The performance of the storage solution will highly depend on the particular connectivity standard.
While choosing between two given options such as SATA and mSATA, it is elementary that you make a comparison between them considering all their aspects.
This means that you will need to know the differences between them to start with.
In This Article
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Serial ATA typically comes in a 2.5 inch casing but the Miniature SATA comes with a much smaller form factor like a business card and therefore can be used in smaller devices.
- SATA is an older technology and is typically used in Hard Disk Drives, Solid State Drives and optical drives as opposed to mSATA that can be used in notebooks, printers and even in small handheld electronic devices.
- The read speed of SATA is just a tad slower than the read speed of an mSATA equivalent but the write speed is a bit higher in comparison to the write speed of mSATA.
The 8 Differences Between SATA and mSATA
1. Year of Release
Serial ATA was released in 2000.
On the other hand, the SATA-IO was first developed in 2009, nine years later which makes it a more modern technology than Serial ATA.
However, the mSATA specification came out in 2011 as a part of SATA Revision 3.1.
2. Full Form
SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, which is also referred to as Serial ATA most of the time.
On the other hand, mSATA stands for Miniature Serial Advanced Technology Attachment.
3. Size
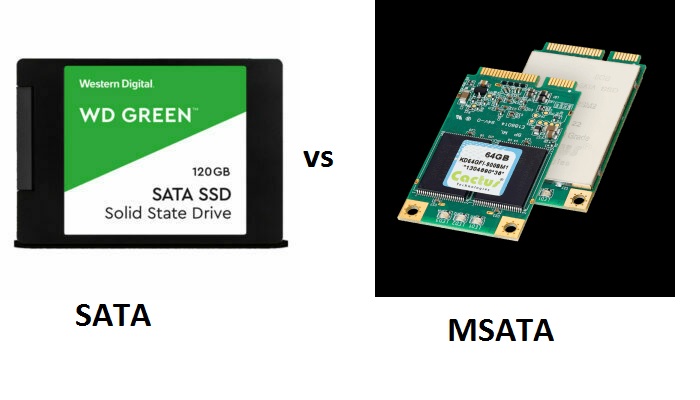
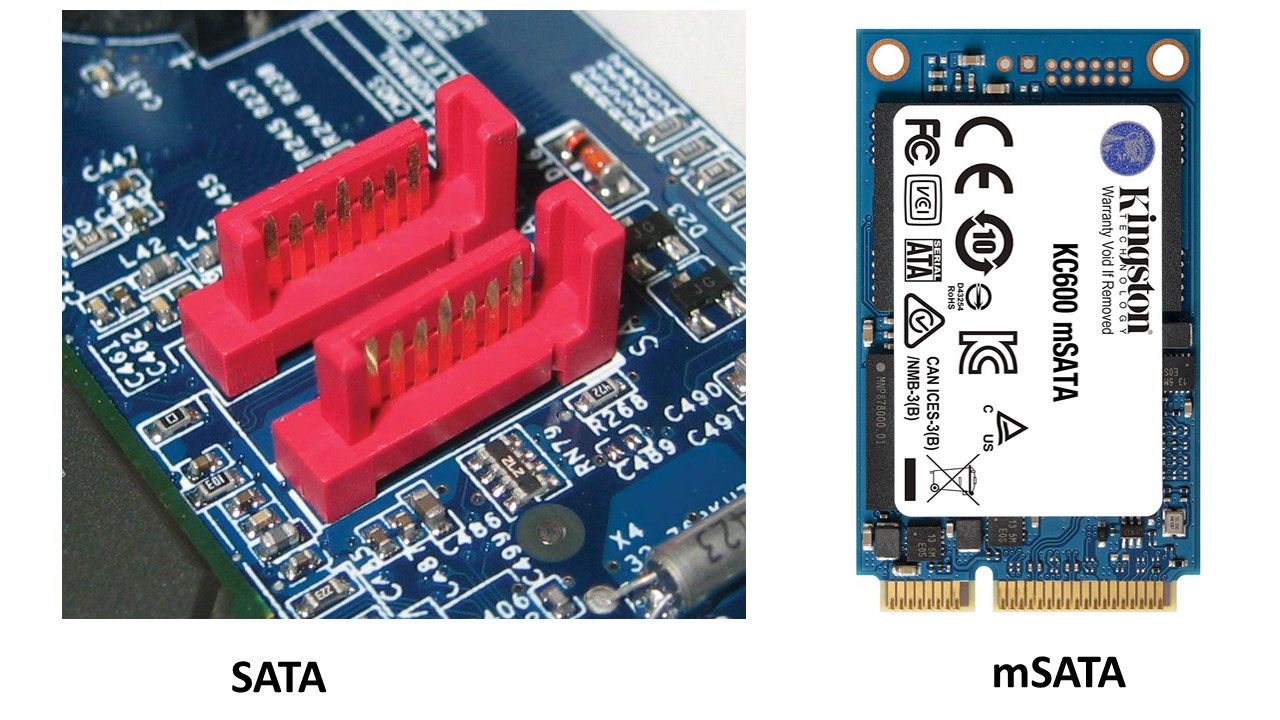
SATA comes encased in a 2.5 inch casing and therefore it is much thicker in comparison to the mSATA. Therefore, it can be fitted only in the larger devices.
mSATA, on the other hand, is specifically designed to come in a much smaller form factor. The size of the mSATA can be as small as a business card.
4. Design and Looks
Typically, the SATA drives come with an outer casing.
However, the mSATA drives usually do not feature any outer casing at all.
This means that the mSATA drives look just like an Integrated Circuit or IC.
5. Used in
SATA, due to its form factor, can be used in optical drives, Hard Disk Drives or HDDs, and Solid State Drives.
mSATA, on the other hand, can be used in much smaller devices such as notebook computers, printers, retail kiosks, and other smaller electronic handheld devices that have power constraints.
6. Capacity
Though storage capacities are determined by the drive and not by the connector itself, the SATA drives usually offer larger storage capacity in comparison to the mSATA drives.
On the other hand, due to the smaller form factor of the mSATA drives, they come with much smaller storage capacities in comparison to any full size SATA drives.
7. Temperature Grade
The temperature grade of the SATA is commercial, industrial and military but, in comparison, the temperature grade of mSATA is only commercial and industrial.
8. Read and Write Speed
The read and write speed of the 2.5 inch SATA ranges between 510 MB/s and 550 MB/s and 430 MB/s and 530 MB/s respectively.
On the other hand, the read and write speed of mSATA ranges between 540 MB/s and 550 MB/s and 420 MB/s and 520 MB/s respectively in comparison to a 2.5 inch SATA..
Which is Better to Use – SATA or mSATA?
Just like any other product, making a choice between SATA and mSATA will also depend on your needs and preference.
And, of course, on the points that differentiate one from the other which are mentioned above.
Still, finding out which one among SATA and mSATA is better will need some more information.
You will find those necessary facts below.
Normally, mSATA drives come in two different variants.
If you are looking for reliability in storing data, you should go for the mSATA drives that come with SLC or Single Level Cell flash but the capacity may not be very high.
On the other hand, those drives that come with MLC or Multi-Level Cell flash will offer you more storage space but less reliability.
However, the SATA drives will offer much more capacity in comparison to the mSATA drives of both types.
But, to the SATA drives the distinction between SLC and MLC is also applicable.
Serial ATA is considered to be the successor to the earlier Parallel ATA or PATA standard and has now become the most dominant interface that is used in most of the storage devices.
It is the most successful and popular bus interface of the computer which allows connecting the bus adapters of the host with different types of mass storage devices.
The mSATA also refers to the interface and both these match with the interface specification developed by the Serial ATA International Organization or SATA IO.
Talking about the specifications, as well as a few other important aspects, there are a few similarities between the mSATA and SATA.
These are:
- Both SATA and mSATA designs follow all of the design specs determined by the SATA-IO
- The upper limit of the bandwidth is the same in both being 6 GB/s
- Both SATA and mSATA use Advanced Technology Attachment or ATA as the command to transfer data between the storage device and the host device and
- According to the SATA-IO specs, both SATA and mSATA must meet SATA III speed guideline which is 6 GB/s.
While you make a choice between the two, you should look at the features of each. This will make things easier.
Some of the notable features of SATA are:
- These inexpensive interfaces will offer more advanced data encryption.
- You will also be guaranteed much better power management, SMART analysis, and Power loss protection.
- Apart from large storage capacity, you will also get the benefit of using features like hot plugging to add or remove devices while your computer is running.
- You will also get to access the settings from the BIOS or Basic Input/output System software of your computer because the drive will be connected to the motherboard of the computer directly.
In comparison the mSATA offers some similar features such as a maximum bandwidth of up to 6 GB/s and data storage reliability of up to 1.5 to 2 million hours.
The SATA drives are however perfectly compatible with the desktop and laptop computers.
For smaller devices and ultra-thin laptops, something much smaller is required, such as the mSATA.
This variant, due to its smaller form factor can be easily used as 16 GB or 32 GB cache drives.
When you cache your files, it will automatically expedite the speed of performance of the system overall.
If you want to stick to mSATA, there is one specific thing that you should keep in mind.
That is, mSATA is being replaced at a rapid pace by M.2, though you will find it still in a few legacy devices and commercial products such as:
- POS or Point of Sale devices
- Digital signs and
- Multifunctional printers.
Typically, the mSATA specs describe the way SATA signals should be mapped into the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express or PCIe mini-card connector.
This enables it to be used in a much wider range of applications.
And, if you have a notebook equipped with a solid state cache you can configure it with some installation hacks in order to hook up with an mSATA drive as well.
This will give you larger space for data storage and a much speedier solid state boot drive for the operating system and other programs.
Most users switch from SATA to mSATA to gain some serious benefits in the performance of the system such as reduced wait time for completion of a task by the computer with no compromises made with the high capacity hard drive.
However, just as in all other cases, the final choice and decision is yours.
Conclusion
So, now, coming to the end of this article, you already know that the SATA and mSATA not only connect differently but there are also several other basic points of differences between them.
With this knowledge you can easily figure out which one of the two is more suitable for you.