In This Article
What is LGA (Land Grid Array)?
LGA or Land Grid Array refers to the physical interface or a socket that connects the processors to the motherboard. From a technical point of view, an LGA is a chip package that comes with contacts with a very high density.
These are designed quite differently from the traditional chips that come with pins sticking out and are inserted into a socket.
At the bottom of the LGA chip package there are flat pads that touch the contacts on the socket of the motherboard.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The Land Grid Array is a kind of surface-mount packaging for the Integrated Circuits in a computer with pins on the socket, when it is used, but not on the ICs.
- The LGA can be connected to the Printed Circuit Board electrically either by soldering it directly onto the board or by using a socket.
- The emergence of LGA is attributed by the industry experts to the LGA platform of Intel Pentium chips during the initial millennial years.
- Intel uses different variants of LGA sockets in their CPUs with each having a better design and a higher number of pins for expanded functionality.
- The LGA design is related to Pin Grade Array and Ball Grid Array design but can be soldered unlike the PGA and have flat contacts unlike the BGA.
Understanding Land Grid Array
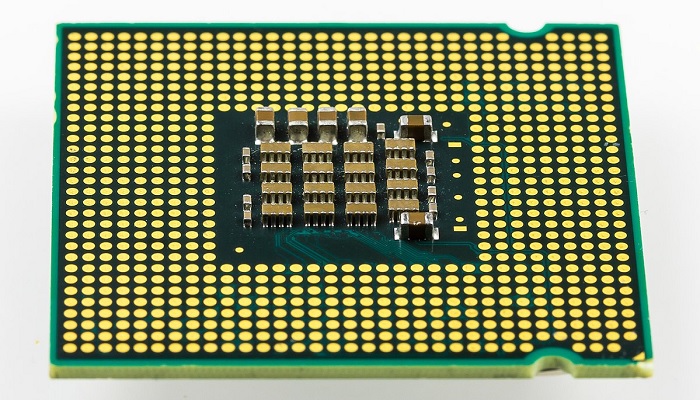
A Land Grid Array refers to an integrated circuit design. This comes with a square grid of contacts that helps it to be connected to the other components of a PCB or a Printed Circuit Board.
Ideally, the term refers to a special type of socket design. The unique aspect of it is that there are a few components in it that are disconnected from the real circuit board.
These parts are typically integrated into the structure of the board in a very different way as compared to the older designs.
It can be either soldered onto the board or connected via a socket.
Whatever the case may be, it always establishes a direct connection with the circuit board.
Typically, the LGA is configured to have pins in the socket and not on the chip.
This means that the processor package has the pins well protected inside the socket on the motherboard.
These pins connect to the flat contacts that are at the base of the processor chip.
This packaging technology does not require using all of the rows and columns of the grid. This adds to its performance and power delivery.
This grid is also quite unique. The elements on the grid may be rectangular, circular or even polygonal in shape and may come in different sizes as well. It may also come in a honeycomb pattern.
Ideally, the design of the LGA is optimized based on different factors such as:
- Likeness of contacts
- Tolerances
- Electrical gap to the nearby contacts and more.
Ideally, the Land Grid Array packaging is related to Ball Grid Array or BGA and Pin Grid Array or PGA packaging.
However, LGA packages can be soldered onto the board using surface mounting technology or fit in a socket, but the PGA cannot be soldered down.
On the other hand, usually there are balls on the underside of the BGA package that serve as the contacts between the PCB and the IC, but LGA does not have any balls.
They have flat contacts that allow it to be soldered down to the PCB directly.
Processor manufacturers use a wide range of configurations of LGA sockets, including Intel and AMD, for their CPU chips.
And, these sockets are named differently by different manufacturers as well.
For example, Intel typically names their LGA sockets according to the number of contact pins used.
For example, the first Intel LGA socket was named LGA 775 because it had 775 pins and the later ones were called LGA 1156 with 1,156 pins and so on.
As for AMD, they follow a sequential naming format which is pretty much the same as their PGA sockets.

What is a Land Grid Array Used for?
A Land Grid Array is used as a physical interface for several different types of microprocessors from Intel such as Pentium, Xeon, and Intel Core.
AMD has also started to switch to LGA through its Opteron, EPYC, Threadripper, and Ryzen processor families.
This is quite contrary to PGA design which is suitable especially for the majority of AMD processors and a handful of Intel microprocessors of the older generations. And, the BGA design is used for the Integrated Circuits primarily.
Is the Intel CPU an LGA?
Yes, Intel CPU is an LGA unlike the AMD CPUs that typically uses its own equivalent called the PGA sockets.
Intel, on the other hand, prefers to stick with the newer LGA 1200 for their 11th generation processors as well, though these are built on the newer 500-series chipsets.
Therefore, you will find the LGA 1200 socket on the B460, H410, H470, Q470, W480 and Z490 chipsets.
However, Intel also uses the PGA socket but the majority of their CPUs use the LGA socket.
Intel is known for updating the LGA sockets continually over the years by using different designs and adding more pins to increase their functionality.
Some of the different types of LGA sockets used by Intel are:
- The LGA 1200 socket, which is built on 400-series motherboards
- The LGA 2066 socket which is designed mainly for high-end desktop computers replacing the LGA 2011-3 socket
- The LGA 3647 socket with improved features to be used in the Skylake-SP and Xeon processors
- The LGA 1151 socket which is for using in the 14 nm Skylake class processors
- The LGA 1150 socket that supports the 4th generation Haswell and a few 5th generation Intel Core processors
- The LGA 1155 cross-generation socket that accepted Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge processors
- The LGA 2011 socket for use in high-end chipsets for Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP CPUs.
A few older versions of LGA sockets from Intel are LGA 775, LGA 1156, and LGA 1366.
Land Grid Array Socket
The Land Grid Array socket typically comes with a few key features and attributes with regards to the socket body, load plate and contact array that make it so preferred by Intel and useful for using in different types of microprocessors.
As for the contact array, these come with metal contacts, which, however, are vulnerable to mechanical damage.
As for the load plate, it is designed to distribute the load evenly across, and also ensure a better connection with the socket contacts and the package pad.
And, as for the socket body, it comes with package orientation keys that are vital for the DSL or Digital Subscriber Line mechanism to ensure better connectivity.
The package with finger cutouts is aligned perfectly but is not removable.
Some of the other key attributes of the LGA socket are:
- A small square package
- Stepped HIS or Integrated Heat Sink which offers the interface for socket load plate
- Exposed land pads with no pins
- Orientation control notches on the substrate.
In addition to the above, it also comes with a load level and the Pick and Place or PnP cap that protects the contacts of the socket from damage, though it may vary according to the supplier.
Advantages
- More durability since the contact pins are in the socket on the motherboard
- More space efficiency due to smaller pins
- A much higher contact density
- Higher power delivery
- More pin count
- Lower amount of lead resulting in better thermal dissipation and conformation to Restrictions of Hazardous Substances or RoHS directives
- Naturally protected pins that make them damage resistant.
Disadvantages
- Harder to repair the fragile pins of the LGA socket on the motherboard
- Accidental bending or breaking of pins will require replacing the whole motherboard.
LGA Vs PGA
- In LGA, the processor is placed on the pins, but in PGA, the pins are placed on the processor and then inserted into a socket in the right holes
- There are no pins in the LGA which comes with a flat pad but PGA comes with protruding and visible pins
- In LGA, since there are no fragile pins, they are damage resistant and more durable as opposed to PGA
- The pins in the LGA are smaller in size, which allows putting in more pins in the same space, but in comparison, PGA design does not offer such space efficiency
- Due to the design of the LGA, it is not easy to repair bent pins on an LGA motherboard, which is not the case with the more durable PGA motherboard
- LGA is supported by Intel processors but PGA is supported mainly by AMD processors
- Installation of LGA is a bit more complex than installation of PGA
- It is easy to uninstall LGA because the CPU does not stick to the cooler as it does in the PGA
- LGA supports high performance CPUs, but PGA supports relatively low-performance processors
- LGA is a more expensive option for getting higher performance but PGA is relatively cheaper.
Why is AMD Switching to LGA?
Instead of sticking with the PGA sockets, AMD is moving to LGA mainly because it will reduce the incidence of contact pin damages.
The LGA design protects the fragile pins more naturally and quite efficiently by nestling them in the socket on the motherboard.
These pins are covered until seconds before installing the CPU. Also, the more pin count will offer a much higher overall performance.
Conclusion
LGA offers a lot of convenience to the users along with some significant benefits. Though a bit costlier option, it supports high performing CPUs.
However, higher durability and a higher pin count, with the pins protected more efficiently on the package, will offer much higher returns.