In This Article
What is Graphics Memory?
Graphics memory refers to the amount of memory that is used particularly by the graphics processor for a graphical representation. It mainly stores the data and calculations related to the graphics only.
In a discrete graphics card, this memory is exclusive while in the case of integrated graphics cards, it refers to the portion of the main memory of the system that is exclusively reserved for graphical representation.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The graphics memory increases the graphics capability of the computer whether it is shared or dedicated.
- Graphics memory is a volatile memory used for graphical representation where more of it signifies faster and better graphics performance.
- The amount of graphics memory needed may vary according to the needs. For basic graphics anything between 2 GB to 4 GB is good to have while mid level and professional needs can be best met by more than that amount.
Understanding Graphics Memory
The graphics memory of your PC is the amount of volatile memory dedicated to one purpose only, producing images on the monitor.
So basically, it is the RAM put on a graphics chip, which may be internal or external, and is also attached to the motherboard.
But it isn’t asked by the CPU for the basic processing and is only used for graphics and used by the GPU or Graphics Processing Unit, which may be present already on your PCs motherboard, or you might add one separately later.
The more graphics memory you have on your PC, faster would be the graphics processing.
But the overall graphics performance depends on the type of video memory you use, and whether or not you use an external GPU for better graphics.
The GPU holds all the memory to be used by the graphics interface, but in some cases it can also be used in place of a processor for a specific purpose like in supercomputers and workstations.
The concept is called GPGPU (General Purpose computing on graphics processor unit), where multiple GPUs are used for a more parallel form of processing, which can be utilized to process data which includes lots of 3D or 2D imagery.
Types of Graphics Memory
Every PC requires graphics, and while not all have a fancy GPU, every working PC has some basic graphics memory installed already, which is shared from the RAM.
This leads us to the distinction in graphics memory, which is divided into two types.
- Integrated or shared Graphics
The Integrated graphics refers to the graphics capacity of your PC by default.
Here the GPU is pre-installed and placed directly on the motherboard, without the use of PCIe slots.
In some cases, both the CPU and graphics are placed in the same die.
The main brands, Intel and AMD have their own set of integrated GPUs, but not all the processor models come with them.
In Intel’s case, it provides different generations of integrated graphics for various types of processors like the HD Graphics 610, HD Graphics 620, UHD Graphics 620, and so on depending on the generation of the processor you choose.
AMD has provided it’s users with integrated Radeon Vega Graphics options. Some of these integrated graphics options are so good that for entry-level purposes, you wouldn’t need to buy an external GPU.
It is also called shared graphics since there is no separate memory allocated for this kind of graphics, and it is taken from the RAM.
What happens is when you buy a PC (laptop or desktop), some part of the RAM is already secluded from using by the CPU and provided for graphics work.
In some latest BIOS improvement, you can alter the default settings and increase the amount of memory towards graphics, but it wouldn’t make too much of an improvement whatsoever.
No matter what the case, this amount of RAM is not part of the primary RAM anymore, and even if all of it isn’t being used by graphics, the CPU cannot use it, unless you restore the settings.
This has to be done cautiously, as allocating more memory for graphics may reduce valuable RAM from the main system, and the performance of the PC will suffer.
It isn’t necessary for a PC to only have integrated graphics. With the presence of PCIe slots, a GPU can be added to every PC, with or without graphics present onboard.
Similarly, not all CPUs come with integrated graphics. If you are really into it, make sure you know whether the CPU you are buying has graphics present or not.
The latest AMD 4000 series of APUs (Accelerated Processing Unit) for desktops do not have enough PCIe slots, but have integrated graphics present.
Dedicated Graphics is present alongside the specialized unit known as the GPU, both available on a video card.
You cannot just add more video RAM in your PC without a GPU attached to it.
There are two main brands at play, AMD and NVIDIA which provide you with even the most powerful video cards if you are ready to pay the price.
Now when a decent level of performance is concerned, there are two types of GPUs that you will find from NVIDIA, the GTX and RTX (these use the Ray Tracing Technology and are expensive) series of GPUs.
In AMD’s case, the Radeon RX series of GPUs are present.
Dedicated GPUs typically use GDDR5, GDDR6 and GDDR5X VRAM, but there are other types as well like GDDR7 used by high-performance ones and hence GPUs don’t bother the system RAM.
Thus, you have two sorts of memory present, one that the CPU uses for usual processing like it used to, and the other that is installed entirely for anything related to graphics, be it rendering, editing, gaming, and along with the simplest jobs.
Now when a dedicated GPU is installed, the integrated graphics loses its importance and you might as well disable it.
The GPU memory is multiple times faster than the CPU and has greater bandwidth.
Adding a GPU after sales is easier on a desktop than on a laptop, so if you’re going for the latter it would be better to buy one with a decent GPU installed at the time of the purchase.
The Lifespan of Graphics Memory
The graphics card doesn’t face any physical damage by itself. However, shock or excess heat can damage it, and you might have to replace it.
This is the case for both internal and dedicated GPUs. Some other reasons for external GPU damage also include excessive voltage and overclocking.
Any GPU should last about 5-10 years, but overclocking it reduces the GPU’s lifespan drastically.
The more serious matter is that it is outdated, and this is more of an issue when you are using a low or mid-ranged GPU and your usage patterns change frequently.
So apart from any damage, how long the GPU or the amount of graphics memory remains to be useful to you, thus depends upon your usage.
How Does It Work?
A GPU does sound somewhat like a CPU, but is widely different in its working.
Unlike a CPU, where there are a few numbers of cores like 4 or 8 on average, a GPU has hundreds of cores and every core inside it is similar to that of a core inside a CPU, only smaller and slower.
There are memory banks, cache and registers. In integrated graphics the GPU is soldered on the motherboard, same as the CPU socket, while dedicated graphics requires addition of a GPU through the PCIe slots.
Now what does the GPU process? Multi-core CPUs have the capability of processing multiple tasks at the same time, while the GPU only processes graphical data, that is large in number but simpler in nature.
But processing inside it takes place in a parallel manner, that is, the same task is done by all the cores at the same time which makes the processing faster.
When all of the cores work together, graphical data can be processed much faster than a CPU, which may be able to handle different varieties of data, but the less number of cores cannot process graphics at the same pace.
Graphical data in the simple language is more like geometry. For creating a scene in a video game for example, the different points are taken as vertices and using the X, Y and Z axes of coordination their locations are pointed out.
The GPUs have the capabilities to add colors, textures and the related information that completes and creates a scene.
Next, with tons of mathematical calculations these are sent into the GPU, and are then converted into analog signals ultimately which can be understood and portrayed by the display unit.
The RAM in the graphics adapter is present so that the finished images can be stored somewhere, and video RAM or the GDDR RAM has better speeds than primary DDR4 RAM.
The location, colors of each pixel, and such info are stored temporarily in the different memory addresses of the RAM.
These graphical inputs when processed by the CPU would take a lot of time, and hence proper visuals wouldn’t be available. The GPU does all of this much faster, and that is its only speciality.
Questions & Answers:
What does Graphics Memory do?
The graphics memory provides your PC with the necessary graphics capability. No matter what kind, integrated or dedicated, without graphics you cannot have your monitor running and hence won't be able to use the computer altogether.
In gaming, editing and other performance-oriented rigs, for example, the GPU does a lot more than just running the monitor. It is responsible to provide the GPU with the necessary information to start processing, or holds data relevant to such processing.
How much Graphics Memory do you need for gaming?
The graphics memory required for gaming depends on what games you intend to play. Also, keep in mind that you will need to have a lot more than the minimum requirements allotted for a particular game, and chances are you wouldn’t be playing only a single game.
For basic gaming: To play the simplest of the games on your PC, whatever the default graphics memory is present would be sufficient. You will not even require a dedicated GPU.
For entry-level games: For gaming on the casual level, up to 4 GB of graphics memory should be sufficient. There is no point in spending more for better memory if you aren't going above this level.
Mid-level gaming: The GPUs that have 4-6 GB of graphics memory should be enough for running games at 1080p and you may even try 1440p at decent frame rates as well as VR gaming. RTX cards should also be worth it at this point but GTX cards are cheaper so your budget should be considered.
Professional gamer: If you are a professional gamer, you might also be interested in streaming, and hence must be using a multi-monitor setup. Thereby, based on your budget you can have everything above 6 GB. The GPUs with 8 GB memory would be the best for running games comfortably at 1440p, or on 4K.
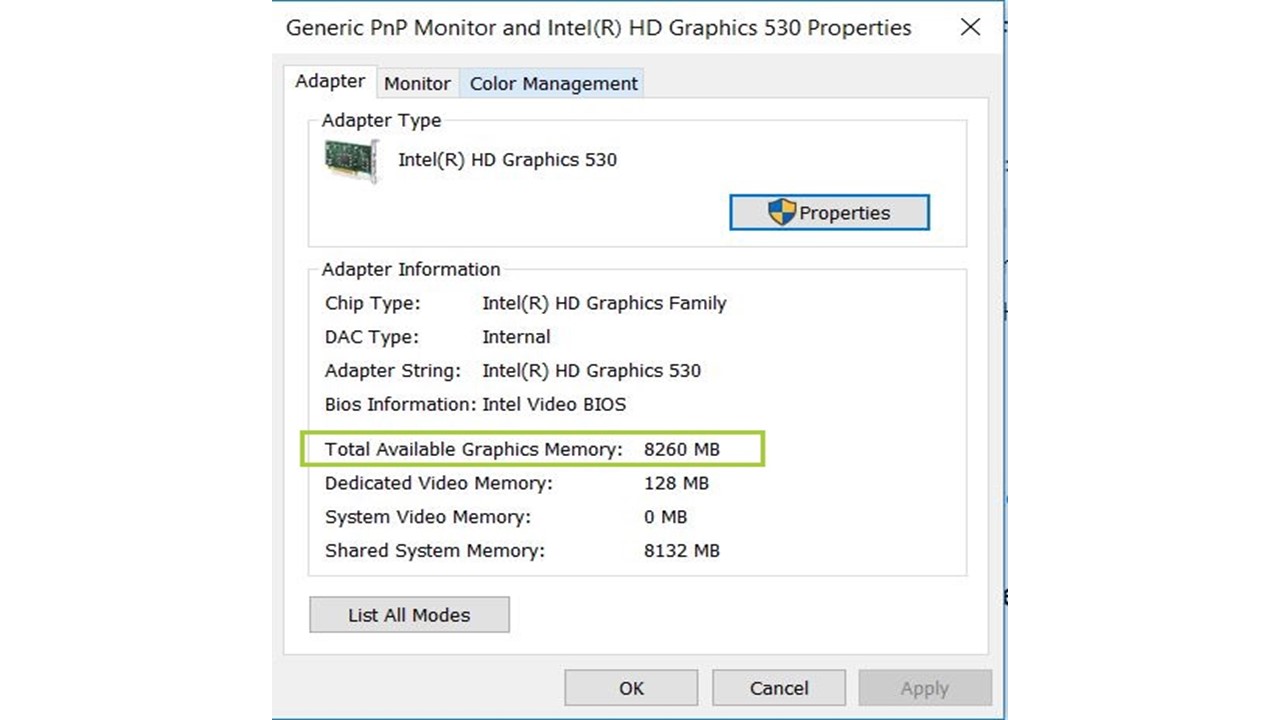
What is available Graphics Memory?
The available graphics memory is the integrated memory present on your PC without any modifications or an external GPU. This is the basic amount of memory that your PC requires for proper functioning.
Conclusion
The graphics memory is one of immense importance. A PC may work without an external GPU, but it won’t be able to display anything without the integrated graphics. Thus, each is necessary in its own sphere.
Talking about GPUs, are you interested in some GPU hunting for your PC? Then make sure you consult our article on choosing GPUs that will be made available very soon.