In This Article
What is Motherboard?
A motherboard is a plastic sheet, in layman’s terms. It is more commonly known as a PCB or Printed Circuit Board. All different crucial circuits, including the Central Processing Unit, RAM, and other internal components of a computer are either fixed on or connected to it.
It is the combination of the hardware and software of a computer that makes it work properly. One of the most important parts of all computers, of course, along with others, is the motherboard.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A motherboard is a non-conductive board made of plastic material that contains copper or aluminum foil printed on it called traces.
- This printed circuit board comes with different sockets and slots to hold different components of the computer and the traces complete the circuit between them.
- A motherboard comes in different types, versions and features.
- Two most important sections of the motherboard are the Northbridge and Southbridge.
Understanding Motherboard in Computer
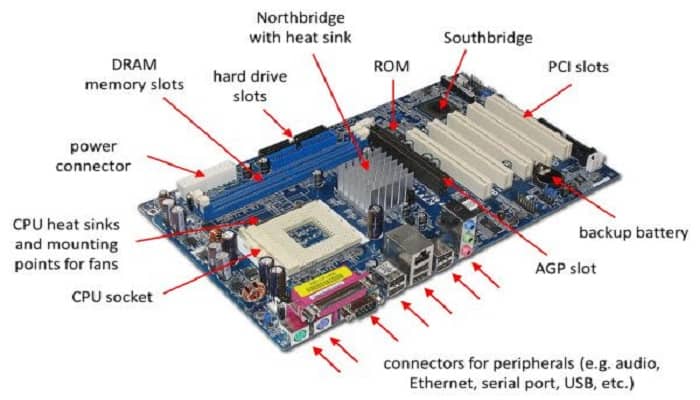
The motherboard sheet is made from a solid plastic material that is non-conductive in nature. On this plastic sheet, you can see very thin layers of aluminum or copper foil printed.
These are called ‘Traces.’ These traces actually form the circuit, when the components are fixed on the motherboard. Check out CPU Vs Core Vs Socket.
In addition to that, you will also see a variety of slots and sockets on the motherboard, such as:
- Processor sockets
- HTX
- 2
- PCI
- PCIe and
- DIMM
These slots connect all other components of your computer system. It will also have slots to make power supply connections.
Apart from that, it also allows you to make additional connections using a Southbridge chip. This chip includes SATA, PCI, Thunderbolt, and the most common, USB.
As for the PCIe and CPU to RAM connections, these are done through point-to-point connectors using Ultra Path Interconnect or UPI, Quick Path Interconnect or QPI, and Hyper Transport or HT.
Different Types of Motherboard

Most of the motherboards today follow the original AT or Advanced Technology design of IBM.
However, due to its large size, 13.8 by 12 inches to be precise, it was difficult to install the other drives on it.
The developers later modified it and came up with the most commonly used motherboard now, called the ATX Motherboard, where ATX stands for Advanced Technology Extended.
There are different forms of ATX motherboards, such as:
Modern ATX motherboards have also gone through some significant upgrades in recent times, and now you will find motherboards called Mini or Micro ITX and Nano ITX.
These modern versions of ATX motherboards offer a host of advantages with its improved features that include:
- More stability in power supply
- Additional power for cleaner
- More space near the CPU to install the large heatsinks and
- More gaps in between the slots that promote the cooling of the graphics card.
All these features of the advanced ATX motherboards add to the functionality and speed of modern computers. Check out how to choose a motherboard.
Different Components of the Motherboard
There are several crucial components attached to the motherboard, either directly or indirectly, for your computer to function properly. These are:
- USB
- Mouse and keyboard connectors
- Parallel port
- RAM slots
- ISA slot
- CMOS Battery
- IDE controller
- PCI slot
- AGP slot
- CPU slot
- CPU chip and
- Power supply plug-in.
There is also a CMOS battery that keeps the CMOS RAM chips functional when the power of your computer is off.
This means that you will not have to reconfigure the date and time every time you switch on your computer because it is updated automatically by the Real Time Clock or RTC.
Finally, there are different switches and jumpers found in a motherboard. Previously, motherboards had Dual In-line Package or DIP switches that are small and operated just as normal switches. Now, modern systems have jumper pins.
These small pins are connected or shorted using a metal bridge or jumper cap. This closes an electrical circuit to get a specific configuration or to change the parameters of the motherboard.
Lifespan of a Motherboard
Typically, all motherboards have a very long lifespan. If you get branded ones, it may last anywhere between 7 to 10 years. However, with proper and regular maintenance and care, you can even extend its life to 13 to 15 years!
This is a simple process where all you have to do is:
- Keep it clean to prevent heat buildup due to accumulation of dust, hair, and lint that may cause shorts and prevent a smooth communication between the components
- Keep it away from heat sources and use your computer in a well-ventilated room making sure that none of the fans and air vents of the system are blocked and
- Always use a quality surge protector to prevent unexpected spikes in electricity that may damage your motherboard.
Finally, make sure that the power supply is stable so that there are no abrupt changes in voltage that may fry the internal components of your system.
Check your PSU for abnormal noise, frequent shutdowns, and failed booting. If you see any of these symptoms, it is time to change it to prevent damages to your motherboard.
The Working Process
All the components of the motherboard work together in tandem when you switch your computer on, and some even work when it is off, as the CMOS battery.
When on, the motherboard receives the power from the power supply and starts transferring data through the data buses. This data then passes through the southbridge and northbridge sections of the chipset as follows.
- The southbridge section passes data to BIOS, SATA, PCI, and USB. This signal starts booting up your computer, and the data received by SATA brings the hard disk, optical, and the solid-state drives to life. It also powers up the sound, video, and network cards.
- The northbridge section sends data to the RAM, CPU, and PCIe. The RAM sends signals to the CPU to interpret them as its output. The data received by the PCIe is transferred to the extension card.
All these data and signals are sent in harmony and in a binary manner.
Questions & Answers:
Can the motherboard be repaired?
Well, you can repair almost any type of motherboard, but it depends on the type of damage. It also depends on the feasibility, efficiency, and economic aspects.
For example, you can easily fix blown capacitors, because these are made from basic components. On the other hand, a dead southbridge or northbridge will need a complete replacement.
Is it OK to touch a motherboard?
Yes, you can touch it because, in most cases, nothing will happen. However, it is recommended that you do not touch it because there may be static discharge.
If you really need to touch it, make sure that you ground yourself and discharge the extra charge in you. Also, make sure that there are no skin oils or anything that can conduct electricity.
Conclusion
A motherboard is a crucial component of a computer that connects all the internal components together.
It is made of a non-conductive plastic sheet with copper or aluminum traces printed on it.
There are various types of motherboards available, and the most commonly used one is the ATX motherboard.
The different components of a motherboard include USB, mouse and keyboard connectors, RAM slots, and power supply plug-in.
With proper maintenance, a motherboard can have a lifespan of up to 15 years.
The components of a motherboard work together to start and run a computer, making it an essential part of any computer system.