In This Article
What is Firewall?
A Firewall refers to that specific network security mechanism that supervises all incoming and outgoing traffic in a network. It is created with its own set of network security rules to monitor the data packets and either permit or block them accordingly.
In simple words, it is a barrier, or a ‘wall’ that prevents malicious traffic, hackers and viruses from entering the network.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A Firewall is software, firmware, or hardware that prevents unauthorized access to a network.
- It is a special type of security network that has its own set of rules and policies to monitor traffic to protect the network from malicious attacks.
- The concept of Firewall can be classified as stateful versus stateless, form factors and next generation Firewall.
- There are different types of Firewalls such as packet filter and circuit level firewall, stateful inspection, threat focused next generation, cloud and proxy firewall, NAT, UTM, and next generation firewall.
Understanding Firewall
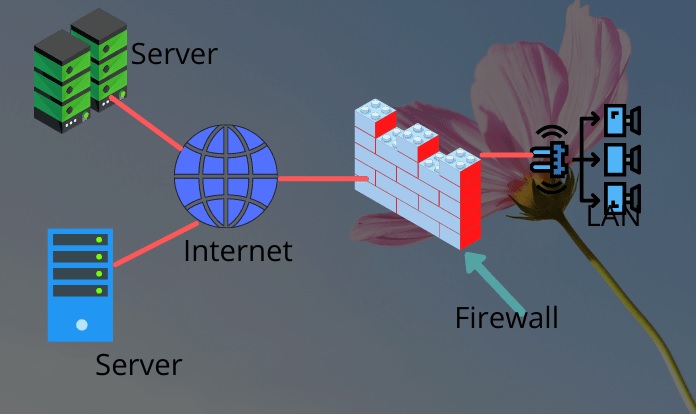
A Firewall is a security mechanism that protects the network by monitoring and filtering the incoming and outgoing network traffic.
It is usually done on the basis of the security policies of the organization that were established previously.
Ideally, a Firewall monitors the network traffic and controls the flow of the data in and out from the device.
It secures the system and the network by becoming the protective barrier between the reliable and unreliable network and the computer network.
In simple words, a Firewall is that essential barrier in your computer which resides in between the public internet and the private internal network.
The main objective of it is to keep the malicious and hazardous traffic out and allow the non-threatening ones only.
With the primary intention to identify and block network threats, a Firewall is used in both environments – personal or enterprise.
It is considered to be an essential component that will ensure security of the network, both within and outside.
Ideally, the outcomes of the data packets passing through a Firewall may have one of the three following outcomes:
- Accepted, or allowed through the Firewall
- Dropped, with no suggestion of failure and
- Rejected, accompanied by information to the source.
These three outcomes are based on the specific properties of the data packets as well as the different protocols.
These are:
- The application-level payload of the data packet
- TCP or Transmission Control Protocol
- UDP or User Datagram Protocol
- The source and destination ports and
- The source and destination IP address.
Today, you will get several systems that are equipped with a Firewall built-in which includes Windows, Mac, and Linux computers.
History

Firewall came into existence in the late 1980 and was initially released as packet filters.
These filters examined the bytes or packets and transferred them to the computers in the network.
These filters are still in use today though Firewall has evolved significantly over the years as follows:
- Gen 1 Virus or Generation 1 – This came in the late 1980s that drove away anti-virus
- Gen 2 Networks or Generation 2 – This came in mid 1990s that drove away internet attacks
- Gen 3 Applications or Generation 3 – This came in early 2000s and drove IPS or Intrusion Prevention Systems products
- Gen 4 Payload or Generation 4 – This came in 2010 and drove sandboxing and anti-bot products
- Gen 5 Mega or Generation 5 – This came in 2017 that provided the latest threat prevention solutions.
Firewall is still the first line of defense for any organization or individual against cyber attacks.
Today, you will get the Next Generation Firewalls and Network Firewalls that comes with advanced features to support a wide range of functions and capabilities such as:
- Application and Identity Based Control
- Hybrid Cloud Support
- Network Threat Prevention and
- Scalable Performance.
The importance of Firewall will continue to grow since attacks today have become more sophisticated making the cyber landscape pretty unsafe and unpredictable.
Therefore, whether it is a network, a data center or cloud, Firewall is essential.
Classification Concepts
Firewall can be classified on the basis of three important concepts.
These are:
- Stateful vs. Stateless – This is the oldest concept where the stateless Firewall checks every single packet of the traffic and stateful Firewall tracks the details of any session right from the start to finish.
- Next Generation Firewall – While the stateful or stateless Firewall inspects traffic on predefined rules, the NGF checks the packet header information to ensure that the incoming or outgoing packets fits into the flow of the current connection logically. It offers added security solutions such as Intrusion Prevention System, application control, and more.
- Form Factors – There can be three categories in it such as hardware Firewall which is deployed in the server room or data center of an organization, software Firewall which is implemented as a code in the computer and cloud Firewall which can be deployed either as standalone or Software as a Service (SaaS).
The different form factors offer different advantages and disadvantages.
A hardware Firewall can access optimized hardware but can be constrained by the uses of the hardware.
The software firewall can be updated easily but may be a bit lower in performance.
However, the cloud Firewall can take all the benefits of the cloud and cloud-based resources.
Different Types of Firewall
A Firewall can be hardware, software or both. Though each of them can have different features and functionalities, they all serve the same purpose.
The hardware Firewall, also known as Appliance Firewall, refers to the physical device such as the internet or broadband routers that is attached between the gateway and the computer network.
On the other hand, software Firewall, also known as Host Firewall, refers to a simple program that is installed and runs in the background of a computer along with Windows or any other operating system.
Software Firewall is found in most of the personal computers. It inspects data packets and compares the information with the given set of threat signatures.
It typically works through the other software installed and port numbers.
In addition to these types of Firewalls, there are also a few other types of firewalls that can be categorized depending on their features, functionalities and the level of security provided.
These are the types of Firewalls that you can deploy as hardware or software:
- Packet Filter Firewall which ideally is the basic Firewall and offers fast solutions and filters internet traffic and blocks the unwanted IP addresses based on the predefined rules
- Circuit Level Firewall which verifies Transmission Control Protocols and others at session levels but does not check the actual data and hence may not be absolutely foolproof
- Threat Focused Next Generation Firewall that comes with extra features to protect the network against a wider range of threats and offers quick detection and remediation with intelligent security automation
- Stateful Inspection Firewall that combines TCP and packet filter Firewall and work on packets to secure traffic based on IP addresses and others
- Cloud Firewall that is also known as Firewall as a Service or FaaS and is controlled by a third-party vendor
- Proxy Firewall that restricts a user to open any malicious site or unwanted sources after checking the chances of security threat or any problem when a request is made by the user
- Next Generation Firewall that comes with features and functionalities of other types of Firewalls such as Deep Packet Inspection or DPI, Surface Level Packet Inspection or SLPI, TCP handshake testing, and more to offer higher levels of security than Stateful inspection and Packet filtering Firewalls against advanced intrusions, malware attacks and external threat by monitoring the complete transaction of data, packet contents, headers, and sources
- Network Address Translation or NAT Firewall that accesses internet traffic and hides the IP addresses of the computer therefore preventing it from hackers by creating unique IP address for all the devices connected in a network rather than individual ones and
- Unified Threat Management or UTM Firewall that comes with the features of Stateful inspection firewall along with IPS and anti-virus protection, cloud services and more but is simple and easy to use.
According to your security needs and usage of computers, size of your organization and availability of resources, you can choose the best one from different types of Firewalls that will offer a foolproof multi-level protection.
If you want to have the maximum protection possible, it is a good thing to have both types of Firewalls installed in your computer system and network.
How Does It Work?
As said earlier, a Firewall typically acts as the protective barrier between the network and your system and resides on the boundary of the network.
The traffic that wants to cross that boundary needs to go through the Firewall.
This way the Firewall can ‘see’ the flow of traffic, make necessary assessments based on the preset parameters and block any traffic that violates the rule or which is deemed to be a potential threat to the network.
These parameters are usually called the ACL or Access Control List.
The ‘packets’ here play a significant role. Typically, the word ‘packet’ signifies the pieces of data.
This data is designed for internet transfer. The data packet also contains some information about the data, such as its source.
It is this information that is used by the Firewall to determine whether or not the data packet follows the set of rules.
If it does not, it will be blocked to keep it away from the protected network.
The set of rules is determined on several factors such as:
- The source
- The destination and
- The content.
However, the characteristics of these factors may vary at different levels in the network.
A packet is reformatted many times when it travels through a network in order to instruct the protocol about its destination.
And, for this, different types of Firewalls are used to read the data packets at different levels of the network.
Why is Firewall Used?
The main use of Firewall is to block malware and dangerous application-layer attacks.
It can detect attacks seamlessly and react quickly to combat it across the entire network.
A Firewall can also execute fast assessments based on preset policies to better protect the network against suspicious or invasive activities and shut the system down in case there is a malware attack.
In short, it protects the internal network in the best possible way.
Typically, the functions that a Firewall performs include:
- Preventing open, easy, and unauthorized access to a network
- Preventing loss of data or the files from being compromised and
- Preventing network crashes.
In addition to that, a Firewall also performs crucial audit and logging functions in order to maintain a proper record of the events.
This record can be used by the administrators to make out patterns and develop the rule sets.
These records also help the corporate and organizations to improve their Security Intelligence and Event Management or SIEM strategy.
They can improve the productivity of their cyber security devices and create properly guarded segments.
In a home setting, the use of Firewall provides alerts against intrusions and also to filter traffic.
This is essentially required for connections that are always on such as Digital Subscriber Line or DSL, cable modem, or others because all these types of connections use static IP addresses.
Essential Features of Firewall
The features of the Firewall increase its functionality and ability to protect a system and a network from cyber threats.
Some of its notable features are:
Integrated Security Management:
This is a very important feature because networks are growing in every possible aspect such as:
- In size
- In sophistication and
- In complexity.
This is actually the result of the inclusion of other devices into the network over and above the computers such as:
- The mobile devices
- The Internet of Things or IoT devices and
- Cloud deployments.
A combined cyber risk management is necessary to prevent the numerous sophisticated threats allowing better monitoring, deploying, maintaining and growing assortment of security solutions.
Threat Prevention:
This is an important feature that will minimize the damage that any cyber attack may cause.
The longer the threat will have an access, the more damage it will make, thereby making it extremely costly to remediate it in a number of different ways such as:
- Exfiltration of sensitive data may result in regulatory and legal penalties
- Ransomware can cause loss of profit and decrease in productivity and
- Rectifying things may take a long time which will also result in loss of productivity.
The Threat Prevention feature will identify and block a threat before it can cross over the network boundary.
This particular feature may include different components such as:
- Anti-phishing
- Anti-bot and
- Anti-malware.
Combination with high-quality threat intelligence sources is also required to enhance the cyber security strategy of an organization.
Application and Identity Based Inspection:
Since the network landscape of an organization is evolving constantly, it is needed to use new applications on the network to achieve specific goals.
Those that are obsolete also need to be phased out.
However, new applications mean new policies that may be different from the existing.
While some applications may involve high-priority traffic, others may need to be throttled, blocked, or managed otherwise within the network.
The Firewall therefore needs to be efficient enough to identify the traffic generated by a particular application and apply application-specific policies accordingly to it.
Moreover, in an organization there are several workers with different job responsibilities.
Therefore, the security policy should be able to configure itself based on the identity of a specific user and detect a threat to the systems and network.
A Firewall should support creating such policies and enforcing them based on the identity of the users.
Hybrid Cloud Support:
Most organizations today are shifting to the cloud to meet with their growing computing and data storage needs.
For better results they are using a hybrid cloud setting where both private and public cloud service providers are used.
These providers have different security necessities.
Therefore, the organization needs to ensure that its security policy is consistent across all cloud-based settings hosted by several vendors.
That is why the Firewall should support hybrid cloud environments.
It should not only be easy to deploy but should also be scalable so that the security team of the company can manage it from a single console.
Scalable and Flexible Performance
Finally, a Firewall should offer scalable and flexible performance. It should be able to offer its benefits both on premises as well as on cloud.
It is only then an organization will be able to build a scalable and strong distributed system which will offer rigid integration of compute, storage, and virtualization layers within the infrastructure.
This will help in creating good and effective single solution architecture.
Is Firewall Software?
Firewall can be standalone software or a hardware device as well which may be embedded with firewall firmware.
The personal Firewall is typically a single product unlike the corporate ones which is a collection of different products.
What Are the Firewall Rules?
The Firewall Rules ensure compliance and therefore describe how exactly the security policy would be deployed by Firewall.
At this point, it is good to remember that cyber protection and laws related to it may vary according to different governments along with the allied security mechanisms. However, here are the basics:
- The Firewall Rules state how exactly a Firewall should deal with the inbound and outbound traffic that may consist of email, web, or telnet
- The Firewall Rules also states how Firewall should be managed and is to be updated and most importantly
- The content of the Firewall Rules determines the actual functionality of it.
In the absence of these sets of rules, it will be practically impossible to implement and administer Firewall which will cause major security issues such as data loss and a compromised network.
Therefore, the advantages of having these set of Firewall rules are:
- It helps in enforcing security policies
- It protects internal networks from any vulnerabilities and the exploitation of the same from outside and
- It helps in establishing trust within the organization as well as with the external connections.
However, the rules are quite complex and therefore may result in slowing down the throughput.
It also needs regular monitoring and updating so that it is productive and effective.
According to the Firewall Rules, the inbound traffic, or outbound traffic, or both may be blocked that:
- Are from any unauthenticated source system
- Are from a source address on a network that is behind the firewall
- Are Internet Control Message Protocol or ICMP traffic
- Are from a source address outside the RFC 1918 range of private networks
- Are from an unauthenticated source system with Simple Network Management Protocol or SNMP traffic
- Contains IP Source Routing information and
- Contain an address that is broadcast or local host address and can be used for attacks.
Even outbound traffic with directed broadcast addresses may be blocked by the Firewall.
In addition to that, there are also a few specific types of executable files that may be blocked such as:
- .ade
- .cmd
- .eml
- .ins
- .mdb
- .mst
- .reg
- .url
- .wsf
- .adp
- .com
- .exe
- .isp
- .mde
- .pcd
- .scr
- .vb
- .wsh
- .bas
- .cpl
- .hlp
- .js
- .msc
- .pif
- .sct
- .vbe
- .bat
- .crt
- .hta
- .jse
- .msi
- .pl
- .scx
- .vbs
- .chm
- .dll
- .inf
- .lnk
- .msp
- .pot
- .shs and
- .wsc.
That is not all. The Firewall Rules also prevent inbound traffic from a few specific applications and services, with some exceptions of course.
The actions to be taken however may vary just as the port numbers.
These applications and services may include particular:
- Login services
- RPC and NFS
- X Windows
- NetBIOS in Windows NT
- Naming Services
- Small Services and
- ICMP.
There are also a lot of other services that are disallowed by Firewall which is why it is better to check their official website for the rules in case you face any difficulty or need additional information.
Where is the Firewall Located?
Typically, a Firewall may be located anywhere on a network. However, most commonly you will find a Firewall between these following components:
- The agents and the application server
- The application server and the console
- The IBM Security Host Protection agent and the agent manager
- The IBM Security Server Protection for Windows agents and the agent manager
- The internet or the IBM Security Download Center and the X-Press update server
- The agents and the event collector and
- The internet and the application server.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Firewall?
A Firewall is designed to offer several benefits to the users in terms of security to the system and the network on the whole. A few of the advantages are:
- Providing protection against viruses by creating a shield between the unwanted network traffic and the computer and blocking the Trojans based on the predefined rules
- Monitoring network traffic to identify unwanted or malicious sources and blocking them
- Controlling hacker activities both on the system as well as on the network by preventing misuse or unauthorized access to the system or network and
- Protecting privacy and securing personal information from being hacked by blocking unwanted sites.
Due to these benefits offered, a Firewall is used extensively today. However, there are a few downsides of using a Firewall as well. These are:
- The hardware Firewall is costlier than software Firewall
- Maintenance requirements of hardware Firewall are also high
- A Firewall alone cannot prevent malware attacks and therefore other anti-virus protectors are also required
- Effects on performance of RAM resources and in the processing power if it is allowed to run in the background and
- Additional cost to retain IT professionals to maintain it.
Still, the benefits offered by a Firewall are much more than its downsides which is why it is a good investment.
Conclusion
So, now you surely know how important a role is played by the Firewall in ensuring cyber security and protecting your computer system and network from external threats and hacks.
You also know the varied benefits offered by it which makes investing in Firewall worthy and productive.