In This Article
What is SATA?
SATA, Serial ATA or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment refers to a computer bus interface. This interface allows connecting different host bus adapters with different mass storage devices such as hard drives and optical drives to the motherboard of the computer.
Technically, SATA is an update to the PATA or parallel signaling and was introduced first in 2005. It was further improved and by 2010 it allowed using a data cable and came with as many as seven conductors with wafer connectors at the two ends.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- SATA is made up of seven connectors out of which three are grounds and the other four are active data lines in two pairs.
- SATA storage interface is much faster in comparison to the conventional PATA or IDE types.
- SATA sends data and information in the form of bits through the cables at a high speed.
- Usually SATA comes with two different types of connectors such as 7 pins and 15 pins.
- The advantages of SATA include faster data transfer, higher bandwidth, more flexibility, less complicated and easily manageable connectivity, smoother functioning, less power consumption and reliability with support for multiple drives.
- SATA interface is however not as fast as an NVM Express SSD and cannot be connected to any older device.
Understanding SATA
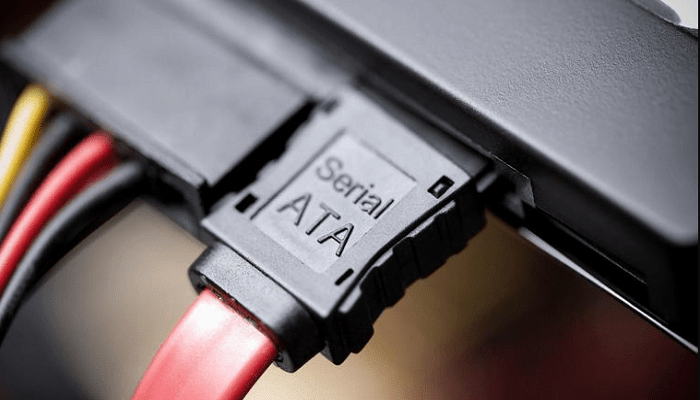

Serial ATA is a type of bus connection through which you can connect different storage drives to the motherboard. This new technology supports both hard drives and Solid State Drives.
Ideally, SATA is considered to be single port but in reality it has two different connectors such as:
- A data connector with 7 pins and a short ‘L’ shape and
- A power connector with 15 pins and a taller ‘L’ shape.
The controller hardware connects to the motherboard and manages data flow. It can be set to the AHCI mode for a higher performance which also offers hot swapping features.
If set in the RAID mode it will then support both AHCI functions as well as data protection features of RAID.
There are three different protocol layers that define SATA specifications and its function such as:
- Physical layer
- Link layer and
- Transport layer.
SATA typically uses a point to point architecture and a topology that involves three aspects such as:
- Host
- Multiplier and
- Device.
There are different versions of SATA available and governed by the SATA-IO industry consortium such as SATA 1.0, SATA 2.0, SATA 3.0, SATA 3.1, and SATA 3.2, with each revision having better features and higher data transfer rates.
How Does It Work?
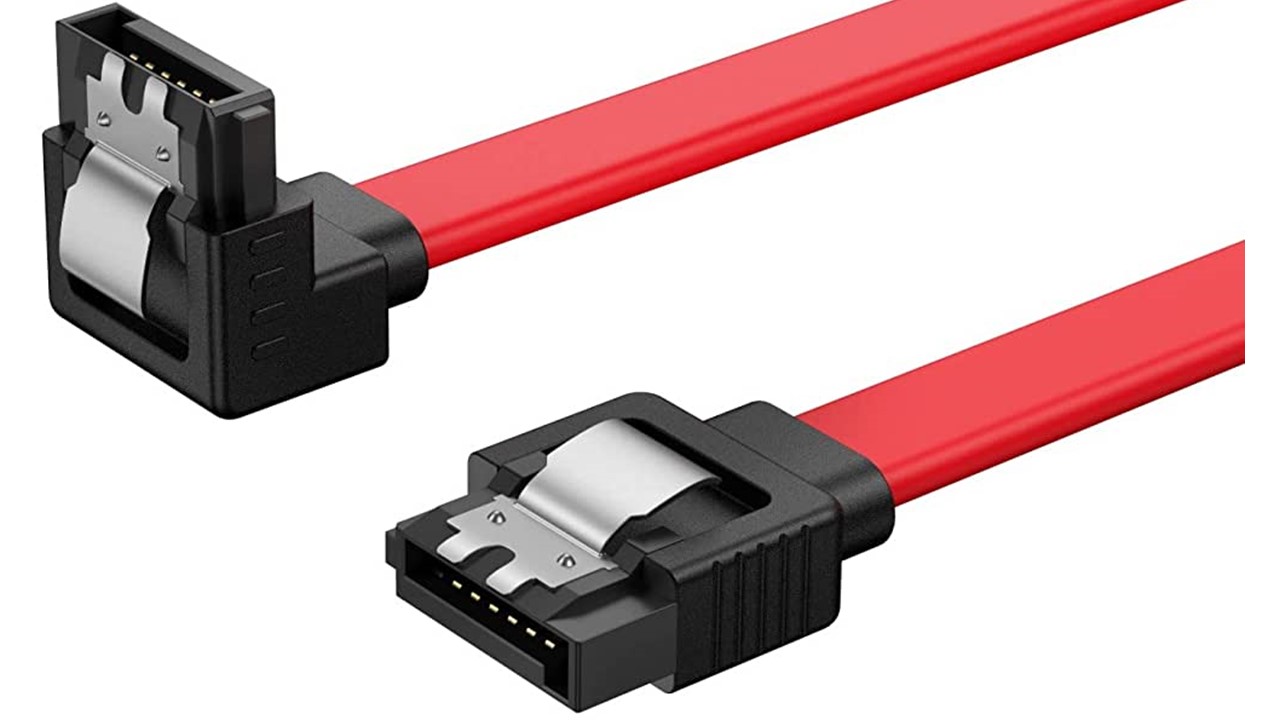
Every computer has a collection of pathways called buses that it uses to send or receive signals.
So SATA, being a newer form of it works in the same way and is used to connect the motherboard to various large-capacity storage devices.
Data and information are sent through SATA cables in the form of bits, and a newer generation of SATA drives (SATA III currently) has more speed of data transfers. A usual SATA cable has about 4 wires.
There are two types of SATA connectors, one with 7 pins called the data connector which looks like a small “L”.
The other power connector has 15 pins. It also looks like a data connector, only taller.
The data connector transfers data to and from the storage devices as required, while the power cable provides the necessary electric power to the drives to function.
How Fast is SATA?
SATA drives found in most PCs are of the 3rd generation, which maxes out at 600 MB per second for the data transfers.
This is yet the fastest speed available ever on a SATA interface.
This SATA III interface provides almost double than what the older SATA II provided (300 MB/s), and even more than the 1st gen of SATA connectivity (150 MB/s).
Pros of SATA
Serial-ATA is much better than IDE or Parallel-ATA connections that were used earlier. This is because of the following reasons:
1. More Speed
SATA bus interface provides better speed than the PATA form of storage (600MB/s and 133 MB/s maximum respectively).
2. Better Bandwidth
The more speed is allowed by a better bandwidth, and hence you can expect good speeds as this bandwidth is not shared in SATA.
3. Manageable Connections
The SATA interface requires thinner wires and is thus less complicated.
Also, the number of wires required is also less. This further allows more airflow inside the cabinet
4. Flexibility
The wires used in SATA are longer than those used in PATA, and hence there is general flexibility.
5. Smooth Functioning
SATA drives allow the user to remove drives from the PC without the need to shut it down. This is a very important advantage one gets.
6. Reliable
In this sort of connectivity, there is a separate cable for each drive. When multiple drives are used, the connections are not shared and thus there are no problems regarding speed.
7. Supports Multiple Drives
There are multiple SATA connections on a motherboard, and hence you get to use many drives at the same time.
8. Lower Power Consumption
PATA drives used to draw a lot of power but the SATA interface is energy efficient. This is why they can be widely used in portable computers like laptops.
Cons of SATA
While there is a new standard of data transfers like NvMe and SAS, some bad sides of SATA storage have also arisen. They are mentioned below:
9. Lower Speed Than NVMe SSD
The SATA is slower than the other forms of storage interfaces.
For instance, the data speed on a NVMe SSD is about 16 GB/s while it is restricted to 600 MB/s on a SATA SSD.
10. Lower Bandwidth
SATA has overall lower bandwidth, and even the early standards of PCIe have more bandwidth than it.
11. SAS supports more devices
Every SATA drive needs an individual port on the motherboard.
Although you can increase the number of drives attached, the number of ports on the motherboard remains the same. SAS, on the other hand, supports a greater count of devices with expansion cards.
12. Multiple Cables
Each SATA drive requires its cable and hence, you need more cables for connecting more drives.
It might be a problem for workstations and those who need to use multiple storage devices on their computer.
13. Inability to Connect with Older Devices
The PATA and IDE connections could be used in most older devices, while only newer computers have SATA support.
This is a not very serious issue but it is still a con that SATA has to bear.
Where is SATA Cable Used?
Depending on the types, SATA cable can be used in different devices. For example:
- Micro SATA is used in 1.8-inch hard disk drives
- eSATA is for external connectivity
- SATA bracket is used to make a system compatible with eSATA drives
- Low profile ultra-thin SATA is used in extended GPU cards
- SATA power cable is used to connect power adaptors, splitters and extensions
- SATA Bridge is used to connect ATA devices to PCI cards and SATA motherboards and
- SATA Express is used in both SATA and PCI Express.
Apart from that this technology is also used in SATA HDDs, SATA SSDs, and M.2 SATA SSDs. It was also used in 3.5-inch optical drives earlier.
Do You Need a SATA Cable for SSD?
It all depends on the specific type of SSD you are using. For example, in a laptop computer, it is more likely that the storage device is connected to the motherboard directly. In such cases you will need a SATA cable.
Also, if you are using a 2.5-inch SATA SSD you will need both a SATA power cable as well as a SATA data cable.
On the other hand, if you are using a M.2 SATA SSD or a M.2 NVMe SSD, you will not need a SATA data or power cable.
What Speed is SATA?
Different major SATA versions come with different data transfer speeds to meet the ever-changing demands of the users. For example:
- SATA I comes with a bandwidth of 1.5 Gb/sec and data transfer speed of 150 MB/sec
- SATA II comes with a bandwidth of 3 Gb/sec and data transfer speed of 300 MB/sec and
- SATA III comes with a bandwidth of 6 Gb/sec and data transfer speed of 600 MB/sec.
Please keep in mind that Gb/s refers to gigabit per second and is not the same as GB/s which refers to gigabyte per second where 1 GB is equal to 8 Gb.
Also, these speeds are just theoretical value and may not be the same as the actual data transfer speed which typically depends on several other internal and external factors.
Can You Plug the SSD into Any SATA Port?
The answer to this question is yes to some extent and no in excess.
The SATA port matters because the performance depends largely on the model of the motherboard and the version of the SATA port it features.
For example, if you are using a very recent model of motherboard in which all the ports are SATA III, any port can be used to connect a SATA III drive.
On the other hand, if it is an older model that has both SATA II and SATA III ports, then the port selection will matter in terms of performance because the data transfer speed of the SATA II port is half of that of the SATA III port.
And, there are even a few specific types of motherboards that feature SATA ports that share connectivity with other slots such as an M.2 slot.
This means that when you use one port, it will automatically disable the other.
So, you simply cannot connect an SSD to any given SATA port. Ideally, you should use a SATA III port to connect a SATA SSD that will offer a data transfer speed of 6 Gb/s.
The bottom line is you should check the SATA configuration in the BIOS and also make sure that the RAID drivers of the motherboard are not installed whether you enable or disable the AHCI.
This is important because it will create a lot of issues due to the conflict with the SATA drivers.
How Many SATA Devices Can be Connected?
The number of SATA devices you can connect primarily depends on the type of motherboard you have.
This is because it will be determined by the number of SATA ports the motherboard has in the first place.
If there are four such ports, which ideally is the case with most of the motherboards, you can connect up to 4 SATA devices to your computer. If there are 6 ports, you can connect up to 6 SATA drives.
There are a handful of motherboards that come with up to 8 SATA ports as well.
If you have one such motherboard, you can connect up to 8 SATA devices to your PC.
Therefore, to find the answer to your question you should physically count the number of ports the motherboard has or look into its specs sheet to figure out how many SATA devices it would allow connecting to it.
If you want to connect more but run out of SATA ports, you can always use SATA expansion cards or port multipliers to add more SATA ports to the motherboard.
These multipliers will let you connect 10, 15 and even more SATA devices to your computer.
However, you can connect as many devices as you want provided you can plug them all into the computer and have adequate space to house them as well as enough power to drive them.
Conclusion
Serial ATA (SATA) is a computer bus interface that allows connecting host bus adapters with different mass storage devices such as hard drives and optical drives to the motherboard of the computer.
SATA is an update to PATA or parallel signaling, which was introduced in 2005 and has been improved over time.
SATA provides faster data transfer, higher bandwidth, more flexibility, less complicated and easily manageable connectivity, smoother functioning, less power consumption and reliability with support for multiple drives.
Although SATA is not as fast as newer storage interfaces like NvMe and SAS, it still remains a popular storage interface due to its reliability, flexibility and cost-effectiveness.