A chipset and a processor used in a computer are two different items that have some major differences between them but most users are not aware of it and think that they are the same thing.
This article will make you knowledgeable about these two vital components in a computer with a separate ‘Which is more important’ section to make your knowledge more comprehensive.
In This Article
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The chipset connects the processor with the rest of the computer allowing it to interact with them and the processor performs all calculations and processes all data and instructions.
- Chipset is a collection of the functional circuits that control flow of data and information to and from the processor.
- The processor is the brain of the computer and will therefore have a direct influence on its overall performance unlike the chipset.
- The major parts of a chipset are the Northbridge and the Southbridge but the major parts of a processor are the ALU, CU, caches, buses, registers and the clock.
The 8 Differences Between Chipset and Processor

1. Functions
The chipset is that which connects the processor or the CPU to the rest of the computer.
It simply provides the way to the processor to interact with the other parts of a computer as well as other programs.
On the other hand, the processor is the main component of the computer that does all the calculations, processes all application requests and performs all high-level functions such as execution of a code.
2. Definition
Based on the definition of the two, a chipset refers to the group of functional circuits that come in a single package and controls data flow and information to and from the processor.
It also interfaces a few peripheral devices and links them with a common bus.
On the other hand, a processor refers to that particular component of the computer that actually performs all the functions and operations on the given data.
3. Reference to Context
On the other hand, without any particular context the term ‘processor’ refers to the CPU or the Central Processing Unit which is ideally the brain of the computer.
However, with reference to a context, the term ‘processor’ may signify the Graphical Processing Unit or the GPU and the Digital Signal Processor or DSP for example.
On the other hand, the term ‘chipset’ simply refers to the set of chips or Integrated Circuits that comes in one package and is a part of the motherboard.
4. Impact on Performance
The chipset may have a direct impact on the performance of the computer apart from a few specific components of it such as the memory, processor and others.
However, being a part of the motherboard, it will have indirect influence on it which is why it is always necessary to make sure that the chipset and the motherboard are both compatible.
On the other hand, the CPU, being the brain of the computer, will have a direct effect on the performance of the overall system, which is why it should be good, reliable and steady in performance.
5. Requirement
Depending on the type of your job and what exactly you are looking for in your motherboard, you may not even need a chipset literally on your motherboard.
However, even for performing basic functions on a computer, you will need a processor, though the power of it may vary according to the complexity of the job you perform on your computer.
6. Purpose
The primary purpose of the chipset on the motherboard is to ensure that the data and information moves to and from the processor smoothly and effectively reaches its destination.
Therefore, it is more like a traffic controller looking after the communications between the different components of the computer mainly.
On the other hand, there are four specific functions performed by the processor of the computer. These are fetching, decoding, executing, and writing back.
7. Design Developments
The chipsets usually tend to have less frequent developments in their designs and therefore you will not find a number of new chipsets being launched every month.
On the other hand, that is not the case with the processor.
The manufacturers are always on the lookout to better their products and therefore you will find new processors are launched quite frequently with one or a couple of improved features.
8. Parts
Typically, a chipset has two major sections in it namely the Northbridge and the Southbridge where the former is the main part that deals with high-speed functions.
However, the latter is not connected directly and looks after low-speed functions such as input and output which is why it is called the Input/output controller hub.
On the other hand, the processor or the Central Processing Unit comes with six major components in it such as the Control Unit, the Arithmetic Logic Unit, the registers, the caches, the buses, and the clock.
Which is More Important – Chipset or Processor?
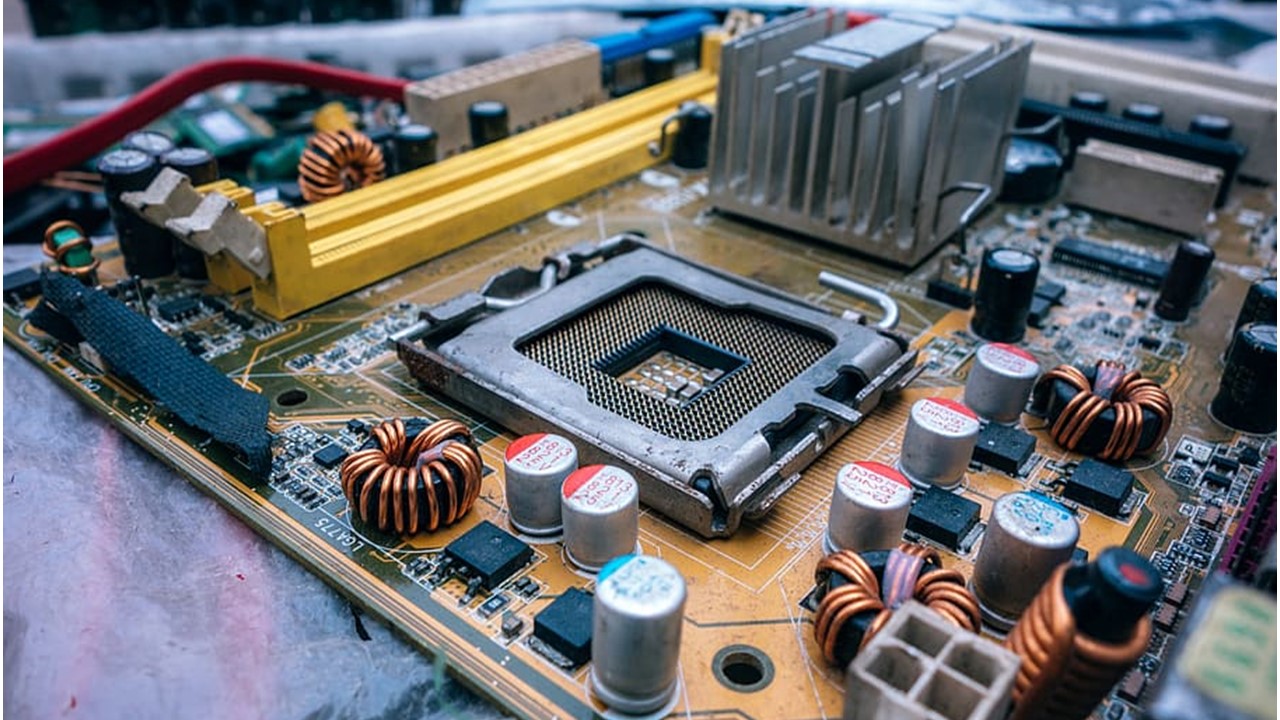
Ideally, a computer will need the contribution of the processors as well as the chipset in order to perform well.
Therefore, they both are quite important to have in a computer.
In this context, you should understand a bit about the design of the processors and its changes over time.
In the past, the processors typically had only one or a couple of major chips in them.
Typically, these chips were discrete components and the processor could even be swapped, if necessary.
As time passed, the design and makeup of the processors as well as the chipsets changed.
Initially, the processors in the computers were quite large and they needed a lot of room to be installed.
Apart from that, these processors also needed an immense amount of power to operate.
Things changed dramatically over time and gradually the room-sized computers got reduced in size to make way for the modern processors.
These processors contain most of the components in one single chip.
As said earlier, the chipsets however, did not change that dramatically over the years but still there is a significant change in their design and functionality noticed in these years.
One of the most significant areas of development is the increase in efficiency and speed.
Speed is very important for the functioning of the chipsets because it acts as the conduit between the processor of the computer and its other areas.
Moreover, the two parts of the modern chipsets namely, the Northbridge and the Southbridge, where the former works with fundamental computer parts and the latter with non-vital or secondary components.
Therefore, it is quite evident that the processor and the chipset work together to make a computer work because they both help in the interaction process between each area of the computer, the installed software as well as the user.
It is true that they do not have any common functions but are still crucial for the operation of the computer.
Ideally, the processor performs as the calculator of the computer and the chipset acts as the courier that moves the information around the computer system as desired and quickly.
Both of these computer components have very specific and clearly defined functions and therefore they do not overlap.
The motherboards you find today come with multiple chipsets for better functionality.
For example, a chip may handle the data transfer between the RAM and CPU while another may be responsible for controlling the data flow to the peripheral devices.
And, as for the processors, the modern CPUs come with several ‘Cores’ which are actually separate execution units that perform different arithmetic and logical operations at a much higher speed.
Typically, when a processor carries out an instruction sent by the operating system, it often has to wait till the software and other devices generate the necessary data for the execution units to use for further computations.
This means that each core of the processor will not be able to run at its highest speed if they do not readily receive the data necessary for them to do the processing job.
It is only when they get a seamless data flow that they will be able to operate at full speed.
This brings the chipsets to the scenario. Since these chipsets can manage the data flow, the processors rely heavily on them to receive the necessary data.
If there was no such chipset in the computer then it would have resulted in bottlenecks and lowered the level of performance of the cores.
This is because some of the cores of the processor will be working and the other will have to wait due to non-availability of data.
However, if there is a chipset and it is not faulty, then a processor, say with multiple cores operating at 2 GHz, all of them can operate at the same time and at the highest speed since they will continually receive all of the necessary data and information during the processing period.
Therefore, it is safe to conclude that both the chipset as well as the processor are important components and are good to have in a computer.
This will improve the performance quite significantly as well as enhance the speed of operation with all the cores of the processor operating at full power.
Just make sure that the processor and the chipset are compatible with each other so that they can work perfectly in tandem to produce great results.
Therefore, make sure that you spend some time on a little bit of research which is quite essential to make your investment productive and get high returns.
Conclusion
Since you are reading this line, it is assumed that you now have gained significant knowledge about the differences between a chipset and a processor.
It is also assumed that you will not ignore any one of them since you know the importance of having both in a computer today.