Both PCIe and SATA storage interfaces are being used in computers for quite some time now. Check out differences between PCIe and SATA.
We have seen each of these storage interfaces individually, but it is now time to make a comparison between the two so that you can have a look at how different they are and which is better.
But mind you that both of these interfaces are necessary, so a single one will not be emerging as a sole champion. Check out PCIe advantages and disadvantages.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The PCIe card offers direct connection to the motherboard being embedded in it.
- Each PCIe lane has two dedicated pairs of wires for data input and output but in a SATA cable there are seven wires in total.
- The bandwidth and speed of PCIe is much more than SATA.
- SATA is suitable for basic and casual computing needs while a PCIe will support advanced computing.
In This Article
The 6 Differences Between PCIe and SATA:
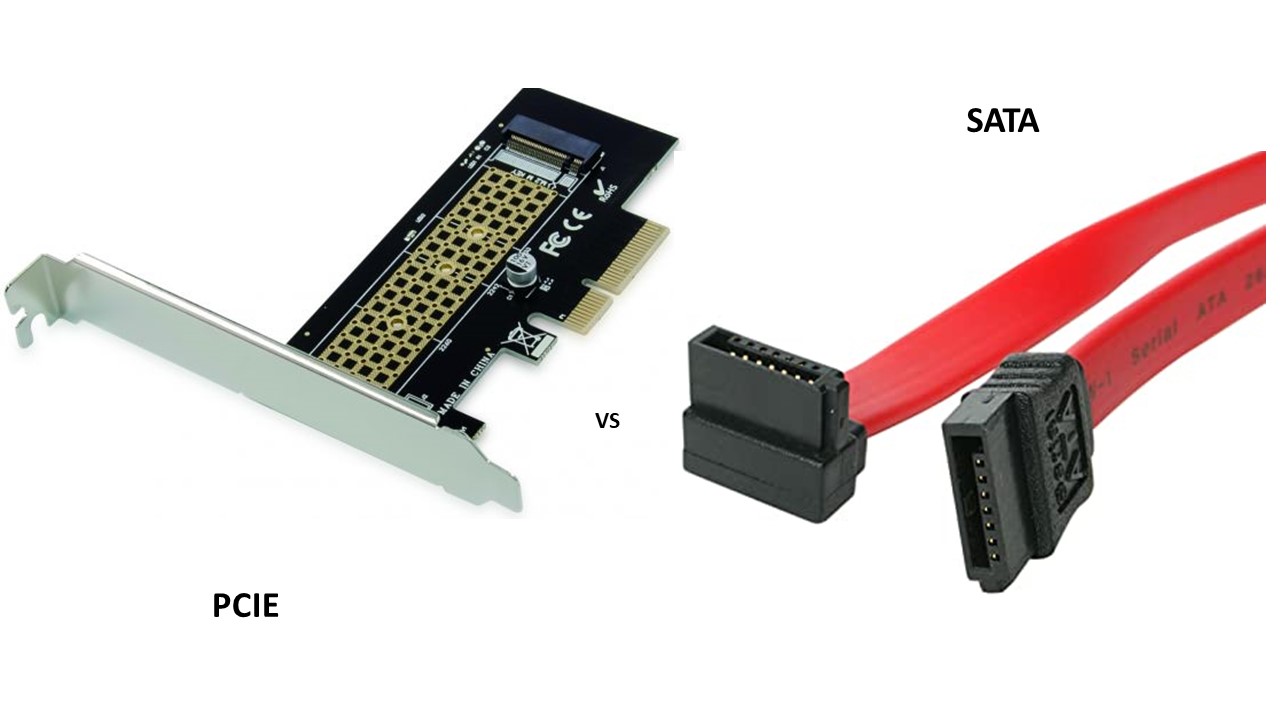
1. Utility
The PCI interface from the very beginning has been intended to replace the need for AGP and other interfaces to add video cards, network adapters, etc. Their use in SSDs is a relatively recent concept, with the invention of the NvMe slot.
SATA was mainly built to build a connection to move data to and from the motherboard and the storage drives. It cannot be used to add a GPU or other components supported by PCIe because of certain limitations.
2. Form of Connection
A PCIe card is embedded directly into the motherboard. They have a direct connection to the components.
The SATA is similar to a 2.5” hard drive casing. It has two ports, one on the storage drive itself and the other in the motherboard.
3. No. Of Wires
Each lane in a PCIe connection mainly uses two pairs of wires, one for data input and the other for output. Thus, an x1 connection has 4 wires, x4 connection has 16 wires, etc.
In each SATA cable, there are a total of 7 wires. 4 of these are used for real data transfers and are present in a pair of two. The other 3 are ground wires and work to safely remove the excess charge from your system in case of a fault.
4. Bandwidth
A PCIe has 4 formats mainly, each with x1, x4, x8,x16 lanes. The total bandwidth, therefore, is large, about 32 GB/s and a single lane in the PCI 3.0 can carry data of 8 GT/s on each lane.
The bandwidth of a SATA drive is roughly at 6 Gb/s. So as you can see, it is quite slow.
5. Speed
Even the earliest forms of the PCIe interface like the PCIe 1.0 had speeds of about 250 MB/s on a single lane, while a collective of 6 Gb/s on the x16 lanes.
The PCI 3.0 has the real-time max speed of about 985 MB/s on an x1 lane, and this is multiplied as you use more lanes. There are yet faster versions of PCIe.
The fastest speed a SATA can reach is about 600 MB/s, and that too in the recent SATA III interface. Hence, it is quite slow when compared to PCIe.
6. Price
SSDs are usually more expensive than hard drives anyway. Now NvMe SSDs are costlier, obviously because of the better reading and writing speeds.
The SATA III SSDs are cheaper, and you can find one at about $60. So, for budget PCs, they are the way to tread on. The same PCIe SSD from the same brand costs way more than a SATA III SSD.
Which is Better: PCIe or SATA?
The answer to this question is a matter of personal preference.
The reason behind it is that for day-to-day computing, the SATA is a cheaper form of data transfer, while the PCIe is necessary for gaming, working with servers and other tasks with a greater workload. It all thus depends on what your needs are.
The SATA III interface is for budget users, while the PCIe is necessary for those who need more performance by paying more price.
Our take in the matter is that for storage purposes at least, casual and home users should be going with SATA.
Those who need more performance, faster file transfers, and other advantages, should invest in NvMe or PCIe SSDs.
Conclusion
It all has been laid in front of you so that your choice is clear.
You need both since SATA has limited usage but is cheap, while you cannot add a GPU in your PC without spare PCIe slots.
Therefore, each has the importance of its own.