In This Article
What is Gigabit Ethernet?
Gigabit Ethernet refers to the data transmission technology following the Ethernet protocol and frame format. It can achieve a data rate of up to one billion bits per second, hence its name.
Usually, it is used in LANs or Local Area Networks and is described in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3 standard.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Gigabit Ethernet offers more flexibility and a much higher data transfer speed, but is usually more expensive than regular Ethernet standards.
- This is a complex technology and it needs specific types of hardware and software, making it unsuitable for average home users.
- Higher bandwidth and speed make Gigabit Ethernet a suitable option for industrial and commercial users engaged in network-intensive jobs.
- It is quite energy-efficient in spite of the fact that it needs larger PoE+-powered devices and a complex configuration.
- The switches for Gigabit Ethernet are offered in a wider port configuration such as 8, 16, and 24-port models to meet varied cabling requirements.
Understanding Gigabit Ethernet
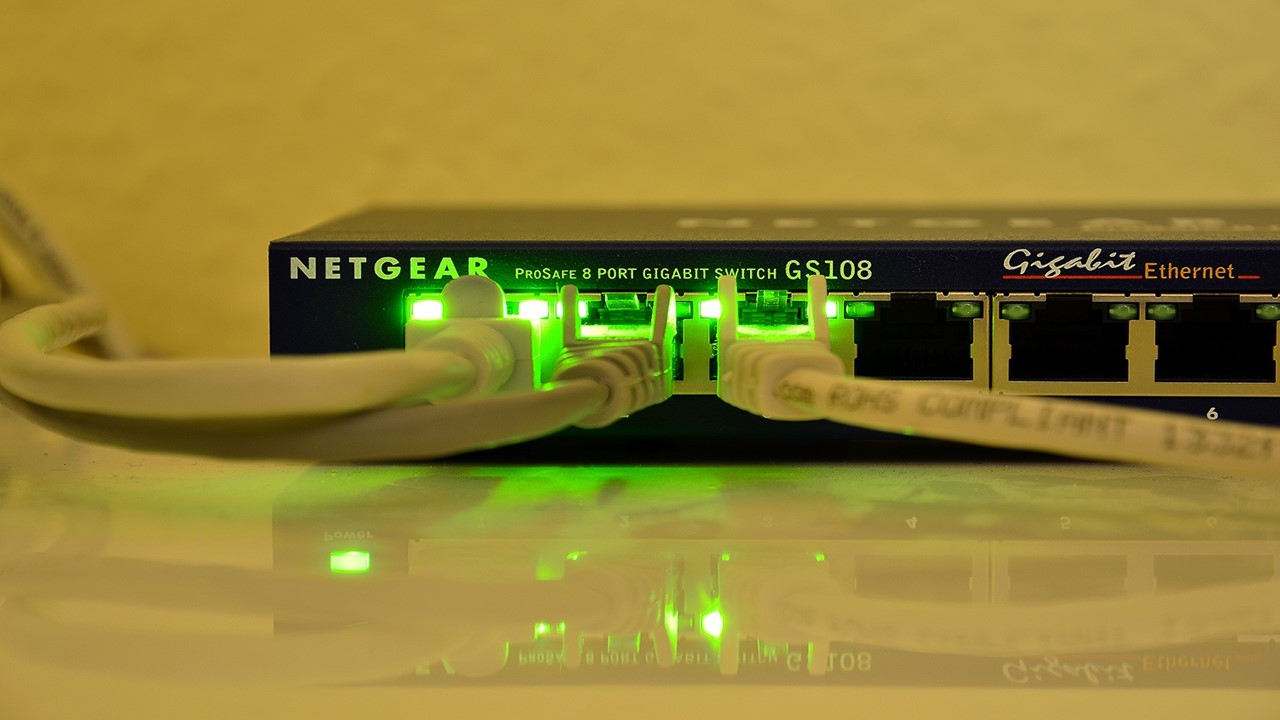

Gigabit Ethernet signifies a specific version of Ethernet technology. It is typically used by large commercial and industrial organizations.
It is the successor to Fast Ethernet and other 802.3 standards of 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps and can support roughly one hundred million Ethernet nodes.
Data is transferred through optical fiber over a long distance of up to 70 KM.
Gigabit Ethernet is typically abbreviated as GbE or GigE and the first standard was labelled as 802.3z and certified by the IEEE 802.3 Committee.
Working
The primary objective of Gigabit Ethernet is to enhance the performance and speed while maintaining all of the standards of Ethernet. It can function in two different ways, such as:
- Half-duplex for shared media
- Full-duplex with Ethernet switches
Supporting the same 802.3 frame, it also uses Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to achieve higher data transfer speeds.
This particular feature can detect and discard the colliding data packets within the network.
Types
Depending on the physical layer standards and cabling, Gigabit Ethernet can be categorized into the following types:
- 1000Base-CX – This uses Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) or balanced twin axial cabling and is usually used for connections up to 25 m.
- 1000Base-SX – This type is used for data transfer needs of up to 220 m and uses fiber optic cables for transferring data over short wavelengths.
- 1000Base-LX – This standard uses fiber optic cables to transfer data up to 5 KM.
- 1000Base-T – This standard uses UTP or Unshielded Twisted Pair copper cables of Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat7.
- 1000BASE-T1 – It uses STP copper cables for connections up to 15 m.
- 1000BASE-TX – It is the same as 1000Base-T and uses UTP copper cables for connections up to 100 m. However, it is costly and needs Cat6 and Cat7 cables.
- 1000BASE-KX – Used for connections up to 1 m, this standard also uses UTP cables.
Features
- Gigabit Ethernet supports both full-duplex mode and half-duplex mode.
- All lines are buffered in it and are internally and electrically connected.
- The only likely sender to the switch is the computer.
- Data transmission happens even when the switch sends a frame to the PC.
Cable
In most cases, Gigabit Ethernet is found to work fine with any standard Ethernet cable belonging to the CAT5e and CAT6 cable standards.
However, nowadays, Cat7 and even Cat8 cable standards are also used for high-speed Gigabit Ethernet.
Adapter
You will need to use a Gigabit Ethernet adapter with your connection.
It is a compact and small device that will allow you to connect your devices to the high-performance Gigabit Ethernet network.
Switch
You will also get a Gigabit Ethernet switch, which is a specific kind of network switch that can support a speed of up to 1 Gbps for every device connected to a Local Area Network.
Usually, you will get these switches for consumer use with four to eight ports. However, for enterprise use, the switches can support many more connections.
Gigabit Ethernet Speed
Typically, the speed of Gigabit Ethernet is believed to be 1 Gbps. However, in practice, the devices using this standard can normally reach up to a speed of 900 Mbps.
This is because, under normal conditions, the average speed of the connection typically depends on a lot of different factors, such as:
- The pending re-transmissions due to temporary failures and collisions of data packets
- Overhead of the network protocol
- Performance limitation of the disk drives
- Limited bandwidth of the connection
- Quality of all the components and devices involved
- Number of concurrent sources and client devices used
- Speed of the network controller
- Quality of the cables used
- The read and write speed of the hard drive
- The level of support offered by the router, switch or hub for the Gigabit speed of the network
- The amount of available memory
- Other services and programs that may be running at the same time
It is also affected by the limited performance and incoming and outgoing data handling capabilities of the Central Processing Units (CPUs) and the Gigabit Ethernet ports of the routers.
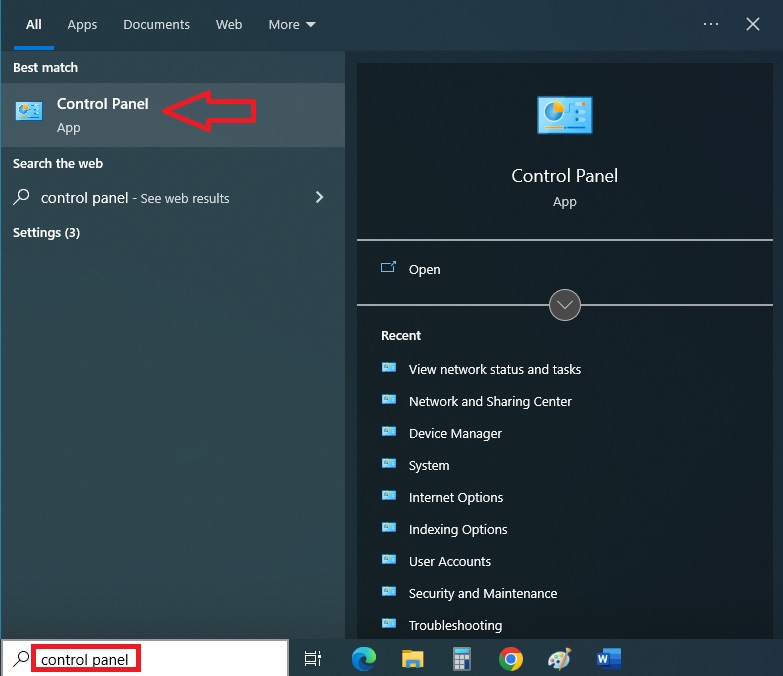
If you want to check the actual speed of data transfer, you can do it in the following ways:
- Go to the Search box beside the Start menu.
- Type Control Panel in the box.
- Press Enter.
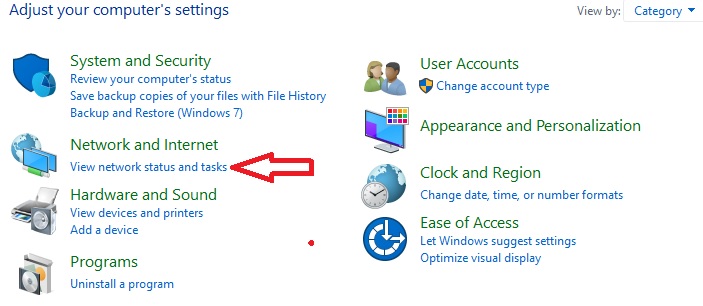
- Look for the Network and Internet option.
- Click on View network status and tasks.
- Select your internet connection and click on it.
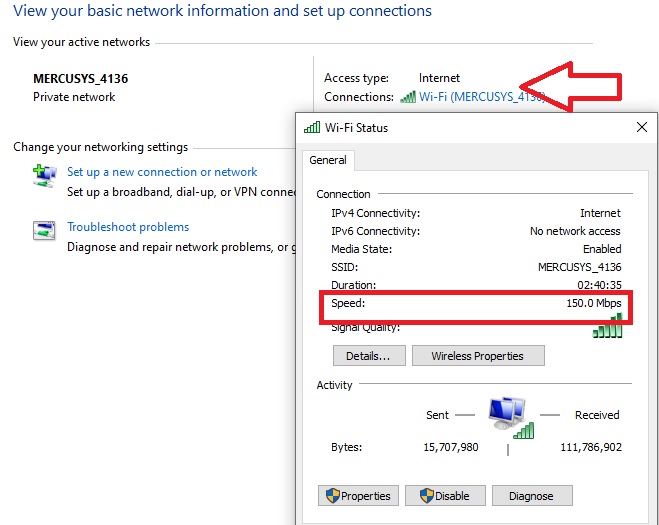
Look at the speed, usually mentioned in Mbps.
Is Gigabit Ethernet the Same as RJ 45?
No, the two are different in the sense that the RJ 45 ports used with the Gigabit networking devices typically follow the Ethernet 1000BASE-T standard.
These cables also support the twisted pairs only for network connections via Category 5, 5e, or 6 cables made from high-quality copper.
They are good for 1 Gbit transmission over a distance limited to 330 feet or 100 meters.
Gigabit Ethernet Vs Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet standard was initiated as IEEE 802.3ab in 1999 and as IEEE 802.3ah in 2004. On the other hand, the Fast Ethernet standard was initiated as IEEE 802.3 in the mid-80s and as IEEE 802.3u in 1995.
- Gigabit Ethernet standard supports a much higher data transfer speed, while Fast Ethernet is typically slower in comparison.
- While comparing on the basis of cost, Gigabit Ethernet is more expensive than Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet technology is difficult to configure because it is a more complex technology in comparison to Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet is difficult to manage when compared with fast Ethernet.
- You may need specially designed network devices or appliances to use Gigabit Ethernet, which is not a necessity in the case of Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet is more scalable because it supports commercial, residential and industrial uses in comparison to Fast Ethernet.
- Smaller hardware and less cables are required to use Gigabit Ethernet, thereby reducing space requirements. On the other hand, Fast Ethernet consumes more physical space.
- Gigabit Ethernet can transfer data over a larger distance, usually up to 70 KM, in comparison to Fast Ethernet, which typically covers a distance of about 10 KM.
- The high-speed bandwidth potential of Gigabit Ethernet enables it to offer support to virtual networks and can be easily configured and managed, which is not possible in the case of Fast Ethernet.
- The Round-Trip Delay or RTD time of Gigabit Ethernet is slightly less in comparison to Fast Ethernet.
- Upgrading from Fast Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet is complex and costly in comparison to upgrading from regular Ethernet to Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet is the successor of Fast Ethernet, while Fast Ethernet is the successor of 10-Base-T Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet is more energy efficient in comparison to Fast Ethernet.
- Gigabit Ethernet supports a wider layer standard set including 1000Base – SX, 1000Base-LX, 1000Base- CX, and 1000Base-T. Of these 1000 Base-SX and 1000-Base LX. On the other hand, Fast Ethernet supports 100 Base-FX, 100 Base-T4, and 100 Base-TX.
Advantages
- Higher throughput capabilities
- Higher bandwidth
- Higher data transfer speed
- Better quality service
- Better virtual LAN support
- Reduces bottleneck issues
- Better scalability across networks
- Easy to maintain
- Supports smooth streaming of 4K video at higher frame rate per second
- Available in different varieties
- Supports a larger variety of software and hardware
- Usually not influenced by radio interference
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Not cost effective for average users and overkill for home use
- Connection is tougher to achieve
- Modular hardware style and need specific types of network devices and appliances
- Lower flexibility
- Subject to physical susceptibility
Questions & Answers
Do You Need CAT 6 for Gigabit?
You can use either a CAT 5e or a CAT 6 for Gigabit transmission since they both can transmit data at a speed of up to 1000 Mbps or 1 Gigabit per second. Both of these categories are pretty fast and reliable in comparison to most of the internet connectors.
How Many MB Is Gigabit Ethernet?
Mathematically, 1 GB is equivalent to 125 MB, which means that a Gigabit Ethernet transfers 125 MB of data every second.
Is Gigabit Ethernet Good?
Yes, Gigabit Ethernet is good since it is faster. Ideally, it is because of its higher speed that most users move from Fast Ethernet to Gigabit Ethernet because it is ten times faster than the former, usually transferring data through fiber optic cable at a speed of 1,000 Mbps.
Conclusion
Gigabit Ethernet is a very good option for those users who want to have a much faster data transfer speed and higher flexibility, but all that comes at a price.
It is therefore best suited for network-intensive tasks. However, the performance and energy efficiency offered balance the high cost of Gigabit Ethernet.