As it is with any other computer parts and peripherals, there are some significant differences between mSATA and M.2 apart from that fact that they have a different time of release.
If you want to make a real and proper comparison between the two, it is paramount that you know the aspects in which they differ.
In This Article
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Miniature SATA or mSATA is an older technology as compared to M.2 that offers little flexibility because it can transfer data only through a SATA interface as opposed to M.2 that support PCIe and other interfaces.
- The speed of data transfer in mSATA is slower than M.2 which has a direct connection with the motherboard of the computer.
- M.2 supports high-end computing tasks such as 3D animation, gaming and video editing but mSATA is usually used in commercial products.
The 8 Differences Between mSATA and M.2
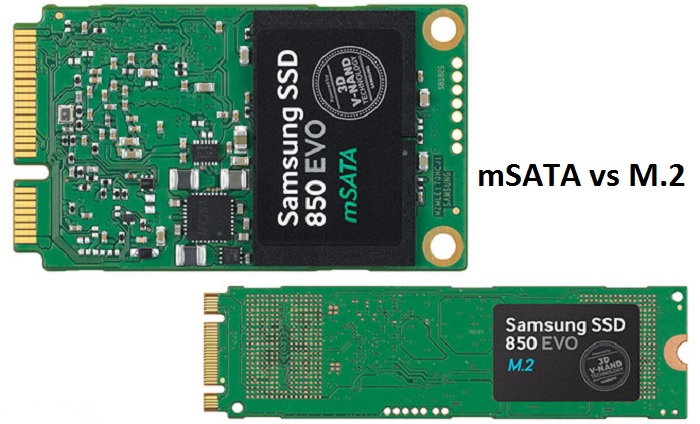

1. Full Forms
The full form of mSATA is Mini SATA but it is also referred to as Miniature STA sometimes.
On the other hand, the M.2 specification was initially known as NGFF or the Next Generation Form Factor.
However, later on it was changed to M.2, which is pronounced as m dot two.
2. Year of Release
The SATA interface, on which the mSATA SSDs are based, was released for the first time in 2009 by the Serial Advanced Technology Attachment International Organization or SATA IO.
On the other hand, the concept of M.2 was conceived and introduced for the first time under the label of Next Generation Form Factor in 2012 by Intel.
3. Flexibility
The mSATA SSDs can transfer data by using the SATA interface only and therefore are considered to be slightly less flexible in comparison to the M.2 drives.
On the other hand, the M.2 drives are more flexible because they can use a variety of interfaces such as Peripheral Component Interconnect Express or PCIe and are not restricted to SATA signals only to transfer data.
4. Speed
The mSATA SSDs are pretty slow in comparison to the M.2 SSDs when it comes to data transfer speed. Ideally, due to its reliance on the PCI Express the speed is limited to 6 GB/s.
On the other hand, the M.2 SSDs can operate at a much faster rate in comparison to the mSATA SSDs, especially the older versions of them.
One primary reason for a higher data transfer speed of the M.2 SSDs is their direct connection with the motherboard of a computer.
5. Use Cases
The Mini SATA SSDs are typically used in commercial products such as retail kiosks, digital signs, multifunctional printers, POS or Point of Sale devices, as cache drive or as a replacement of the traditional Hard Disk Drives or HDDs, and in electronic blackboards, projectors for commercial use and telephone conferencing systems.
It is widely used in highly portable devices such as laptop computers, netbooks, and tablets.
On the other hand, M.2 SSDs can be used for upgrading or building a computer and also in small portable devices such as the ultrabooks and tablets.
Its use cases also include gaming, video editing, 3D animation, and even in transferring large data files.
6. Dimensions
The different dimensions of the Mini SATA SSDs include a width of 30 mm and a length of 50.95 mm.
The total space (length x breadth) of the PCB or the Printed Circuit Board of it is usually 1528.5 mm.
On the other hand, the width of the M.2 SSD is typically 22 mm while the length can vary and be 30 mm, 42 mm, 60 mm, 80 mm, and 110 mm.
Therefore, quite naturally the total space offered by the PCB is also varied and can be 660 mm, 924 mm, 1320 mm, 1760 mm, and 2420 mm.
7. Storage Capacity
In terms of storage capacities, most of the Mini SATA drives will come with a total storage space of about 500 GB.
On the other hand, most of the M.2 SSDs will come with a much higher storage capacity.
A few specific models of the M.2 Solid State Drives can come with as high storage as up to 1 TB.
8. The Cost Factor
Due to the design and performance, storage capacity, speed of data transfer, all of which are lower of a MINI SATA SSD in comparison to an M.2 SSD, the cost of it will also be relatively low.
On the other hand, all the benefits offered by the M.2 SSDs such as a better design, higher storage and better performance comes at a high price.
Therefore, it will cost you much more in comparison to the Mini SATA SSDs.
Which is Better to Use – mSATA or M.2?
If you are looking for high performance storage devices then both Mini SATA and M.2 SSDs will meet your needs successfully.
Both these drives are designed to perform well in the devices that come with a small form factor such as notebooks and others.
However, the ignorance about the differences between these two storage solutions confuses people when it comes to choosing one between them to use.
Now, with the differences mentioned above known to you, it should not be the case with you anymore.
Still, apart from that mystery unveiled, there are also a few other facts to know in order to make a more accurate and comprehensive analysis of Mini SATA SSDs and M.2 SSDs and choose the right one among them.
And, here they are.
With the use of the PCI Express Mini connectors and physical card layout, the M.2 SSDs offer much more flexibility in physical specifications and also allow different module lengths and widths along with more sophisticated interfacing features.
And, as said earlier, it is also more flexible in terms of interfaces used to transfer data.
Ideally, the M.2 SSDs are considered to be more suitable in comparison to the mSATA SSD applications typically when it comes to smaller computing devices such as ultrabooks and tablets.
You will typically get three type of M.2 such as:
- NVMe – This stands for Nonvolatile Memory Express or NVM Express and was designed specifically for use in the next generation SSDs. The regular NVMe SSDs typically use standard PCI Express connections for the motherboards used in desktops but those with M.2 form factor use a different connector.
- SATA – This specification uses the AHCI or Advanced Host Controller Interface driver. It typically directs to a SATA 3.0 port through the M.2 connector. These devices are usually slow but are widely compatible.
- AHCI – This is for the low budget motherboards and is also quite slow which is why it is more suitable for the older operating system. The SSDs that use AHCI usually perform more like a DRAM or Dynamic Random Access Memory rather than a regular hard drive.
The M.2 provides the computer bus interfaces and it is up to the M.2 module or host manufacturer to determine which particular interface to support. However, it depends on two specific factors such as:
- The type of the device and
- The level of host support desired.
The keying notches of the M.2 connector refer to the diverse capabilities and purposes of the devices as well as the M.2 hosts, both.
These key notches are unique for the M.2 modules which prevent them from being inserted into any host connector that is not compatible with it.
One of the most unique features of the M.2 SSDs is that these also support SATAe or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment Express.
This is also referred to as the SATA 3.2 reversions.
This allows the M.2 SSDs to connect to either SATA or a PCIe interface since the SATAe will tell it whether the host computer supports a SATA or a PCI Express interface.
However, there are a few significant downsides of using an M.2 SSD. For example:
- If the motherboard supports an M.2 SSD but relies on PCI Express, the data transfer speed may be limited to 6 GB/s.
- When an M.2 SSD is connected to the PCI Express bus, it cannot be used as the primary drive of the system.
These issues can be reduced by a significant extent when you use a relatively new main board in your computer.
That is why it is advised that you check your hardware before you choose a particular type of a storage solution between a Mini SATA and an M.2 SSD.
At this point you should know that the design limits of the motherboard of a computer will restrict the interaction of the M.2 device with the rest of the computer system.
And, since the PCI Express bandwidth is itself limited, adding an M.2 SSD will surely work with other hardware.
Therefore, make sure that you check the documentation of your motherboard before you make your final decision so that the setup is not affected adversely when you add an M.2 SSD.
On the other hand, the mSATA SSDs, in spite of the small form factor, offer a reasonably good amount of storage capacity while using a much smaller footprint.
It supports SATA interface but it will mainly depend on the product type as to whether it will support one or all three of the SATA interface specifications.
On this particular factor it will depend whether the performance of it will be offered at 1.5 GB/s or anywhere in between that and 6.0 GB/s.
Therefore, your choice will mainly depend on whether you need a commercial application or an industrial application.
You can go for a lower cost Mini SATA device that comes with Multi-Level Cell or MLC NAND memory.
However, these types of storage solutions will have much lower endurance and will also offer a lower number of write cycles for every logical block.
When it comes to compatibility, it is comparatively pretty simple in the case of the mSATA form factor.
However, the only issue with it is that you cannot insert these particular drives into a Mini PCI Express slot that does not support Mini SATA if the motherboard does not support it in the first place.
If you do not like to spend a lot of money on any storage solution that has a lot of power and loads the files at a much slower rate, as it is in the case with the hard drives, a Mini SATA SSD is just the right choice for you.
Finally, take a look at the pros and cons of the Mini SATA and M.2 SSDs over traditional SSDs to make the right choice.
The advantages of using an mSATA SSD over standard SSDs include:
- A less expensive solution
- A small form factor
- Much lower power consumption
- Faster read and write speed of up to 551 MB/s and 304 MB/s respectively
- A higher storage capacity
- Much higher shock and vibration resilience and
- Good compatibility with a variety of devices.
On the other hand, the advantages of an M.2 SSD over the traditional SSDs are pretty much the same with the addition of light in weight and long lasting.
As for the downsides Mini SATA SSD over traditional SSDs, the list includes:
- The higher price
- No notable difference in performance since both operate on the same SATA III speed
- Need for a distinct Mini SATA connector and
- A limited PE or Program/Erase cycle.
On the other hand, the downsides of the M.2 SSDs as compared to the traditional ones are its numerous complications that result in compatibility issues with the computer hardware and motherboard.
Now, with all that said, your knowledge about the M.2 SSDs and the Mini SATA SSDs are more or less complete.
Conclusion
So, now with all the necessary information regarding the M.2 SSDs and the Mini SATA SSDs known to you, courtesy this article, you will find it very easy to make a choice between these two given storage solutions and get higher returns and performance.