In This Article
What is Base Clock Speed in Processor?
The base clock speed refers to the default or guaranteed clock speed of the processor when it is adequately cooled and used for typical and not peak operation.
Technically, the base clock speed is an indicator that represents the number of cycles the processor can complete in a second and is typically represented in gigahertz.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The base clock speed, also called the clock rate, CPU frequency or PC frequency, says how fast the processor can move each bit or process data.
- Base clock frequency is the indicator of the baseline or minimum clock frequency when the processor is used for minimum workloads.
- The base clock speed can be increased depending on the architecture of the processor and its features but it may not be always significant or effective.
- The base clock speed of the desktop processors is usually higher than a typical laptop processor.
Understanding Base Clock Speed in Processor
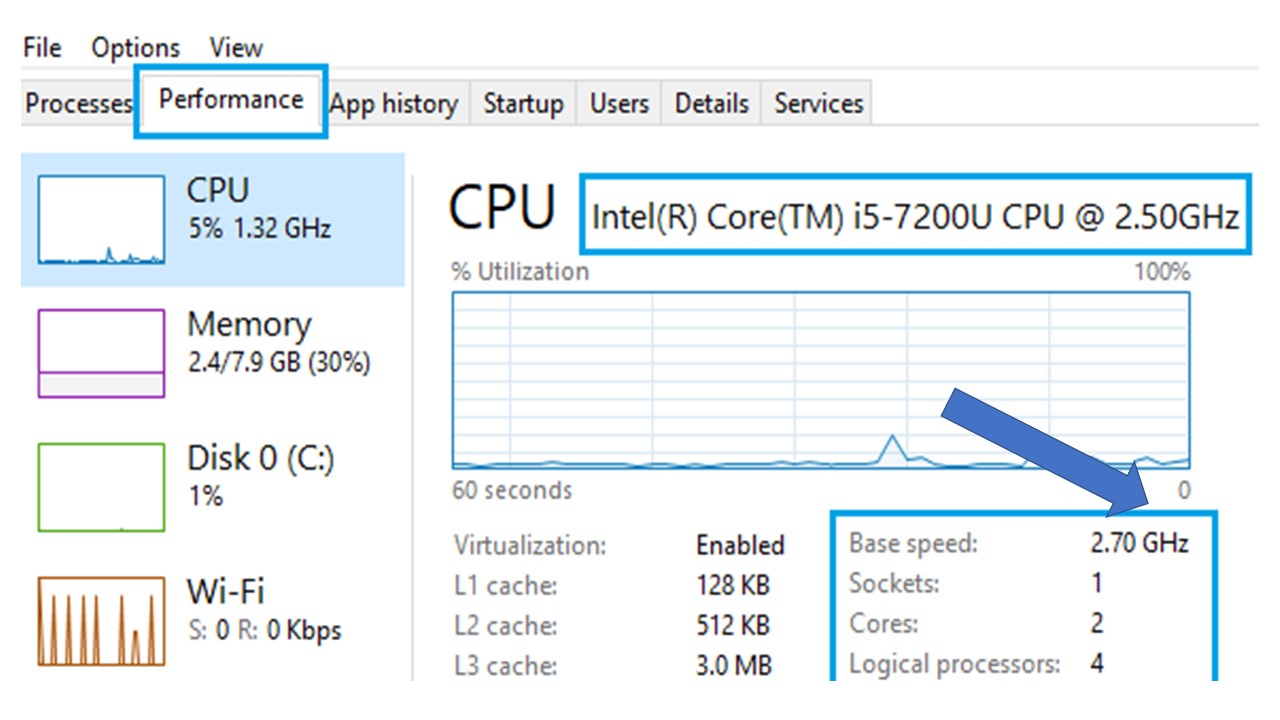
The base clock speed of a CPU is actually the measure which indicates exactly how many cycles the processor can perform in one second.
To define it in a way that any layman would understand, it can be said that the base clock speed of a processor is the minimum speed of operation of the cores in it.
Technically speaking, the base clock speed implies using the hardware fully at the declared clock speed but not using at its peak so that it does not violate the TDP or Thermal Design Power.
To explain it in more complex terms it can be said that the base clock speed, often referred to simply as BCLK speed as well, is the frequency at which the processor of the computer communicates with the northbridge or the southbridge, which are often called the ‘partner’ chips, around it.
The main purpose of using the base clock speed is to have a baseline or reference line of speed of the processor in a computer system.
Depending on the architecture and features of the processor, the base clock speed can be increased, though it would not be remarkably effective always.
Typically, technical persons refer to it as a kind of ‘heartbeat’ of the motherboard.
This means that it is the frequency at which the heart of the system that consists of the motherboard and its supporting chips are beating.
Base clock frequency also signifies the effective minimum clock frequency at which the cores of the CPU are supposed to operate when the system is sufficiently cooled.
When it comes to power savings, the base of it will be the lowest of the CPU clock speed.
However, when you use the system in the highest performance mode typically while using any heavy software or playing games, the highest will be when you use the maximum of the CPU clock speed.
However, at times, it may depend on the number of tasks you perform on your system or process or programs that you run on your system.
The more tasks you perform or the more resources you use, you will need higher clock speed.
Most people often mix up the base clock speed of the CPU with its idle clock. However, these two are not the same thing.
The primary reason for it is that this will be down-clock or under-volt far below the base clock speed. This is done typically to save power.
At this point, you may wonder why exactly the base clock speed of the processor varies so much across different microprocessor models and even in a particular CPU. Well, there are several reasons for it.
First of all, the primary intention to create different varieties of models is to build market segmentation.
This is deliberately done in order to legitimize the diverse price tags of the CPUs and at the same time ensure that these are offered to a large range of users who typically look for different price points.
Now the clock speeds of the CPUs, both the base clock speed and boost clock speed, are set by the different manufacturers differently by using a process called binning.
This is also done in the case of the number of cores and threads of a CPU.
Moreover, the silicon chips manufactured are not always perfect.
Still, those that are pretty near-perfect usually are able to get into higher clock speeds and even then stay within the power budget that was set previously.
Therefore, the near-perfect silicon chips can be designed into processors that have excellent base clock speed and boost clock speed.
On the other hand, those silicon chips that are far from perfect can only manage to get to a much lower clock speed inside the equivalent power envelope.
These particular products can only be designed into a cheaper SKU which has much lower base clock and boost clock speeds.
While that is the reason for the variance in the base clock speeds and boost clock speeds of different CPU models, as for their differences within the same CPU, the primary reasons behind it are:
- Ambient temperatures
- Thermals
- Workload and
- Power delivery.
The base clock speeds, and also the boost clock speeds, of the CPU also vary due to devices in which it is used.
For example, a CPU used in a laptop computer will have much lower base clock speed as compared to that of the CPU in a desktop computer.
This means that the CPU used in the laptop computer will not drain the battery of the laptop instantly since it will draw much less power as compared to the CPU of the desktop computer.
On the other hand, the CPUs used in a desktop computer have a higher base clock and boost clock speeds because these usually have much stronger PSUs or Power Supply Units that are typically not restricted by batteries.
Moreover, in the desktop computer casing, there is a lot more space available that is required to accommodate bulkier and much stronger CPU coolers.
This keeps the temperature inside the computer at a pretty low level and therefore facilitates in handling much higher clock speeds with utmost ease.
However, if you compare the CPUs of the laptop computers and desktop computers with the server CPUs and HEDT or High End Desktop CPUs, this may not be the case.
This is mainly because these specific processors come with a much larger number of cores and are designed to be extremely stable.
Also, these specific types of CPUs generally do not clock as high as any mainstream consumer CPUs.
Instead, their primary goal is to deliver higher performance within a realistic power budget.
This is facilitated by the high number of cores present in these processors that do not let it compromise with the stability.
Finally, there are different types of workloads that may perform differently, in terms of speed in particular, depending specifically on the base clock speed of the CPU installed in the computer.
The specific types of passive workloads that will be benefited to the maximum due to the higher base clock speed of the CPU include and are not limited to:
- CPU rendering
- Video rendering
- 3D rendering and
- Effect processing.
However, as a general rule of thumb, any type of work that needs multi-core processing at a very stable speed will be performed quicker and produce much better results if the CPU comes with a higher base clock speed.
Does Base Clock Speed Matter?
Yes, the base clock speed matters significantly in the performance of the computing device.
It will not only increase the speed of processing data by the processor but it will also have a notable positive effect on the power consumption and heat generation aspects of the CPU apart from that.
Though not always, higher base clock will also signify higher turbo clock and it will also generally mean a much better processor die.
However, how important is base clock speed of the CPU to you will depend on a few specific factors such as:
- The workloads of your system
- Your budget as well as
- The cooling solution of your computer.
But, remember that a higher boost clock speed of the CPU will also translate into higher single-core performance at the same time. Therefore, the choice is yours.
What is a Good Base Clock Speed?
Typically, anything ranging between 3.5 GHz and 4.0 GHz is generally considered to be a good clock speed to have in a CPU.
This will allow you to play all basic games on your computer along with a few modern titles as well, not to mention the basic and a few ‘more than the basic’ jobs that you can do on your system as well.
However, you should also not forget that the most important thing to have is a good, if not the best, single-thread performance.
This is because it will help the CPU of your computer to understand a single task and complete it in the best possible way.
But, do not mix it up with a single core processor, which is an entirely different matter.
Therefore, if you restrict your computer usage to light workloads such as sending and receiving emails, browsing the internet, and working on simple Word applications that have minimal requirements, a base clock speed of the CPU of up to 3 GHz will be enough.
However, do not go for those low-end 1.6 GHz processors.
More often than not, these processors will not be able to handle even the lightest of tasks at a time and produce the results fast.
Anything higher than that will use the Turbo Boost feature, provided the CPU is equipped with it.
Typically, you will need a CPU with a higher base clock speed than 3 GHz for high-end office or professional computing tasks, gaming or rendering.
Is a Higher Base Clock Better?
Yes, it is pretty obvious that, the higher the base clock speed of the CPU the better the performance of it will be.
So, you should go for a CPU with a higher base clock speed to be able to perform any type of computing tasks on your system.
Typically, you should go for a higher base clock speed in a CPU if having higher and more stable performance is your primary objective.
Yes, Turbo Boost technology will help in that for sure but that is designed to be invoked only in specific situations depending on the percentage of the workload and processing.
It will also run for a short period of time and you will not be able to use it consistently across different stages of data processing.
Moreover, the Turbo Boost will be used only when the algorithm that is already embedded into the memory controller of the CPU thinks there is a need for it.
You cannot fiddle with this algorithm to make use of the Turbo Boost feature as and when YOU desire, if you do not want to damage the CPU on the whole, especially that of your laptop in general.
Also, several applications and programs do not need higher CPU clock speeds to operate. This is exactly what the algorithm decides.
On the other hand, if you are more focused on better power savings, it will be better if you go for a CPU with a lower base clock speed irrespective of the Turbo Boost.
While the lower base clock speed of the CPU will save power, the Turbo Boost technology will offer a much higher performance when there is a heavy workload.
However, at this point you should also remember that, if the CPU comes with a higher base clock speed, it will naturally need more power and have a higher TDP.
This means that it will consequently guzzle more battery power of the mobile devices such as the laptop computers.
However, advanced CPUs such as those from Intel that come with its unique Turbo Boost technology as well as Windows that utilizes an exclusive power management setting will face less of these issues.
This is because these specific processors will use these features in order to determine the clock speed depending on the extent to which the processor is being stressed.
Sometimes, when it comes to performance, even a processor with a lower base clock speed can offer much better and faster performance as compared to those CPUs that come with higher base clock speeds.
This is because the performance is typically affected by the workload of the computer, or the processor to be precise. Apart from that, it also depends on other factors such as:
- Pipelining
- Superscalar execution
- Multiprocessing need and
- The architectural decisions.
All these influence the most important metric of a CPU – the IPC or the Instructions per Cycle.
Since the CPU needs to do calculations always and pretty fast in order to run the apps, it is good to have a CPU with a higher base clock speed.
This will ensure quicker completion of the calculations and the applications will also run smoother and faster as a result of this.
All in all, it can be said that the base clock speed of the CPU, even the boost clock speed for that matter as well, is just one particular aspect that will influence its performance.
Conclusion
So, reaching to the end of this article, now you know what base clock speed of a CPU is and what is the importance of having a higher amount of it in your computer.
You can now easily compare and choose from different processors of the same generation and determine the type of workloads it can handle.