In This Article
What is Heat Sink?
A heat sink, in general, is a metallic component of many cooling systems that moves the heat away from the vital components, into the air outside or a cooling medium like water or oil. In computers too, they work in unison with other cooling equipment in order to remove heat from the processor.
Not only that, but there can also be heat sinks in other places as well like the RAM modules, motherboard, etc and while they may differ in shapes and sizes, they have fundamentally the same job to do.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The heat sink removes the heat from the inside of the computer and has different parts to facilitate the process such as base plate, fins and heat pipes.
- There are usually two types of heat sinks namely active heat sinks and passive heat sinks.
- By removing the heat tirelessly a heat sink maintains the temperature of the interior of the computer thereby increasing its life and performance level.
Understanding Heat Sink in Computer
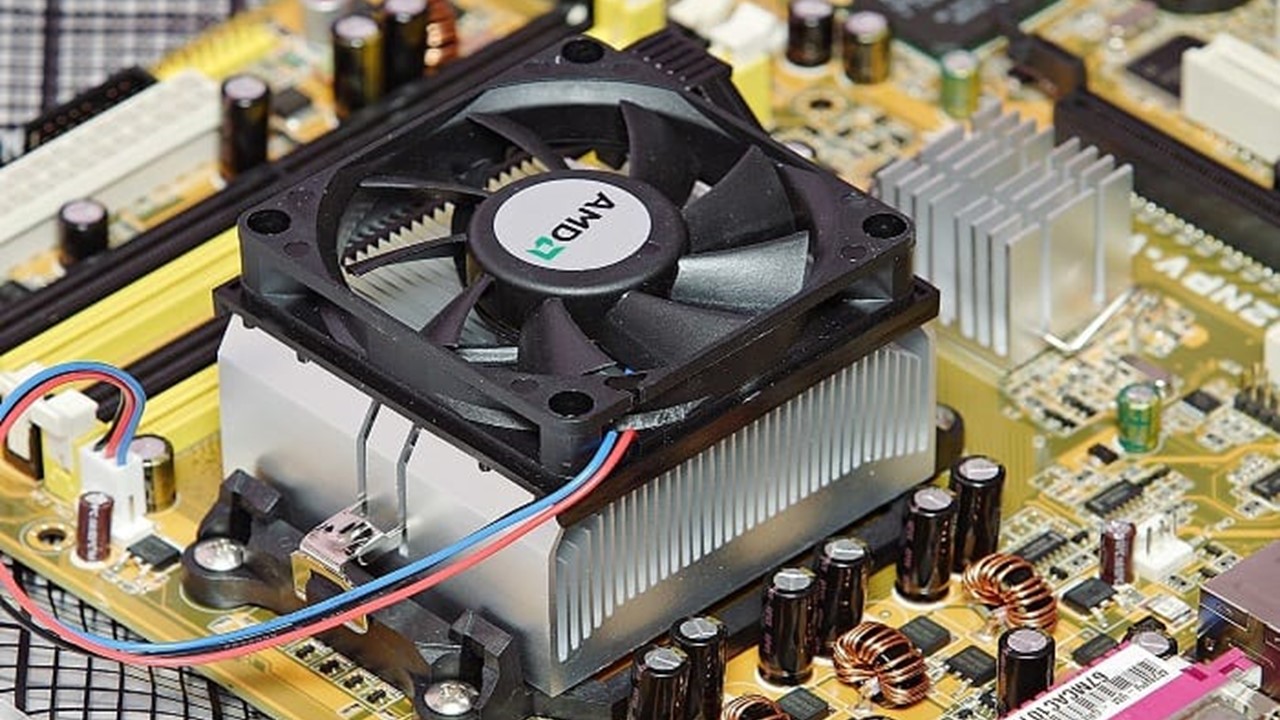
Heat sinks help in the process of thermal management by increasing the heat flow to prevent a component or a device from getting excessively hot fast.
The technology basically increases the surface area for the low-temperature fluid to flow on.
The heat is transferred to the fluid medium which eventually dissipates the heat away from the device thereby maintaining its desired temperature.
Usually, this fluid is air but other liquid coolants are also used in a heat sink.
In computers, a heat sink is used to keep the CPU, GPU, RAM and a few other chipsets cool.
There are different factors that may affect the eventual performance of a heat sink such as:
- The material of thermal interface
- Air velocity
- Surface treatment
- Protrusion design
- Attachment methods
- Thermal paste or adhesive
- Thermal resistance
- Volumetric resistance and
- Fin geometry, spacing, and density.
Metals with superior thermal conductivity such as copper, aluminum and diamond are used to make a heat sink.
The heat sinks typically follow the principle of thermodynamics which involves four basic aspects such as:
- The heat source
- Heat transfer
- Heat distribution and
- Dissipation.
The entire process uses thermal convection and diffusion and the larger surface area plays a major role in it.
The importance of heat sinks is immense since it prevents damage of the components such as CPUs, GPUs, transistors, ICs, and others due to heat related issues.
However, in low temperatures, the heat sinks release thermal energy to provide heat for proper functioning of the circuit.
Types of Heat Sinks
Based on their working, heat sinks can be classified into two major types:
- Passive Heat Sink: These are the simplest kind, where metal plates known as fins protruding upwards are attached to the heat sink, which has a metal plate for conduction. This metal base touches the CPU directly and heat transfer takes place.
- Active Heat Sink: The better kind is an active heat sink, which uses one or more fans to blow out the heat absorbed by the heat sink. These are more efficient and are a necessity when your PC tends to run hot due to the use of powerful parts inside.
Heat Sink Functions
- Heat Removal
The heat sink’s primary function is heat removal. Depending on where it is placed, it removes heat from sensitive components and directs it towards the open air. For the normal functioning of the components, the heat sink works tirelessly.
- Increases CPU efficiency
When the CPU is at working temperatures, it can work efficiently for a longer duration without a decrease in its efficiency.
How Can a Heat Sink Perform Better?
A good heat sink can save a lot of your money by keeping the components attached to it safe. Below are some of the ways that you can make sure it performs better.
But some of these are decided by the manufacturer and it is not much you can control.
Generally, a heat sink made of copper would perform better than one made out of any other material like aluminium, and choosing the former already ensures better heat removal, but at a costlier price.
If you have the space, you may attach more than a single fan on the heat sink as well.
- Increasing airflow
One of the best ways to reduce heat is to make sure there is enough airflow, both inside the cabinet and its surroundings.
A closed room, for instance, would surely increase the room temperature, and the heat sink may slow down due to this.
Maintaining a good airflow through the room, and adding more fans in the PC case can solve the problem.
Although, fans take up a lot of space inside and you need to have a large enough case as well.
- Increasing surface Area
Increasing the surface area where the actual heat transfer takes place is one of the best ways to increase the heat sink’s capacity. Thus, bigger heat sinks can move more amounts of air than a smaller one.
- Thickness and arrangement of fins
The heat transfer to the air takes place through the fins, and how they are located plays a big role in the working of the heat sink.
A passive heat sink would do with thicker fins as the entire process is not influenced by any cooling fan.
Also, when arranged in pin fins, the heat sink gets more surface area which is good, rather than straight fins.
Questions & Answers:
What are computer heat sinks made of?
Computer heat sinks are generally made of aluminum and its alloys which come cheap and can be used in an average PC, while copper is the best material that can be used.
This depends on cost and sizes, and since copper has a far better thermal conductivity than aluminum, it is used in expensive heat sink designs.
Moreover, copper also has better heat absorption and anti-corrosion qualities that make it the perfect material to be used for a heat sink.
Where is the heat sink in a computer?
The heat sink is usually noticed above the processor, while you may have noticed heat plates on the RAM modules as well. The high-performance motherboards and graphics adapters have heat sinks.
Is a heat sink necessary?
Yes, absolutely. Without the heat sink, there is a high chance of your processor overheating than the usual limits, which can affect performance and in the long term even damage the processor altogether hence rendering your computer useless.
Every computer, no matter how small or how powerful, produces heat that needs to be removed from the components or else they may be damaged. The heat sink does exactly this and is therefore very necessary unless there is a liquid cooling system installed in your PC.
Conclusion
A heat sink is a metallic component used in many cooling systems, including computers, to remove heat from sensitive components and direct it towards the open air or a cooling medium like water or oil.
There are two main types of heat sinks: passive and active, and factors that affect their performance include material of thermal interface, air velocity, and fin geometry, among others.
A good heat sink is essential to prevent damage to components and increase the efficiency of the CPU.
Increasing airflow, surface area, and thickness and arrangement of fins are ways to improve heat sink performance.
Ultimately, the better the heat sink works, the better the cooling, and the more maximum performance you can get out of your computer.