In This Article
What is eMMC Storage?
eMMC (embedded MultiMediaCard) is a type of flash storage that is commonly used in mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
It is a form of non-volatile memory, meaning that it retains its data even when the power is turned off. eMMC storage consists of an embedded controller and NAND flash memory, which are housed in a single package.
It is a cost-effective storage solution that offers reliable performance and is designed to be soldered directly onto the device’s circuit board. eMMC storage is typically slower than other types of flash storage, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), but is still capable of providing sufficient storage and performance for most everyday computing tasks.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The eMMCs are small in size but can store data and system files without needing electricity.
- The speed for data transfer of an eMMC can be as high as 400 MB/s which is much higher than an SD card and close to a regular SATA SSD.
- The design of this storage makes it quite cheap and efficient in booting the system and operates silently.
- The eMMC however offers low storage capacity, upgradability option being embedded and low expandability.
Understanding eMMC Storage
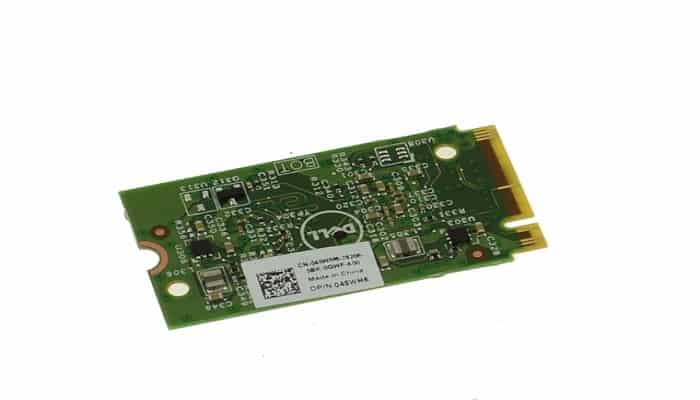

An eMMC storage is developed by JEDEC and the MultiMediaCard Association. It is pretty similar to the flash storage with respect to the NAND flash memory cells.
The eMMC come with an 8-bit parallel array and are connected to the motherboard directly but are much slower and smaller than a Solid State Drive. Typically, the storage capacities of these drives are 32 GB, 64 GB, 128 GB and the latest 5.1 version comes with 256 GB.
This means that it cannot store a large amount of data. Still it acts as the primary device in small and portable devices such as tablets, cell phones, laptop computers, cameras and others.
These storages are quite fast with the latest 5.1 version being able to attain a speed of up to 400 megabytes per second which is as good as an SSD using a SATA connection.
The integrated controller of the eMMC relieves the CPU of the device from the responsibility of placing data into the storage. And, the flash memory consumes little power while operating.
The specific features that separate the eMMC from the other storage drives are:
- Its size, which is not larger than a postage stamp
- Its simple design standard that reduces cost of production and
- Its bootable nature due to the built-in controllers.
These features and benefits are the reason that the eMMCs are used in different embedded applications other than in the consumer products such as robotics, Single Board Computers, automotive, medical devices, and IoT.
Lifespan of eMMC
An eMMC run device can last up to 5 years.
This timespan is indirectly proportional to the storage capacity of the drive, meaning a 16 GB eMMC is likely to last longer than a 32 GB one.
Also, the more you use one the further its lifespan decreases.
They have a tendency to degrade and once that happens, you cannot use the concerned device anymore.
How Does eMMC Work?
The eMMC card is soldered directly into the motherboard of your device, and this is where the prefix ‘e’ comes in to play.
It is composed of NAND flash cells, and like other sorts of permanent storages, it can be used to store data without needing electricity.
It can also be used to store system files and has therefore been used in smartphones as well until 2016. Check out flash drive advantages and disadvantages.
In eMMC, the storage cells and the controller are put together in a small BGA (ball grid array) IC package.
The width of such a card is very small, and therefore easily fits in a motherboard. They basically work in the same way a USB drive works.
The Pros of eMMC
The advantages that this mode of storage have are as follows:
1. Small Size
As said already, the eMMC is a small storage drive. Thus, it is easy to fit one in the motherboard of your PC, while leaving space for more flash storages later on.
Its compact size makes it perfect for smaller laptops, smartphones and tablets. You will find some mini PCs with this form of storage as well.
2. Faster than an SD card
The speed of the latest eMMCs is about 400 MB/s. This is much faster than an SD card, and hence you get faster file transfers out of your computing device. It can be compared with SATA drives.
3. Cheap
One of the main advantages of the card is its price. It is very affordable and the use in laptops and Chromebooks lowers down the price of the entire device as a whole. So if you need a smaller amount of storage, they come handy.
4. Non Volatile
Like SSDs, HDDs, and other flash drives, an eMMC can hold data without electric power. This is a very useful quality when one wants a cheap storage option.
5. Can be used for a boot drive
You can use only an eMMC in your system, and yet your computer/laptop will boot up comfortably.
6. Newer Features
Every new version of the eMMC has brought newer features.
Thus in the current ones you get better security features, the scope of updating the firmware without having to shut down the system, background operation, and so on.
7. Efficient and Noise-less
eMMCs are very efficient and create no noise while working as there are no moving parts. This is an advantage over hard drives.
The Cons of eMMC
The following are some of the disadvantages of eMMC storage.
8. No Upgradability
You cannot upgrade the storage if you use an eMMC storage since it is embedded in the motherboard.
This means that you are stuck with the same limited amount of storage throughout.
9. Less expandability
A device with eMMC storage doesn’t allow you much expandability. The most you can do is add another SD card, or probably an external drive.
10. Problems in Operation
There have been problems reported in systems that rely solely on an SSD.
For example, the overall response of a device when the system and OS files are stored on a hard drive or SSD is much better than that stored in an eMMC.
Also, it is not optimized for multitasking and thereby the performance of the laptop or smartphone is hindered.
11. Weaker than SSD
Although eMMCs have some advantages, being better than an SSD is not one of them.
The latter has better performance, better speed and can outlast them in the long run.
12. Lower Storage
eMMC has limited storage, 256 GB at most to be exact. So, they are not suitable to store large amounts of data and have limited usage.
Even the average PC user would like to have some more storage since some portion of it will also be taken up by the system files.
Conclusion
eMMC storage is a popular form of non-volatile flash memory used in mobile devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
Its compact size, affordable cost, and efficient and noiseless operation make it a popular storage option.
It consists of an embedded controller and NAND flash memory, which are housed in a single package, and is designed to be soldered directly onto the device’s circuit board.
While it may not have the same performance and storage capabilities as other flash storage options, such as solid-state drives (SSDs), it can still provide sufficient storage and performance for most everyday computing tasks.
With the 5.1 version offering a speed of up to 400 MB/s, eMMC storage can transfer data much faster than an SD card and close to a regular SATA SSD.
Its low storage capacity, lack of upgradability, and low expandability are some of its limitations.
Nonetheless, it remains a popular choice for small and portable devices and is used in various embedded applications, including robotics, Single Board Computers, automotive, medical devices, and IoT.