A CPU shuts down all processes immediately and puts itself in an extremely low power mode. You cannot force a system to come out of this state through any action, other than rapid cooling of their system.
You cannot use your CPU normally if your computer does not consider it cool enough.
If you are wondering why CPU throttles and want to prevent your computer from throttling, read on to know more about its causes and how to prevent it from happening.
In This Article
Why Does CPU Throttle – The 6 Reasons & Solutions
In order to understand why a CPU throttle, you need to first understand how a CPU functions and why throttling is necessary.
CPU throttling is an action performed automatically by your CPU under certain conditions.
When your computer gets very hot and your cooling system is unable to function at the same speed, CPU throttling occurs.
It is a response which gets triggered by high CPU temperatures. It ensures the CPU is forced into sleep mode with all its processes suspended, regardless of whatever actions it is performing.
This is done to ensure your computer parts are not fried or become hot enough to melt.
Now, let’s move on to why the CPU throttle. Listed below are some common reasons why your CPU throttles.
Go through each cause and determine if you need to take any action according to specified instructions.
1. High Workload
Most individuals generally keep their computers on for an entire day or more even though they are not working on it actively.
If you have not switched off your computer for more than a day or two, and are using it for a highly resource intensive task or application, chances are your CPU may automatically start throttling.
If you have a heavy workload, you require more CPU cores for any task, thereby increasing its overall frequency. Once your system’s frequency increases, chances are your system might crash.
If you have not turned off your system in a while, its RAM and other components are definitely tired and need to be cut off from their power source, to rest and refresh.
Solution:
If you are thinking about taking a break when working on your computer for an extended period of time, you need to give your computer a break as well.
Putting it on sleep mode might give your CPU a temporary break, but other internal components do not receive a break.
In order to use your CPU optimally, turn off your computer either as soon as your work is done, or if you are considering taking a break of more than 15 minutes.
Turn off your system, or your CPU will enter throttling mode, due to stress.
2. Dust
Dust is your computer’s biggest enemy and often the cause of most of its problems.
If you have a new computer, you need not worry about dust, however, if it has been 6 months since the last time you cleaned your system, you need to start cleaning immediately.
Dust enters your CPU through its ventilation system which is used for releasing heat generated by your CPU.
However, by allowing air to flow through your system over time dust accumulates inside your CPU case.
Dust itself is not harmful to your system, however, it obstructs heat from being released by your CPU.
Once all surfaces inside your CPU are covered in grime, all metallic surfaces lose their inability to release heat through their surface area.
Additionally, grime starts trapping more dust inside your CPU, leading to overheating and eventually CPU throttling.
In order to prevent dust from damaging your system permanently, you should clean it once every one or two months.
Also, ensure to place filters around your system’s fans and vents, preventing large dust particles from entering.
Large dust particles often collect smaller dust particles, which would otherwise flow out with heated air that flows out through your system’s vents.
Solution:
Open up your CPU case and clean up all accessible internal components with a microfiber cloth and ethyl alcohol.
Use small brushes to access corners and crevices of your CPU and remove dust. You can use a compressed can of air if your CPU has dry dust only, but be careful so that it does not blow into your face.
3. Pre-set Limits
Every computer has a set of pre-set instructions and values that cannot or should not be modified, especially if you do not know how to correct any problems caused by it.
Solution:
If your CPU has some previously fixed value in its BIOS settings regarding when to start or allow CPU throttling, you cannot do anything about it yourself.
You can however, seek advice or assistance from an expert technician, who will be able to solve your problem immediately.
A technician knows which values to modify within your BIOS settings and can get this task completed immediately.
4. Blocked Airflow
Computer components generate heat during normal use, so internal cooling systems are built to keep these internal components cool and in good working order.
If your computer’s cooling system is not working properly, heat will stay inside and cause your CPU to overheat.
If your CPU remains hot even after removing dust, there may be a problem with your computer’s cooling system.
If air is not allowed to circulate and pass by heat generating components, your system’s air flow is blocked.
There are two types of cooling methods: airflow cooling and liquid cooling. Airflow cooling system is the most common cooling system for computers.
Airflow cooling system can be divided into two parts namely, fan and heat sink. A heatsink is a piece of metal that provides a surface for heat to flow.
A CPU heats up a heatsink and a fan blows hot air out of your PC’s (Personal Computer’s) case. These two parts must be inspected to repair the airflow cooling system.
Solution:
Poor heat sink efficiency: If your CPU heatsink performance is low, its heat cannot dissipate in time. Then you should replace it with a better sink.
Your computer’s heatsink draws heat away from your CPU, preventing its tiny and sensitive circuits from overheating.
The large surface of a heatsink, which consists of many thin metal fins, allows your processor to cool efficiently.
Over time, under normal operating conditions, your computer’s heatsink will become clogged with dust and other debris.
Dust reduces surface area available for cooling and reduces cooling performance of your system’s heatsink.
Ultimately, this reduced cooling capacity can cause your CPU to start overheating. Clean this heatsink regularly to prevent clogging.
Often a sign of a clogged heatsink is a noisy, overloaded computer fan that runs at all times. As dust accumulates on this heatsink, it becomes less efficient at drawing heat from your CPU.
As this heatsink becomes less efficient, your computer’s fans will have to work harder to keep your system cool.
If you notice your system’s fans running harder than normal, clean your CPU and GPU heatsink immediately.
At some point your system’s fan will not be able to cool your CPU sufficiently. A system error may occur at this point.
5. Overclocking
This is when you increase your processor’s speed beyond its default settings; you are essentially making the engine run faster than it was designed to.
While overclocking can give your computer a performance boost, it also puts more stress on your CPU and causes it to heat up more quickly.
Solution:
If you are experiencing regular CPU temperature spikes, one of the first things you should do is check if you are overclocking your processor.
If you are, try lowering the speed to see if fixes your CPU’s overheating and throttling problem.
If you are not comfortable reversing your overclocked processor on your own, there are many software programs and online tools that can help you do it safely.
Just be sure to research which program is right for you and follow instructions specified carefully.
Once you have reversed overclocking, you can easily prevent your system from becoming so hot so quickly, thereby preventing your CPU from throttling.
The fact that the old thermal paste no longer works is one of the causes of overheating CPUs.
A faulty thermal paste will not propagate to the fan, causing it to malfunction. So you have to change the thermal paste yourself or go to a computer shop.
6. Thermal Paste
Thermal compound (also known as thermal grease or thermal grease) is a substance that is applied between your processor and heatsink.
You can purchase a small tube of thermal grease at any electronics store. In some cases, it can be purchased with a small shovel-like tool called an applicator.
When building your PC, you need a tube of thermal grease to keep your PC running smoothly. Some CPU heatsinks come with pre-applied thermal grease so you can install and start using them right away.
However, some hardware enthusiasts remove it and apply their favorite brand of thermal paste manually.
The role of thermal paste is to transfer heat from your CPU to its heatsink. Heatsinks carry heat away from your hardware.
This helps in keeping your CPU cool, especially when this task is hard to handle.
Solution:
If your computer is still under warranty, do not try to fix it yourself. If you are sure your computer is out of warranty, try to fix this problem yourself.
Shut down your computer completely and disconnect it from its power source.
- Open your computer case.
- Clean if it is dusty inside.
- Carefully remove the fan. Wipe off your CPU and old thermal paste.
- Clean your hands and surface where it will be applied.
- Apply a small amount of thermal paste to both sides of your CPU and fan.
- Reset your CPU’s fan.
- Close your computer case.
What Does CPU Throttling Look Like?
If you are gaming or performing any other CPU resource intensive task and your system is overheating, you might experience a sudden shutdown or extreme slowing down of your system.
This is when your system performs an action called throttling which is done to ensure your system does not self-destruct.
However, if you are doubtful and want to determine with solid proof issued by some program or software that your computer is definitely experiencing throttling you can do this in multiple ways.
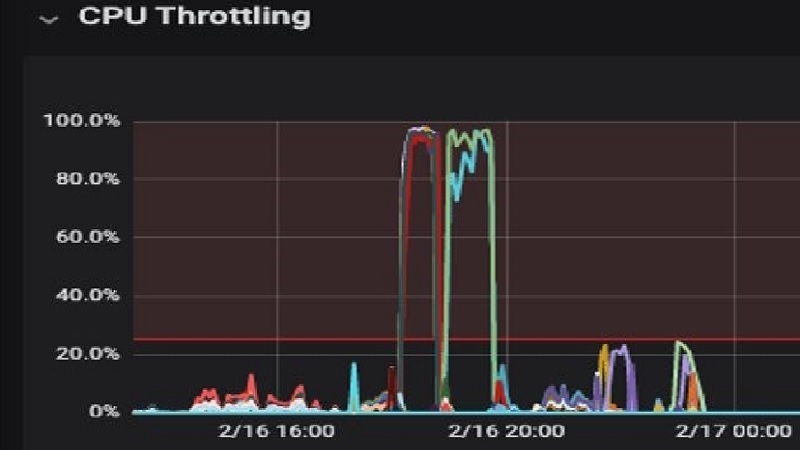
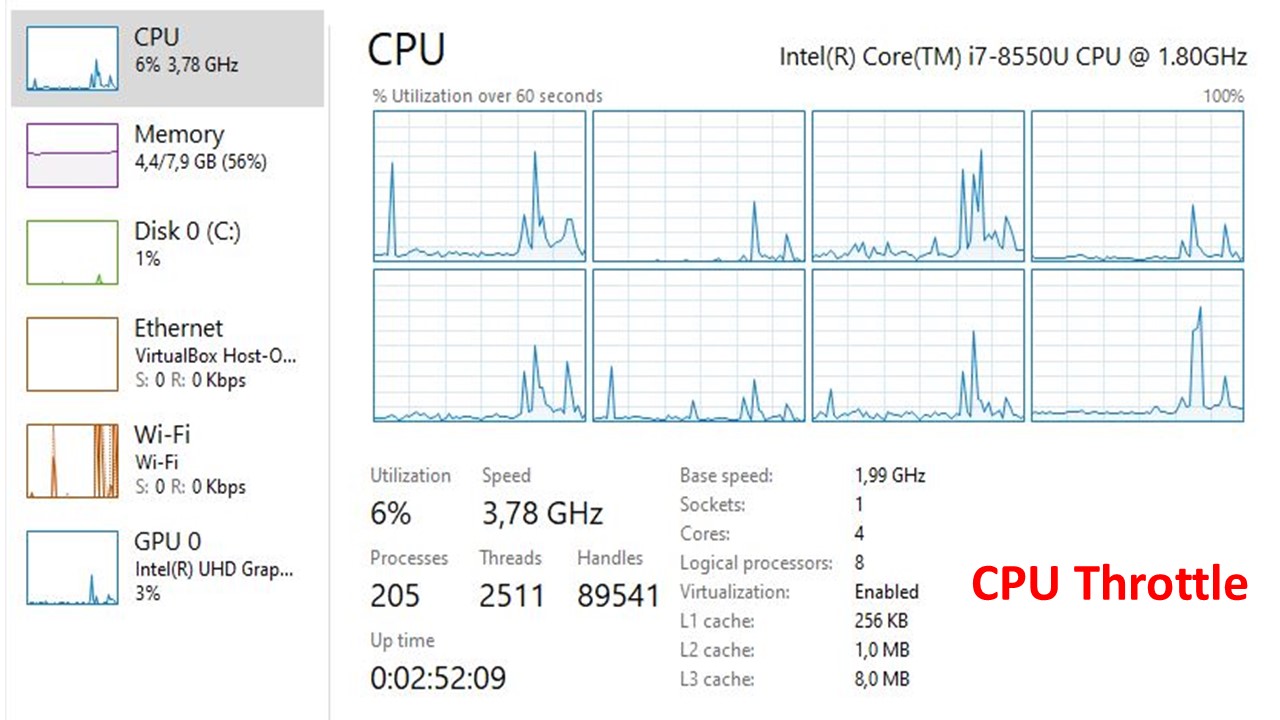
Windows 10: If you have Windows 10 as your system’s OS (Operating System) you can immediately check whether or not your CPU is actually throttling as this OS comes with an in-built monitoring tool.
This tool monitors hardware statistics making it possible for you to determine this through your CPU’s stats.
Start by clicking on Windows Key + R or simply open the Run command box by searching for it on your system.
Open this Run command box and type in “perfmon.exe/res”, now hit enter key on your keyboard or click on run.
A window called Resource Monitor opens giving you a clear view of how your CPU’s resources are being utilised. In order to analyse and determine if your CPU is being forced to operate at limited power, you need to open different programs with varying hardware requirements.
Try opening both low and high CPU resource intensive tasks and see how values in the Resource Monitor window change.
In the Resource Monitor window there is a little blue square which is located at the top right corner, labelled as Maximum Frequency.
This value is displayed as a percentage and tells you your CPU’s current speed. However, the value displayed is your CPU’s relative frequency when compared to its base clock speed.
You can also view this value in a graph which is given on the right side of this window. If you notice this value capping out at a certain value, your CPU is definitely throttling.
Intel: If you are using an Intel processor, you can download its XTU tool, also known as Extreme Tuning Utility.
This tool can be run for any generation of Intel processors.
So regardless of whether you have a new CPU or an old one, you can determine through this tool whether or not your CPU is throttling. CPU’s temperature, frequency and its resource utilization can also be tracked through this tool.
These are two ways you can monitor CPU power throttling, however if it is thermal throttling you might not be able to detect it through these methods.
While the term thermal throttling is often used interchangeably with CPU power throttling, they do not mean the same.
They are closely related terms but do not mean the same.
Is CPU Throttling Good or Dad?
If you have gone through these causes of why CPU throttle, you have understood how throttling impacts your CPU.
The CPU throttling is mostly considered good, since it prevents permanent hardware damage which is often fairly expensive to replace.
However, for some people it might be a bad thing as allowing CPU throttling to occur multiple times lowers your CPU’s processing power significantly, thereby making it fairly slow and time consuming.
CPU throttling can be considered as dynamic scaling of CPU clock/frequency.
It has been named after the throttling function in cars, and is also based on similar logic. If there is little to no load on your CPU, when you operate it at a lower speed it uses less power and remains cooler.
For battery powered devices CPU throttling will give your device a longer runtime.
If you run a demanding software on your device when it is consuming low power, any software will start lagging as its processes do not get executed at a normal speed.
CPU throttling has varied effects on your system depending on which brand’s CPU you are using. Some of these brands and their individual throttling processes are listed below:
Intel:
If you have an Intel processor, it is equipped with either SpeedStep or Enhanced SpeedStep, which is used for decreasing frequency or clock speed.
Intel’s new processors are also equipped with a dynamic setting known as Turbo Boost.
This setting allows monitoring of your CPU activity and then increasing CPU processing speed by overclocking one or two cores of your CPU if all other cores are fairly inactive.
This automatic overclocking is allowed by this manufacturer since, owing to its dynamic nature, it is not permanent and will be reversed as soon as other cores of your CPU become active with tasks of their own.
Furthermore, your computer’s cooling system is designed keeping in mind this extra heat generation.
Consequently, it should be under your system’s control and not lead to a serious reaction like CPU throttling.
AMD:
AMD originally started with a system known as PowerNow, which was designed for mobile processors.
It was then modified for all types of CPUs and named Cool’n’Quiet. This version was then modified to Turbo Core once processor speeds started further improving.
AMD’s latest Ryzen model processors have a completely new and efficient power management module. This boost is known as Pure Power and Precision and its method of throttling differs from other CPUs.
If your CPU is overclocked, you don’t even need to remove or reverse this overclocking as this new boost reduces power being transmitted to your CPU without affecting its performance or clock speed.
This is accomplished by conducting a complete analysis of heat in your computer system, rather than just checking load on each of your CPU’s cores.
If heat being generated is very high or if heat is being dissipated too slowly, this module checks the temperature of all main components in your CPU before throttling your CPU.
VIA Technology:
This is not a high-end CPU manufacturer, however, their low-end x86 processor chips are used for embedded systems.
Its first throttling system was known as Long Haul and its current throttling system is named Power Saver.
This system is fairly similar to Intel and AMD’s technology for throttling, where CPU’s clock speed/frequency and core voltage are both affected equally when power usage is reduced for throttling.
CPU throttling is not always desirable, because even if it protects your CPU, it also stops some processes from occurring.
Additionally, you will need to analyze why the CPU throttle and troubleshoot your system so that it does slow down permanently.
Conclusion
Now that you know all about why the CPU throttles, you can easily diagnose if your system is actually throttling and if it is, how you can stop it from throttling repeatedly.
You can easily prevent this from happening by proper and regular maintenance of your computer software and hardware.