In This Article
What is Daughterboard?
A daughterboard refers to a specific type of printed circuit board or PCB that can be plugged into another PCB such as the motherboard or any other card like sound card or any other board that is already installed in the computer system.
Technically it is a computer hardware that acts as a secondary circuit board in a computer system which extends its circuitry.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- A daughterboard is an expansion or a circuit board that plugs into the motherboard directly to expand the circuitry.
- Usually, these boards are released as an update after the launch of an expansion card or a motherboard.
- This board does not function like an expansion card using the bus and serial interfaces because it is embedded through soldering.
- A daughterboard just like a motherboard comes with pins, plugs, sockets, and connectors that allow connecting it to other boards.
- These boards are usually smaller in size than a motherboard and do not offer new functions but simply extend its circuitry to support its performance.
Understanding Daughterboard
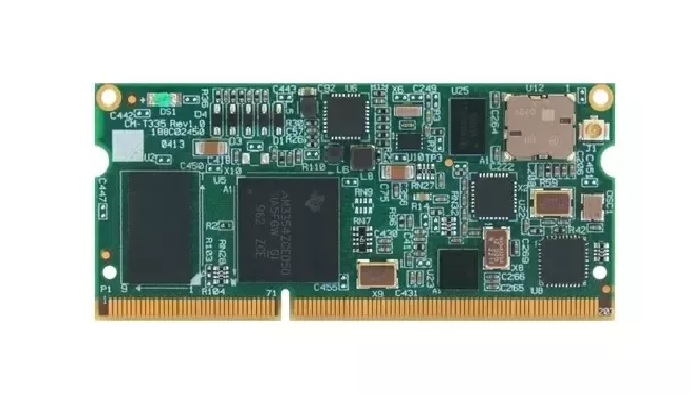

In simple terms, a daughterboard is that printed circuit board connected to the motherboard directly but is much smaller in size than a motherboard.
It can also be attached to an expansion card that does not perform as it.
This is because an expansion card adds new functionalities to the computer system whereas the daughterboard provides support to the motherboard mainly in performing its functions.
A daughterboard can be referred to in different names such as:
- A daughter card
- A riser card
- A piggyback board or
- A mezzanine board.
It is called a mezzanine board because it is installed on the second level of the motherboard in spite of being in the same plane.
Ideally, in a computer system a lot of different components are needed to be installed so that new features and functionalities can be added to it. This is usually done with the help of separate circuit boards.
When these circuit boards, which can be of different types and perform different functions, are connected to the motherboard directly they are called the daughterboards of the computer.
As said earlier, a daughterboard can even be connected to a different type of daughterboard where both perform different functions.
Ideally, there is a huge range of these daughter boards available in different categories and subcategories that can perform a wide range of functions.
Just as adding a daughterboard is ideally the simplest way to add more features and functionalities to a computer system, it is also the best possible way to expand any existing feature.
The principal feature of the daughterboard is that it is either soldered to the motherboard or is connected via a socket instead of traditional cables.
This means that an M.2 SSD or Solid State Drive is an example of a daughterboard since it is connected through a socket to the motherboard.
On the other hand, a 2.5 inch Serial Advanced Technology Attachment or SATA SSD is typically not a daughterboard since it is connected to the computer system with the help of specific types of cables.
As for the form factors of the daughterboards, as said earlier, these are smaller in size than a motherboard and those that are used in the desktop computers especially are typically designed in such a way that they stick out of the motherboard as well as away from it.
There are a few specific reasons behind designing the daughterboards in such a way. The primary reasons are:
- This design offers a lot of space to install other components on the motherboard along with other daughterboards on it as well and
- The design also helps in providing sufficient airflow required within the system to keep the daughterboard cool.
The second reason is also extremely vital for the GPU or the Graphics Processing Unit which is known to produce a lot of heat during operation.
If you consider the desktop computers, not all daughterboards designed for use in such systems are placed at right angles to the motherboard.
For example, the M.2 slot is exclusive in that sense since it is parallel to the motherboard just like the mSATA network cards.
The main intention behind this design is to ensure that this particular standard can be used properly in both a desktop computer as well as in a laptop computer system, provided cooling is not a big issue.
Talking about cooling, it is quite a serious concern for laptop computers.
It is for this reason, in these small form computers, the concept of daughterboard designing is however entirely different.
Also, since the size of the laptop case is not large and high, it will not allow using larger daughter boards because these will stick out from the motherboard.
This is extremely problematic if the manufacturer intends to design a slim laptop computer system especially.
It is for this specific reason that the laptop computers characteristically use mezzanine cards. These cards typically lie parallel to the motherboard.
However, whether a daughterboard is to be used in a desktop or a laptop computer, both these designs offer significant benefits with respect to space and cooling efficiency.
Finally, you may wish to disable a daughterboard in your computer system but mind it, it cannot be done directly.
You will have to remove it from the motherboard physically.
This means that, if it is soldered into the motherboard, you will need to remove the whole motherboard for that matter.
Daughterboard Uses
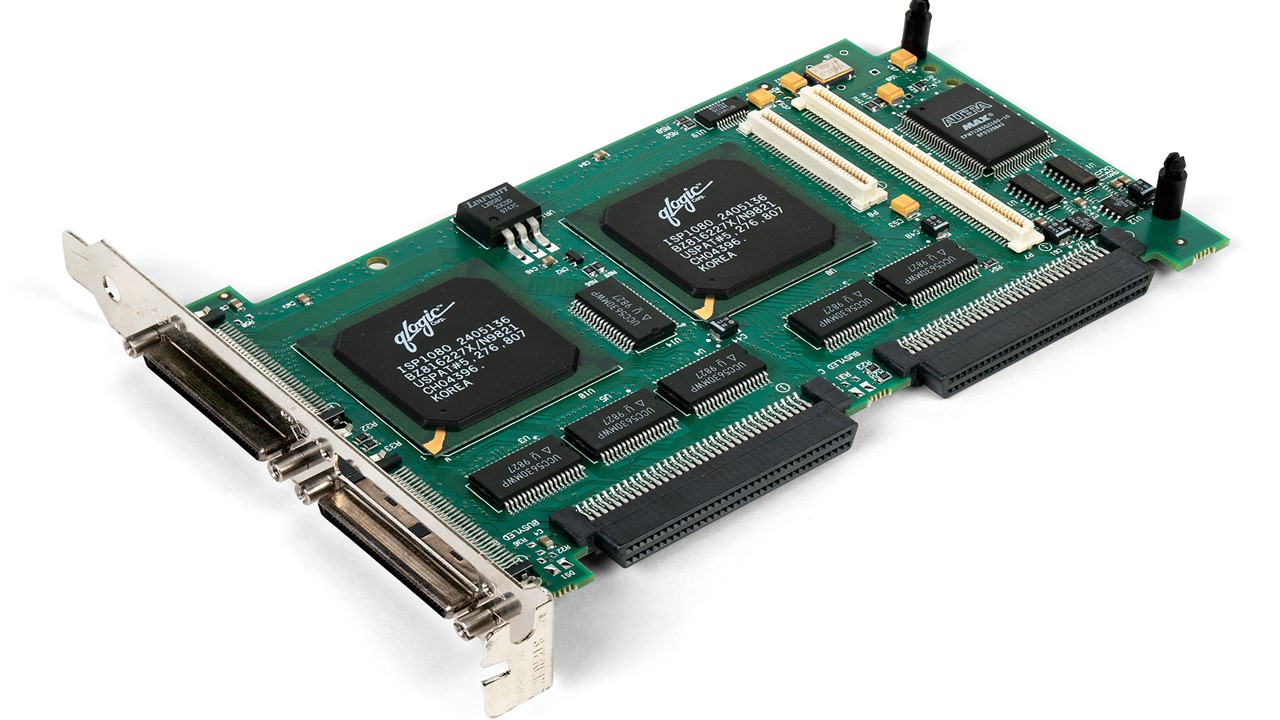
Daughterboards in the computers are used especially to fit expansion cards on it, upright or on their side and parallel to the motherboard of a desktop computer. This helps in maintaining a slim and small form factor.
In addition to that, over the years these boards can also be used to extend the fundamental functionalities of the electronic devices including game consoles and game controllers.
However, it is seldom used in desktop computers but more commonly used in the custom mechanical keyboards, both in their high-end and entry level variants.
A few streamers use a PCIe capture card for encoding the stream video which is also a daughterboard.
Types of Daughterboard
There are mainly three main types of daughterboard available with different functionalities, sizes, and capacities.
These are Memory Board, Interface Board and Interconnection Board.
Some other types of it include CPU socket daughterboard, Bluetooth daughterboard, and Network Interface Controller or NIC daughterboard.
Daughterboard Examples
Any circuit board that is connected directly to the motherboard by soldering and enhances it circuitry but are not expansion cards using the bus and other serial interfaces can be an example of a daughterboard.
Some common examples of daughterboard are:
- The sound cards that are not the onboard audio cards
- The RAM modules if these are not soldered to the motherboard directly
- The modems
- The RAID or Redundant Array Of Independent Disks cards
- The video capture cards
- The I/O cards
- The M.2 storage devices
- The TPM or Trusted Platform Modules and
- The DRAM or Dynamic Random Access Memory sticks.
Even a MIDI daughterboard that is used to enhance the functionality of a sound card can be considered to be a daughterboard.
However, modern computers seldom come with a daughterboard but it was very commonly used in the past.
Daughterboard and Motherboard
- Daughterboard is an expansion board connected directly to the motherboard to improve its functionality but motherboard is the main circuit board of the computer system which is also known as the system board
- Motherboard acts as the base to connect all other components of the computer system and performs the core functions by interconnecting the rest of the components and daughterboard is a specific part on it and
- The daughterboard normally performs the non-essential functions of the computer system because it is logically functional if it is not a CPU but a motherboard performs the fundamental operations.
Is GPU a Daughterboard?
Ideally, going by the definition and functions of a daughterboard, it is a separate circuit board that is joined to the motherboard and performs few functions of the motherboards. Considering that, a GPU or Graphics Processing Unit is not a daughterboard.
However, looking at it in a different way, the card that adds to the USB ports but is not an expansion card can be considered to be a daughterboard.
Technically, the graphics card is one type of daughterboard anyway but usually all the components in it are soldered to it already and it is sold as a single package.
So, in the true sense, this does not make a graphics card a daughterboard even though a few specific manufacturers design custom printed circuit boards that do not follow the reference design of motherboard from NVIDIA, for example, but their own design.
However, the graphics chip still remains the same.
Is RAM a Daughterboard?
Typically, a Dual inline Memory Module or DIMM RAM is perhaps the best and most common example of a daughterboard. It allows high speed access to the RAM by connecting through a socket placed near the Central Processing unit or CPU of the computer.
For that matter, you can say that even a CPU is a daughterboard because the die is placed on a small printed circuit board and is connected to the motherboard directly through a socket.
What is a USB Daughterboard?
A USB daughterboard refers to a board that is equipped with USB Type C and is built to fit into the Unified Daughterboard project of ai03 and other contributors.
This is an open-source daughterboard designed according to the standard dimensions and specifications of several keyboards.
This specific type of daughterboard comes with the following features such as:
- A JST SH 4-pin connector
- Unified daughterboard with ESD Protection and
- A fairly long cable with heat shrinks protection over most of it.
Are Daughterboards Used Today?
Typically, the daughterboard is not found in desktop computers today.
This has been replaced with several other different on-board options such as Peripheral Component Interconnect or PCI cards, ISA or Industry Standard Architecture cards and more.
However, you will find it to be used in a few laptop computers.
What is Unified Daughterboard?
The Unified Daughterboard actually refers to the project or attempt made by the major designers of the mechanical keyboard sector to homogenize the Universal Serial Bus daughterboard so that these can be used as custom mechanical keyboards.
The chief attributes of this specific type of daughterboard is an integrated USB Type C connector into the chassis of the motherboard along with the required circuitry that will support USB 2.0 operation in a miniature Printed Circuit Board.
The most significant benefit of this characteristic feature of the daughterboard is that it simplifies the assembly and the design of the primary circuit board quite significantly.
The latest daughterboard version is named C3 and comes with specific features as follows:
- Electrostatic Discharge or ESD protection offered to the data lines of the USB connector with the help of a special chip
- A PTC or Positive Temperature Coefficient fuse or thermistor to protect from over-current
- A bidirectional TVS or Transient Voltage Suppressor diode for protection against overvoltage
- A ferrite bead that shields noise decoupling
- Single-path grounding for the daughterboard attached to the metallic chassis and
- Backward compatibility with both C1 and C2 versions having the same dimensions, positions and screw hole sizes.
The ESD protection not only makes the daughterboard safe to use but also makes it super fast offering very low capacitance.
When there is a sudden spike in the voltage in one of the data lines passing through the USB Type C connector, the chip grounds it immediately and therefore protects the circuit carrying the data from damages.
The resistors are actually CC or Carbon Composition resistors that help the USB host to know which side of the connector is connected as well as recognize it as a downstream device.
The TVS diodes protect the power rails or the forward circuitry of the connector when there is a spike in voltage by shorting Voltage Common Collector or VCC and ground.
The ferrite bead avoids noisy currents travelling through the signal ground by presenting very low impedance between the signal ground in the DC schedule and the power ground and a high impedance while experiencing high frequencies in an ESD event.
There are four screw holes in the daughterboard to attach it to the metal chassis where the top left one is shorted to the power ground signal.
This grounds the metal chassis of the board.
The other three screw holes, on the other hand, are not shorted and are instead isolated from it.
This offers a single path to the discharge current through the board to the power ground when a discharge event happens while the user provides charge to the system.
There is also an inductor in the design that keeps the discharge current in the power ground plane and prevents it from reaching the signal ground.
Conclusion
After reading this article you must be more familiar now about the daughterboard and its types, uses, as well as its difference from the motherboard.
Depending on the insights you can now easily make your decision whether or not you should use it or remove it from the motherboard, which however is to be done physically.