In This Article
What is iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface)?
The Internet Small Computer System Interface, or iSCSI in short, refers to the Internet Protocol (IP) for transferring data through different types of networks such as LAN, WAN, and SAN by using storage arrays in the data centers.
Technically, iSCSI is a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) or a data transport layer protocol that defines exactly how the Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) packets should be transmitted over the protocol.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The Internet Small Computer Systems Interface signifies a data transfer protocol that is followed over TCP-based IP networks, such as LAN, WAN or SAN, and is standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force.
- iSCSI is actually a block protocol designed for storage networking. This is mainly based on the widely used SCSI storage protocol followed across a given network connection, typically using Ethernet.
- Just like Fiber Channel, iSCSI also allows creating a Storage Area Network and the traffic can run through a dedicated storage or a shared network. This specific data transfer protocol also allows for multiple transports.
- The Internet Small Computer Systems Interface, however, does not support object storage or Network Attached Storage access. This is because both of them follow different kinds of data transfer protocols.
- It offers decent block storage performance at a low cost. It is widely supported by nearly all hypervisors and major operating systems. It can also work pretty well with specific Host Bus Adapters or standard network cards.
Understanding iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface)
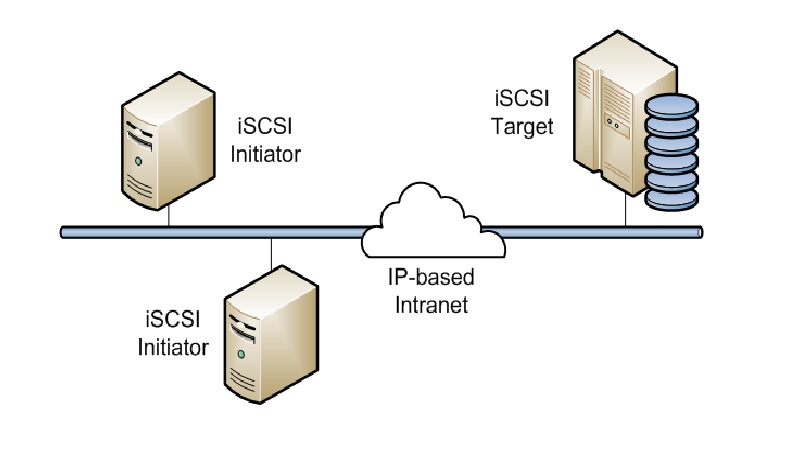
Internet Small Computer System Interface is the Internet Protocol for data transfer for the internet itself and different other networks, such as:
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
Ideally, this is mainly due to the enhanced performance offered by the SANs in terms of data retrieval, in particular.
However, iSCSI does not support accessing Network Attached Storage (NAS) or object storage due to their varied transfer protocols.
Still, in terms of block storage performance, the Internet Small Computer System Interface protocol offers reasonably good performance at a low cost.
Typically, most of the storage based on this particular interface data transfer protocol is hard disk storage. However, there are quite a few tape-based and medium changer devices available on the market as well.
Usually, in iSCSI, the most commonly used transport is TCP/IP over Ethernet, but it also allows using Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) with iSER, which is actually the short form of the iSCSI Extension for RDMA.
However, while using it with iSER, the transport is either InfiniBand or RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE), where the underlying network for each is InfiniBand and Ethernet, respectively.
Typically, iSCSI can be expedited through the network adapters that come with an iSCSI hardware offload and, optionally, with a TCP Offload Engine (TOE).
The HBA in the former offloads the functions of the iSCSI initiator to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of the server.
And in the latter case, TCP processing is offloaded by the adapter from the CPU and the server kernel.

Operating System Support
It is supported by different major operating systems and hypervisors, such as:
- VMware ESX
- macOS
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
- Free BSD
- AIX
- Windows
- Linux
- Solaris
- IBM i
- NetWare
- OpenVMS
- HP-UX
Implementation
- Provisions of iSCSI storage can be implemented as an iSCSI client by activating or installing the client computer.
- The iSCSI client initiators are added to initiator clusters for iSCSI client identification on the storage device.
- An iSCSI Logical Unit Number (LUN) is created on the storage after configuring the initiator and is assigned to the client definition or the initiator group.
Working
While working, this is what happens at the receiving end of the iSCSI system:
- When a request is initiated by the end user for the structured workload to be sent to the operating system, a suitable data request and SCSI command are produced.
- If configured, this will go through encryption and encapsulation and a packet header will also be added to it.
- The subsequent IP packets are transferred through the Ethernet connection.
On the other hand, at the receiving side of the data packet, this is what happens:
- If the data was encrypted earlier, it goes through the decryption process.
- The data packet is disassembled, and the requests and SCSI commands are discerned.
- The commands are sent to the SCSI controller, from where they are diverted to the specific SCSI storage device.
Since iSCSI is a bi-directional protocol, it can be used to send data in return for a response to an initial request as well.
Components
There are basically two major components of iSCSI. These are:
- iSCSI initiator – This is a piece of hardware or software installed in a server. It sends data to and from an iSCSI target device or an iSCSI-based storage array.
- iSCSI target – This refers to the storage system itself, which is basically a server. It not only hosts the resources of the storage but also allows access to it via one or more NICs, iSOEs, or HBAs.
Performance
Ideally, for iSCSI performance, the base configuration considered is 10 GbE, though most of its applications are built on a 1 Gigabit per second Ethernet (GbE) structure.
The multipathing technique allows setting up various paths between the storage resources and the client servers by a storage administrator for the following benefits:
- The process enhances its performance further due to the throttling of bandwidth to balance loads, thereby allowing more efficient access to storage.
- It also enhances the reliability and fault tolerance of iSCSI storage systems.
Other techniques that enhance the performance of iSCSI are:
- Jumbo frames – This Ethernet protocol enhancement allows shipping larger amounts of data by the iSCSI storage systems than what is permitted by the ordinary Ethernet frame size.
- Data Center Bridging – The DCB standard, authorized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), makes the Ethernet-based storage more consistent to enhance performance by mitigating dropped frames and assigning more bandwidth to performance-hungry applications. Data center bridging also prevents data loss with the help of the Ethernet extensions.
Alternatives
Here are some Ethernet alternatives to iSCSI:
- Fiber Channel over IP (FCIP), also called Fiber Channel Tunneling
- Internet Fiber Channel Protocol (iFCP)
- Fiber Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)
- ATA over Ethernet (AoE)
What is iSCSI Used for?
The Internet Small Computer System Interface protocol is mainly used to create a shared storage network used by multiple clients and servers to allow them access to a central storage resource.
Ideally, the first storage based on iSCSI was used in 2000 with Windows NT. It was followed by IBM with a Linux operating system in 2001. After that, it has been available for other operating systems.
It is the features of iSCSI that make it so popular as a Tier-2 application for shared storage among different hosts that need good, if not the best, block storage performance.
Allowing the users to consolidate their data through different storage arrays of the data centers, this particular protocol makes it look like they are using a local hard disk for storage and not that of a data center storage.
You can also use it with almost all types of enterprise storage arrays.
The protocol is also usable with special types of Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) and even with regular Network Internet Cards (NICs).
It is extensively used among the large cloud service providers and the hyperscalers with the help of a block storage solution over Ethernet.
Ideally, iSCSI is best to use when:
- Cost saving is a priority
- Multiple connections to a single storage are required
- Talent is a concern
Can iSCSI be Encrypted?
Yes, the data transferred through iSCSI can be encrypted to ensure the confidentiality of information sent over this framework.
Ideally, data integrity in iSCSI is provided at five different levels, such as:
- The iSCSI itself
- The Ethernet
- The IP
- The TCP
- The IP Security (IPsec) checksums
How To Connect to iSCSI Storage?
Ideally, to use the Internet Small Computer Systems Interface storage, you will have to connect the iSCSI target to the Windows iSCSI initiator.
This will show the volume on the computer system as a local physical hard drive. You can use this for video storage as well.
The steps to follow to go ahead are:
- Go to the Control Panel
- Select Tools
- Open the iSCSI initiator
- Go to the Properties page of the initiator
- Click on Discovery
- Enter the IP address of the Network Attached Storage
- Click on OK
- Click on Target
- Select the iSCSI targets that you want to connect from those available
- Click on Connect
- Click on OK
When the changes are successful, the status will change to Connected.
Advantages
- Built on familiar and stable standards and technology
- Creates a SAN to reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Easy to use, install and maintain due to the use of SAN and involvement of TCP/IP
- Reduces the cost of operation
- Eliminates the need to hire trained and specialized personnel
- Eliminates practical distance restrictions
- High degree of interoperability between different networks
- No need for specialized hardware
- Works on commonly used networks and TCP/IP protocols by the data centers in particular
- Little or no investment is needed for setting up a new network technology
- Faster and more efficient access
- Multiple feature support improves performance and security
- Eliminates deduplication, mutable snapshots, and thin provisioning
- Supports long-distance IP routing through TCP/IP without needing additional gateway hardware
- Offers high flexibility
- Provides a large storage network environment
- Uses Internet Security Protocol such as authentication and encryption of individual data packets and others such as Internet Protocol Security (IPsec)
- Additional Access Control List (ACL) support provided to ensure secure console management and user data access control
- Non-disruptive changes
- Supports faster and more efficient block-level file sharing
- Challenge/Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) support ensures credibility while logging into a specific server on a SAN
- Reusability and reliability
- More leverage
Disadvantages
- Needs additional effort to configure the iSCSI initiator and target
- Needs 10 GbE for a better and higher performance
- Additional best practices to follow to handle traffic loads
- Higher latency is a common issue
- Susceptible to packet sniffing
iSCSI Vs Fiber Channel
- The Internet Small Computer System Interface storage systems and components are less expensive in comparison to the Fiber Channel.
- While iSCSI allows using it on an existing network, Fiber Channel does not since it needs dedicated, and often expensive, hardware and infrastructure.
- iSCSI does not support robust data flow management such as Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) or avoiding transmission retries, but in comparison, the Fiber Channel protocol does.
- The iSCSI protocol does not support an embedded service infrastructure as opposed to Fiber Channel.
- The iSCSI design does not support network isolation by design, but Fiber Channel does.
- The data transfer speeds supported by iSCSI are 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps, and more. On the other hand, the transfer speeds available in Fiber Channel are 2 Gbps, 4 Gbps, 16 Gbps, 32 Gbps, and more.
- The load on the CPU is higher in the case of iSCSI, but in comparison, the CPU load is lower in Fiber Channel.
- Access and communication control in iSCSI are typically done through the ACL or Access Control List. On the other hand, in Fiber Channel, zoning is used for the same purpose.
- Typically, iSCSI is more suitable in settings that have fewer I/O requirements. On the other hand, Fiber Channel is more suitable for high I/O requiring and latency sensitive applications.
Questions & Answers:
Is iSCSI TCP or UDP?
The Internet Small Computer System Interface is typically a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and not a User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Is iSCSI a Block or File?
The Internet Small Computer System Interface is a block protocol rather than a file protocol. For every volume, this protocol supports one single client on the server, but it allows the applications to run on the machine of the single client while sharing remote data.
What Port Does iSCSI Use?
The iSCSI protocol typically uses TCP 3260 ports for the protocol itself, along with names of higher levels for addressing the objects in it.
Since the protocol is constructed in Clustered Data ONTAP (Open Network Technology for Appliance Products), it does not allow altering the port number.
Typically, the port number 3260 is registered as a specific part of its specification. Usually, this port cannot be used by any other service or application.
What are the Types of iSCSI?
There are basically three types of Internet Small Computer System Interface protocol, and special name formats are used to identify its targets as well as the initiators.
The types include the Extended Unique Identifier (EUI), iSCSI Qualified Name (IQN), and T11 Network Address Authority (NASA). However, for all three types the switches are very similar to those of the Ethernet network TCP/IP.
Is iSCSI IP Based?
Yes, iSCSI is IP-based and is standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force and is described by RFC 3720.
This IP-based standard transfers data that supports host access. It allows carrying Small Computer System Interface commands via different IP networks.
What OSI layer is iSCSI?
Typically, the Internet Small Computer System Interface protocol functions on layer 5, or the Session layer of the International Organization of Standardization – Open System Interconnection (ISO-OSI) model.
Characteristically, the SCSI commands produced at the presentation layer make their way ultimately through the physical layer in order to communicate with other devices via iSCSI.
What is the Speed of iSCSI?
Typically, the Internet Small Computer System Interface protocol uses the traditional Ethernet switches and cables and therefore can operate at different speeds such as 1 GB/s, 10 GB/s, 40 GB/s, and sometimes more.
Do People Still Use iSCSI?
Yes, people still use the Internet Small Computer Systems Interface data transfer protocol because most of the infrastructures available today depend on the iSCSI standard to link the storage with the servers.
This is the network version of the bus SCSI protocol and helps to transmit the SCSI commands over the TCP/IP network to provide the users with block-level access to the shared and centralized storage devices.
Conclusion
iSCSI is a useful data transfer and storage protocol. It offers reliable, predictable, and improved performance.
Its popularity has grown because of the rising need for better traffic congestion management and Quality of Service (QoS) and the need for faster speeds on Ethernet switches.