“Antimalware Service Executable” runs on your computer and actively scans out all the corrupted files, viruses, and even more. Thus, it eats up loads of CPU. Let us see what are the main reasons.
In This Article
6 Reasons Why Antimalware Service Eat CPU (with Fixes)
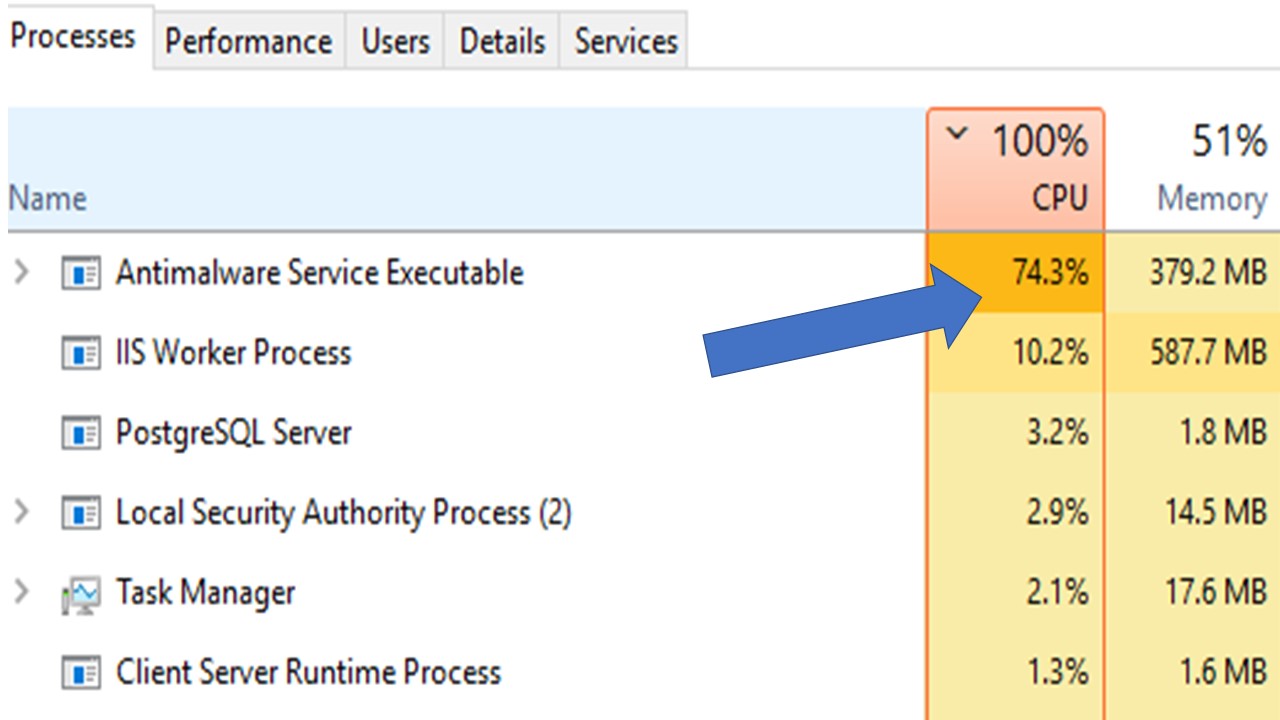
Listed below are the reasons why your CPU might be experiencing high CPU usage due to antimalware service.
1. File Corruption Detection Feature
If you have noticed antimalware service consuming higher CPU processing power than it normally would, you should start by checking for corrupted files. Since, if Windows Defender files are corrupted they might try to consume more CPU power.
Solutions:
To check for corrupted files, you have two options, you can either use a third-party repair program or choose Windows’ inbuilt repair install procedure.
Third-party repair programs are created to automatically scan your system files once they are installed on your system.
Some might ask for permission before rectifying the underlying issue, while others might automatically make minor modifications to fix your system files.
Once your Windows installation issues are fixed you can easily track CPU usage through the Task Manager window.
The repair install procedure of Windows replaces corrupted system files efficiently without affecting your data, documents, applications, games, and other files.
Once you have confirmed that your high CPU usage is caused by corrupted system files, you can move on to check the next option on this list.
2. High Task Frequency Feature
Numerous individuals who have suffered from this issue often report this reason being the main cause in their case, so check task frequency for antimalware service. Since this program has an administrative task that runs in frequent intervals.
Solutions:
Open Task Scheduler through the Task Scheduler utility which can be found under the Administrative Tools category.
Under the Windows Defender option, you will see its scan task and reduce its frequency to once a week or once a month.
Do this only if you are using a low-end or old CPU as newer models and high-end CPUs might not have a problem with a higher frequency.
3. Protecting Overlapping Security Systems
If you are using an antivirus service offered by a new or small company that is still not recognized by Windows, Windows Defender remains active at the same time as this antivirus application.
Solutions:
You need to manually turn off Windows Defender in your system, so start by accessing the Gpedit utility. Now, click on Ctrl+Shift+Enter to gain admin access while entering Local Group Policy Editor.
Under the Computer Configuration option on your left side menu, go to Administrative Templates, then choose Windows Components and then go to Windows Defender.
In its central pane, double-click on the Turn Off Windows Defender option. Once you disable it restarts to save this option.
4. Antispyware Function
Windows 10 community insiders say this issue may be caused by a registry key that is still disabled even though Windows Defender is no longer active antivirus.
Solutions:
To resolve this issue, you need to open the Registry Editor and change the value data of the DisableAntiSpyware key.
This method only works if Windows Defender is the active AV solution on your computer or was recently disabled without being replaced by another AV suite.
Typically, when a new third-party antivirus program replaces Windows Defender, Windows Defender’s anti-spyware features are automatically disabled.
5. Malware Function
Ironically, high CPU usage by the MsMPEng.exe security file can also indicate a virus infection. MsMpEng.exe file may be disguised malware masquerading as a system process gaining access to system resources.
Solutions:
To make sure that is not the case, you should run a thorough scan with a reputable anti malware program.
Once this scan is complete, remove all infected instances as instructed, restart your PC, and reopen Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) to see if the CPU usage related to MsMpEng .exe has dropped.
6. Self-scan Feature
This may seem strange, but many users reported that CPU usage dropped noticeably after adding MsMpEng.exe to Windows Defender’s exception list.
Solutions:
This works if Windows Defender is re-enabled for an extended period after another third-party antivirus was enabled.
Some malicious programs are known to disguise themselves as Msmpeng executables to avoid detection by security suites like Windows Defender, so Windows Defender (or another third-party antivirus) can also continuously scan files and give false positives.
If you are sure your computer is not infected, don’t worry. This is probably a false positive and somewhat common on Windows 10 (when Windows Defender is used by default).
If this scenario applies to you, just add the MsMpEng.exe file to the exclusion list and immediately see how CPU consumption is reduced.
Another effective method to reduce your computer’s antimalware service CPU usage is to install third-party antivirus software.
Once an active antivirus or antimalware system is running in your system, your system’s antimalware service assumes the role of a background program and only needs to monitor your antivirus program rather than your complete system.
Therefore, its usage is significantly lowered.
Conclusion
Now that you know why antimalware service eats CPU and the steps to prevent it from consuming too much of your CPU’s power, you can effectively choose between installing and running third-party antivirus software or letting your system’s inbuilt antivirus mechanism protect your system.
Compare CPU usage levels in both cases before making a decision.