In This Article
What is Whiskey Lake Processor?
Whiskey Lake is a microarchitecture that is used in some of Intel’s 8th generation and 9th generation processors.
These processors are primarily used in laptops and other portable devices, and are known for their low power consumption and improved performance compared to previous generations.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Launched on August 28, 2018, the Intel Whiskey Lake processors typically come with 2 to 4 cores and a lot of technology support.
- The features of these CPUs are much more improved than the previous generations, which make these processors fit for use in IoT and similar applications.
- The Whiskey Lake processors will offer high computing and graphics performance along with enhanced video capabilities to enhance media and video consuming experience for the users.
- These processors are offered under different brand names or families such as Intel Celeron, Intel Pentium, Intel Core i3, Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i7.
- The cores of the Whiskey Lake processor can operate at quite a high speed, often hitting the CPU clock up to 4.8 GHz.
Understanding Whiskey Lake Processor
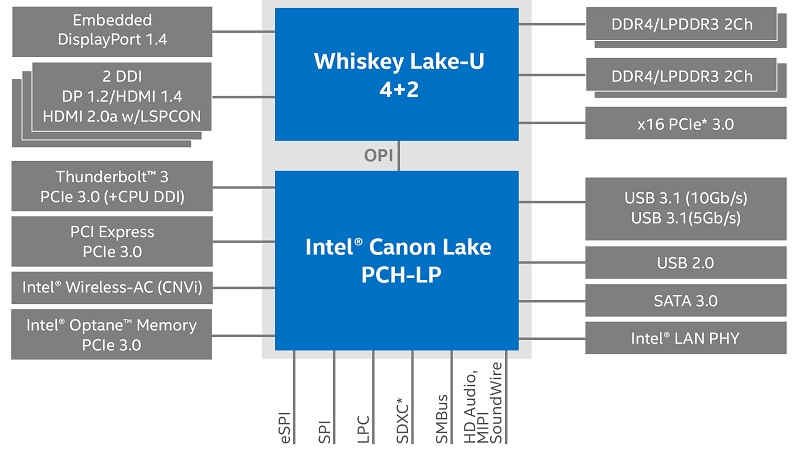
The 8th generation Whiskey Lake processors are fit for IoT applications and embedded use conditions, especially the U series processors.
These processors come with rich features that offer high performance per watt ratio.
The Whiskey Lake processors were launched by Intel on August 28, 2018. With 2 to 4 cores and Intel vPro technology support, these processors come with improved I/O capacities and DDR4 2400 memory support.
These processors have all the features needed to meet all graphics, computing and audio needs.
Some of the significant features of the Whiskey Lake processors are:
- Intel Distribution of OpenVINO and other software optimized tools for more application and data consolidation
- Intel System Studio which helps in developing and accelerating vision applications such as facial recognition, object detection, and people counting
- Intelligent solution development and future-proof platform with considerable ecosystem support
- Video transcoding for more immersive media and graphics performance with smoother streaming 4K content with enhanced audio playback and speed recognition and others on multiple displays
- Better connectivity options with high-speed Gigabit Wi-Fi, Thunderbolt 3
- Better I/O for faster data movement from the devices to any destination such as on-premise server, network video recorder, the cloud, and others
- Intel Optane memory support to enhance and streamline the performance by connecting different displays, cameras, storage and graphics cards to the same device without any bottlenecks during data transfer
- Remote manageability with Intel Active Management Technology, which helps in streamlining operations and creating a steady approach that helps in managing a wide spectrum of devices connected in a network.
General information:
- Maximum CPU clock rate – 4.8 GHz
- Technology node – 14 nm Tri-Gate transistors
- Architecture – 86-64
- Microarchitecture – Skylake
- Number of cores – 2 to 4
- Socket – BGA 1528
- Brand names – Intel Celeron, Pentium, Core i3, Core i5 and Intel Core i7
- Predecessor – Kaby Lake Refresh mobile processors
- Successor – Ice Lake and Comet Lake processors
Instruction sets and extensions:
The Intel Whiskey Lake processors support x86-64 and Intel 64 and their various extensions such as:
- MMX or MultiMedia eXtensions
- AES-NI or Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions
- CLMUL or Carry-less Multiplication
- FMA3 or Fused Multiply Add
- RDRAND or Read Random
- SSE or Streaming SIMD Extensions, along with all its variants such as SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4, SSE4.1, and SSE4.2
- AVX or Advanced Vector Extensions, along with AVX2
- TXT or Text File extension
- TSX or Transactional Synchronization Extensions
- SGX or Software Guard Extensions
- VT-x and VT-d or Virtualization extensions
- MOVBE or Move Data After Swapping Bytes
- POPCNT or Population Count
- FSGSBASE instructions for FS and GS segment registers
- F16C or 16-bit floating point conversion instructions
- BMI or Bit Manipulation Instructions along with BMI2
- RDSEED or Read Random SEED
- ADCX or Add-Carry Instruction Extensions
- PREFETCHW or Prefetch Data into Caches in Anticipation of a Write
- CLFLUSHOPT or Flush Cache Line Optimized
- XSAVE or Save Processor Extended States
- MPX or Memory Protection Extensions
Pipeline:
The pipeline in the Whiskey Lake processors has 14 to 19 stages and is able to support the following:
- Out of order Executions
- Speculative executions
- Register renaming
- 5-way decoding
Cache:
The Whiskey Lake processors come with Level 1 instruction and data caches, Level 2 and Level 3 caches as follows:
The Level 1 instruction and data caches are:
- 8-way set associative and
- 32 KiB per core.
The Level 2 cache is:
- 4-way set associative and
- 256 KiB per core.
The Level 3 cache is:
- Up to 8 MB and
- Up to 16-way set associative.
Compiler support:
The processors also support different arch specific and arch favorite compilers such as:
- ICC or Intel C Compiler
- GCC or GNU Compiler Collection
- LLVM or Low Level Virtual Machine and
- Visual Studio.
A few other specifications of the top-line Whiskey Lake processors are as follows:
- Generation 9.5 Intel Graphics GT2
- Integrated Gen 2 USB 3.1
- Intel Smart Sound Technology
- Intel Turbo Boost Technology 2.0
- Intel Media SDK
Whiskey Lake vs Coffee Lake
- The Level 3 cache of the Whiskey Lake processor is shared and measures up to 8 MB, but in comparison, the Level 3 cache of the Coffee Lake processor is also shared, but it can be up to 16 MB.
- The number of cores in the Whiskey Lake processors can be 2 to 4, but in comparison, the number of cores in the Coffee Lake processors can range anywhere between 2 and 8.
- The socket type used in the Coffee Lake processor is a BGA 1528. On the other hand, the type of socket used in the Coffee Lake processor is an LGA 1151.
- The brand names of the Whiskey Lake processors are Intel Celeron, Intel Pentium, Intel Core i3, Core i5, and Core i7. On the other hand, the brand name of the Coffee Lake processors includes all of these along with the Intel Core i9 and the Intel Xeon.
- The successors of the Intel Whiskey Lake processors are Ice Lake and Comet Lake processors, but in comparison, the successors of the 10 nm Cannon Lake and 14 nm Whiskey Lake mobile processors of the same generation as well as 10 nm Ice Lake mobile processors and 14 nm Comet Lake desktop processors.
What Generation is Intel Whiskey Lake?
The Intel Whiskey Lake processors belong to the 8th generation of Core U series processors used for IoT applications.
These are feature-rich processors that offer high performance per watt.
The Whiskey Lake low-power mobile CPUs, however, belong to the 3rd generation of processors built on 14 nm Skylake microarchitecture.
Conclusion
So, that is all about the basics of Intel Whiskey Lake processors which are quite useful for doing several computing tasks.
These processors come with rich features and support a wide variety of technologies which further helps in enhancing their performance and functionalities.
