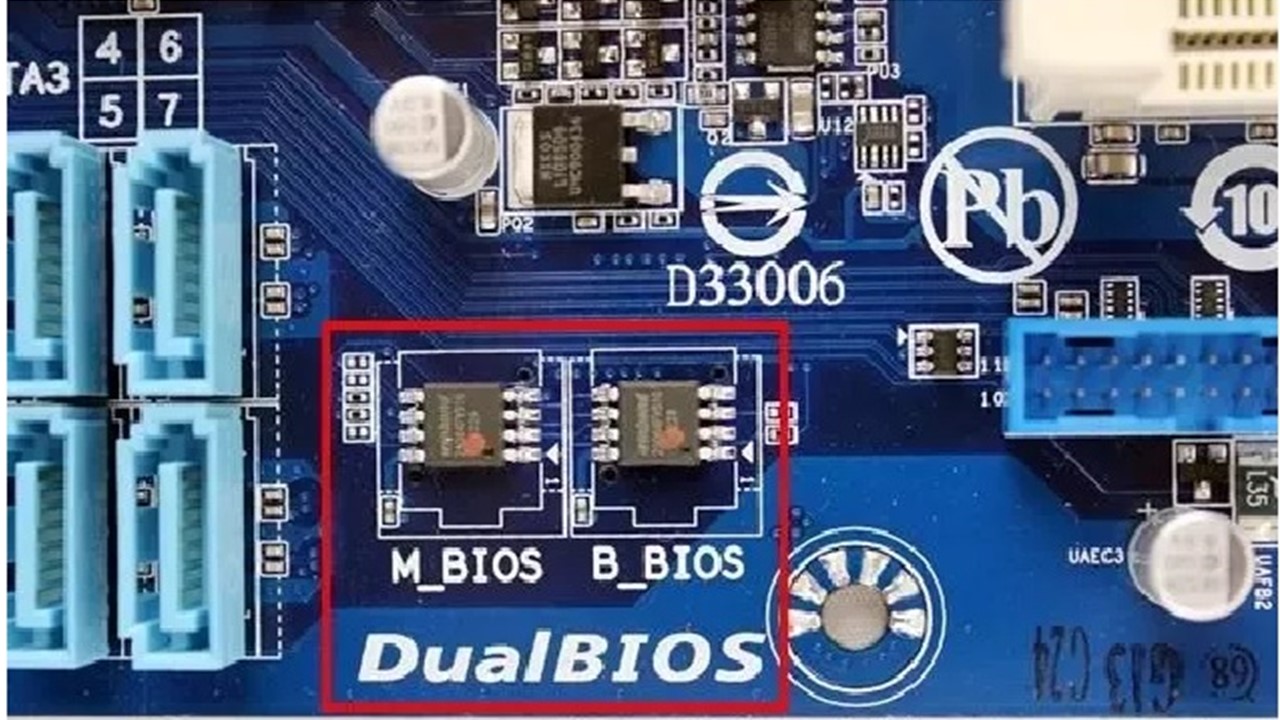
Ideally, the Dual BIOS feature refers to the presence of two physical BIOS ROMs in the motherboard. One of these chips acts as the main BIOS, which is used primarily while booting up the computer system.
The other chip typically performs as the backup BIOS. This usually contains the factory default version of the system in it.
The main function of it is to take over the booting process the next time when you switch on the computer system but the main BIOS fails or has stopped working.
Since this switching is done automatically, there is very little or no down time during the boot up process.
Ideally, the boot up process of a computer happens in this way.
After switching the system on, the Basic Input Output System checks are made and if it passes hardware checks are made which eventually switches on the booting sequence to boot up the system.
However, when it fails after the system is switched on it is then that the backup BIOS sets in. It restores the data in the main BIOS file and then the booting sequence is restarted.
Since the entire process is automatic, the backup BIOS will start doing the job when there is a problem noticed in the main one and you shut down and boot up the computer system again.
There may be a lot of different reasons for BIOS failure which include:
- Power shut down or power loss during the update process of it
- Hardware failure or damage
- Firmware issues
- Virus and other external attacks and
- Incorrect overclocking setting.
In a situation where overclocking is enabled the computer system will always boot into BIOS wherever any default setting is applicable.
It will not boot on advanced settings and in most cases move to the default settings.
A secondary boot up system therefore is a very nice feature to have which helps the system to boot up when the main BIOS fails.
In addition to that, there are a few other specific benefits of using a secondary Basic Input Output System which include:
- Repairing a failed system file right away
- No user intervention required since it is fully automated
- Lower service time and
- Quick, safe, and automatic recovery of data of the main BIOS.
In addition to that, if you have backup or secondary BIOS you will be able to experiment with custom Basic Input Output Systems without any risks.
As for the cards, there is no risk of breaking them and in some specific models it may even allow you to unlock supplementary overclocking potential with just a flip and also improve the fan speed control.
Another surprising benefit of this feature is that it enables better power management of the vital internal components of the computer subsystem such as the Central Processing Unit or the CPU and the Random Access Memory or the RAM.
The BIOS switch can be set to either master or slave position as well and in each case you will gain varied benefits.
If you set the switch in the master position, which is actually the default main BIOS a graphics card is shipped out with, it will result in a few specific things such as:
- The graphics card will have a much lower power target and
- The fan curve will be less aggressive and will not start spinning unless the graphics card attains roughly 60o Celsius.
On the other hand, if you set the switch in the slave position it will act as the secondary BIOS and allow the graphics card to:
- Have a bit higher target temperature and power target which will allow more headway for overclocking but if the card supports Pascal architecture the clock speeds will reduce when the core of the graphic card reaches 60o Celsius and
- The fan curve will be much more aggressive and will keep on spinning, even in the idle state.
Typically, if the main BIOS fails to perform due to any issues in the firmware itself, the Dual BIOS will start to function and recover the file and data of the main one back to the factory default version and everything will be normalized back again.
However, if the issue is due to any hardware failure or damage, it will take over and will function just like the main BIOS.
In short, Dual BIOS is specifically designed and used to streamline the boot up environment by making it extremely user-friendly.
Dual BIOS Setting
Setting Dual BIOS can be done after the computer system posts up successfully. When the BIOS is active, it will be based on the position of the BIOS selector before the system powers up or restarts.
There is however, no need to change this position of the particular selector position when the computer system is posting.
You will need to set Dual BIOS manually if the Delete key does not work.
Ideally, enabling the fast startup feature of Windows 8 and 10 will take the system to the hibernation mode when closed and when you power it on again, this particular feature will not allow the Delete key to work.
This will actually do two specific things such as:
- It will shorten the boot up time and
- It will not allow entering BIOS during POST.
This can create some problems at times and there are two specific ways in which this problem can be resolved.
In the first method, you will need to turn the fast startup feature off and then follow these following steps:
- Open Control Panel
- Go to System and Security
- Go to Power Options.
- Click on choose to select what the power button should do
- Click Change Settings that are not available as of now
- Uncheck Turn on fast startup option and
- Click on Save Changes.
In the second method, you will have to enter BIOS via WinRE. However, this method can only be followed in Windows 8 or later versions.
It also needs the computer system to work on Globally Unique Identifier Partition Table or GPT hard drive + Unified Extensible Firmware Interface or UEFI boot mode and not Master Boot record or MBR + Legacy mode.
The next steps to follow are:
- Clicking on the Start button
- Going to Settings
- Clicking on Update and Security
- Clocking on Recovery
- Clicking on Advanced Startup
- Clicking on the Restart Now.
After the system restarts, you will be in WinRE and on this particular window you will need to click on the following in this specific order:
- Troubleshoot
- Advanced options and
- UEFI Firmware Settings.
Finally, you will need to click on the restart button when you will be allowed to enter the BIOS window to set it.
Depending on the system type, there are also other solutions to enter and set Dual BIOS.
You may enter the setting by pressing the F2 function key immediately after switching on the computer and on some particular devices you may need to press the Delete key.
The process to follow after it is to use the arrow keys to change the Boot tab and select the drive priorities.
When the menu opens, you will need to set the Windows Boot Manager as Boot Option #2 and to Boot Option #1 if you are using Ubuntu.
When it is done, you will now have to Press F4 to save the settings and exit from the BIOS. The system will reboot properly and the Dual BIOS will work just as desired.
Use of Dual BIOS
The most significant use of this specific feature is to start the backup BIOS and set the computer system up and running automatically when the primary BIOS ROM chip fails for any reason such as incorrect flashing of the Basic Input Output System by the users or a virus attacking the computer system.
Adding to that, using Dual BIOS onboard offers double protection to the computers system against outside attacks from firmware and viruses as well as from any physical damage.
Apart from that, Dual BIOS is also used to offer more convenience to the users or enthusiasts since they can switch manually between two different BIOS when there is any hardware failure.
Most importantly, this feature is used to add safety to the computer system on the whole.
In short, the main purpose to use Dual BIOS is to have a backup that will work as a recovery agent that will be invoked automatically when the main chip fails to perform normally.
How to Switch to Dual BIOS?
Usually, switching to Dual BIOS is quite easy where in the normal process all you have to do is press the Delete key while starting up the computer system PC and then press the F8 function key to enter the Dual BIOS setting.
Ideally, you do not have to press the F1 key while starting the computer as it may be mentioned in a few instruction manuals.
The process to follow is:
- Turning the computer system off
- Locating the BIOS selector
- Switching the BIOS selector to secondary position
- Boot up the system again.
- You should now have the secondary BIOS functioning.
If you want to get access to UEFI BIOS the steps to follow are:
- Clicking the Start button
- Navigating to Settings
- Selecting Update and Security
- Selecting Recovery option from the left menu and
- Clicking on Restart Now under Advanced startup.
This will make the computer system to reboot to a particular menu where you will have to follow these steps:
- Clicking on Troubleshoot
- Clicking on Advanced options
- Selecting the UEFI Firmware Settings and
- Clicking on Restart.
How to Add Dual BIOS?
If you are facing issues with the old Basic Input Output System then you can add Dual BIOS without corrupting it by flashing a new one in three different ways such as holding the power button, holding the power and reset button, and by shorting pins 1 and 6.
The steps to follow in each of these methods are as follows.
In the first method all you have to do is:
- Shut the computer off
- Hold the power button till it starts and shuts off again
- Again press the power button.
This should trigger the backup BIOS in your system and re-flash it if there is something wrong in the new BIOS.
The steps to follow in the second method are:
- Shut the computer off and
- Hold the power and the reset button for nearly 10 sec and release them.
This should automatically add and booth the backup BIOS.
And in the third method, which you should follow only if the above two methods are not able to boot the Dual BIOS, the steps to follow are:
- Shorting out pins 1 and 6 by holding a jumper on the main BIOS to connect the two pins
- Pressing the power button while holding onto the jumper to the pins and
- Removing the jumper as soon as the system beeps.
This should start the boot up process of the backup BIOS.
What is Dual BIOS in GPU?
If there is a Dual BIOS feature in the graphics card such as in the EVGA graphics, it will allow you to make a switch from one BIOS version to another different version of it.
Though only a few specific models of graphics cards have this feature in them you can use it to flash the secondary BIOS if you need to hot fix or overclock.
How to Fix Dual BIOS?
You can fix corrupt Dual BIOS if it is not damaged physically with the help of a BIOS Switch and following the steps mentioned below.
All you have to do is:
- Switch the computer off
- Adjust the SB switch to Single BIOS mode
- Adjust BIOS switch to the functional BIOS
- Boot up the computer system
- Enter BIOS mode for loading the BIOS default setting
- Adjust BIOS Switch to the non-functional BIOS
- Use Q Flash for flashing the BIOS
- Reboot the computer system
- Confirm whether or not the BIOS is working
- Shut down the computer
- Adjust the BIOS Switch to original BIOS
- Boot up the system and
- Confirm whether the BIOS is working properly or not.
Depending on the situation, you may also be able to fix an issue with corrupted BIOS by simply removing the battery of the motherboard.
When you remove the battery the Basic Input Output System will be reset to default which will eventually resolve the issue.
Conclusion
After going through this article, now you surely know how useful it is to have Dual BIOS in your system motherboard or graphics card.
It will offer safety and convenience and even restore the main chip if it fails or if you set anything wrong while overclocking or tweaking.
However, having this feature is not a necessity.