In This Article
What is High-Level Formatting?
High-level formatting refers to the third part of the formatting process where a new file system is typically generated on the hard disk. In other words, it is the process where root directory and file allocation tables are created and configured.
Technically, high-level formatting is a method of creating vital file system areas by initializing parts of the hard drive.
It typically uses the data structures used by the operating system. This is vital to find the contents of the logical drive or partition.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- When a part of the hard disk is initialized to create new file systems on it, it is called high-level formatting. It comprises data structures used by the operating system for finding the contents of the partition or logical drive.
- High-level formatting is the third part of the formatting process. The other two are low-level formatting and partitioning, respectively.
- When the format command in MS-DOS is used, it is said to be high-level formatting. It may also occur when the operating system is installed or while a new disk is added.
- This type of formatting is usually done by the users when they want to erase the hard disk and install the operating system back on it.
- High-level formatting is usually done on hard drives that are free from errors. If there are any errors, then low-level formatting should be done before high-level formatting can be completed.
Understanding High-Level Formatting
High-level formatting is a specific type of formatting a hard disk which, in simple words, means creating a new file system within a hard drive.
A high-level format is called ‘format’ simply, and the program or the format command used to perform high-level formatting is usually called format.com, which is the same disk format utility used to frame floppy disk drives.
Typically, formatting involves three different parts namely, low-level formatting, partitioning and high-level formatting, in that order. The three stages can be summarized as follows:
- Low-level formatting is the first part of formatting and involves preparing the basic medium. This involves pretty simple steps and basically involves erasing a drive and resetting it back to its factory settings.
- The second part of the formatting process is commonly referred to as partitioning, which involves dividing the drive into several subparts. However, in some instances, it also involves writing information to the device. This allows it to boot the operating system from it.
- The third part of the process is commonly known as high-level formatting and it mostly refers to the process of creating a new and empty file system on the disk partition or a logical volume.
The process of high-level formatting does not erase all of the data stored on the hard drive. The actual process of high-level formatting involves the following:
- Erasing the path to access the data stored on a partition or a logical volume
- Rebuilding the prevailing data structures such as the boot sector
Therefore, after high-level formatting, data can be easily recovered from the formatted hard drive.
In this typical process of erasing and recreating the data structure, the existing data is not wiped off the drive. It is a process to actually prepare the drive to install different apps or software or upgrade the system.
However, depending on the circumstances, high-level formatting may also refer to different other tasks and performing other functions and processes, and they are abridged as follows:
- The process of installing a boot sector
- The process of erasing the hard drive to reinstall the operating system back onto it
- Creating and configuring File Allocation Tables (FATs)
- Creating the root directory to build the subdirectories and files on it
Usually, the high-level formatting process cannot be initiated if there are errors already existing on the hard drive.
In that case, low-level formatting has to be performed first on the disk so that high-level formatting can be done on the drive successfully.
Moreover, if you consider the z/OS Unix System Services in particular, high-level formatting is typically performed at three different levels. These are:
- Setting the volume with ICKDSF
- Setting a VSAM Linear Data Set (LDS)
- Setting a zFS aggregate in the LDS by using ioeagfmt
While creating a file system on the disk partition or a logical volume, high-level formatting uses the data structures that are typically used by the operating systems.
This is a significant aspect of the process because it helps in identifying the contents stored in the partition or the logical volume.
In high-level formatting, which may also occur when a new disk is added or while the operating system is being installed, it is common for the distributed file system or the disk to specify other things such as:
- A non-compulsory boot block
- Various volume and directory information of the operating system
Typically, formatting a complete partition or a logical drive may take a considerable amount of time because it may optionally scan the entire hard disk for any defects.
On the other hand, high-level formatting, in comparison, is usually a pretty fast operation, which is why it is also referred to as quick formatting at times.
Example of High-Level Formatting
One of the most common examples of high-level formatting is the use of the format command in MS-DOS.
It is also done when a hard drive is erased by the users to reinstall an operating system on it or to create and configure new file allocation tables or root directories on it.
In addition to the above, high-level formatting may also be needed to be done during several other situations such as:
- On floppy disks, along with low-level formatting
- As a part of the process of allocating a file
- By different operating systems
- By a utility program designed explicitly for a particular file system
- While removing write protection from a hard disk
- During the process of restoring a hard drive to its full capacity
- Freeing disk space for writing new data on it
Such type of formatting is also useful to fix a few specific problems such as:
- Errors existing in the file system
- A corrupted hard drive
- The developing bad sectors
Sometimes, it is also needed while new data is written on the fly in a few specific older access methods.
What is the Function of High-Level Formatting?
In simple words, the main function of high-level formatting is to write on a file system, a partition label, a cluster size, and others for a newly created volume or partition.
However, some other functions of high-level formatting involve the following:
- It clears the data on the hard disk.
- It generates boot information.
- It initializes FAT.
- It labels the logical bad sectors when a partition existed.
In general, the function of high-level formatting is not to do any harm to the hard disk. On the contrary, it is useful to manage the file system and the hard drive in a much better way.
How to Perform High-Level Formatting?
Performing high-level formatting is not a difficult process at all. It can be done easily in different ways such as with the Administrator, DiskPart, the Windows built-in Disk Management tool, and others.
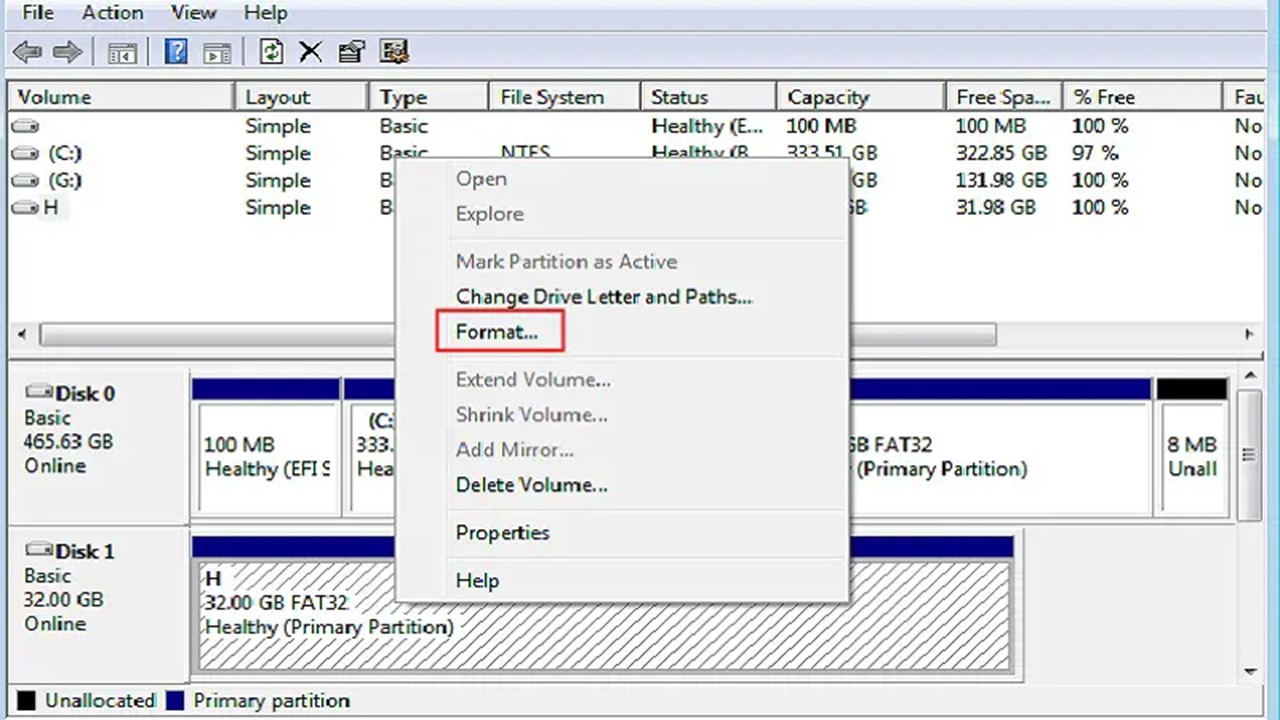
Performing high-level formatting on a hard drive by using the Windows Disk Management tool involves the following few steps:
- Pressing the Windows and R together on your keyboard to launch Run
- Typing ‘diskmgmt.msc’ on the Run Box
- Pressing Enter to open the Disk Management utility
- Right-clicking the hard drive that is to be formatted
- Choosing the file system
- Start formatting
Performing high-level formatting on your hard drive by using DiskPart involves opening the Run box in the same way as above, but typing ‘diskpart’ this time in the Run box.
When Diskpart opens, you will need to implement the following commands:
- list disk
- select disk n (where n is the disk number of the hard drive to be formatted)
- clean
- create partition primary
- format fs=fat32 quick (if you want the FAT32 file system, or input others)
- exit
Normally, both of these methods will successfully complete high-level formatting on your hard drive for Windows 7.
Windows 8, and Windows 10. However, they may not work every time, especially when there are the following limitations and conditions to formatting:
- If the storage capacity of the hard drive is in excess of 32 GB, they will not be able to format it to FAT32.
- If the hard drive is infected with a virus, has errors on it, or is write-protected, they will not be able to format it.
- If any unexpected mistake is made during the operation, which is highly probable for the beginners specially to make, recalling the operation immediately is not possible.
A better, safer, and more useful alternative is to use a reliable third-party software utility program designed specifically for performing high-level formatting on a hard drive, AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard, for example.
Usually, the functionalities of these software programs are not restricted by the type of the file system or the capacity or type of the hard disk.
You can use them for any type of storage system apart from the traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) including the following:
- Solid State Drive (SSDs)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB) flash drives
- Secure digital (SD) cards
You can use these programs for different types of file systems as well such as:
- New Technology File System (NTFS)
- FAT32
- Ext 2
- Ext 3
- Ext 4
- Extended File Allocation Table (exFAT)
- Typically, these are the steps to follow to use these software programs:
- Download and install the software
- Click it to open it
- Right-click on the drive you want to format
- Click on the ‘Format partition’ option
- Choose a file system
- Specify the cluster size if you want
- Click ‘OK’
- Click ‘Apply’
High Level Formatting Vs Low Level Formatting
- High-level formatting is recoverable. On the other hand, low-level formatting does not allow recovery of data because it will wipe the entire hard disk of its data, preventing almost all data recovery tools from restoring the formatted data.
- The high-level formatting process is much faster in comparison to low-level formatting.
- High-level formatting is typically the third and final part of the entire formatting process. On the other hand, low-level formatting is the initial process, which is followed by the disk partitioning process.
- The high-level formatting process typically refers to the creation of a new file system. On the other hand, low-level formatting typically involves erasing the contents of a hard drive and restoring it back into the original factory settings.
- High-level formatting is also the process of creating the Master Boot Record (MBR) and the File Allocation Table (FAT) on the hard disk. On the other hand, in the low-level formatting process tracks and cylinders are outlined for a blank hard disk and then dividing them into various sectors.
- High-level formatting usually does not have as big an impact on the hard disk drive as low-level formatting, which may shorten the service life of the hard disk.
- High-level formatting is used more widely in a wide range of different conditions, but in comparison, low-level formatting does not have such a wide application range.
- Viruses that may be existing in the MBR cannot be removed by high-level formatting, but they can be removed by low-level formatting since it will erase all the data stored on the disk.
- The high-level formatting process is typically used by Windows users, both beginners and professionals. It is used for internal and external hard drives and USB or SD card owners. On the other hand, low-level formatting is used by computer processionals or geeks, storage device manufacturers and providers.
- The high-level formatting process allows using different formatting tools such as Disk Management, DiskPart, File Explorer, Command Prompt, and third-party formatting tools. On the other hand, low-level formatting, in comparison, usually allows using only third-party format tools.
- The command used for high-level formatting is Format, but in low-level formatting, DM commands of different tools and software are used.
- The features of high-level formatting include clearing data, checking sectors, deleting marks, initializing boot information, and upgrading partition table information. On the other hand, the features of low-level formatting include media check, dividing tracks and sectors, disk media testing, setting cross factors, numbering each CHS.
- High-level formatting cannot be initialized or completed if there are errors or bad sectors in the disk. On the other hand, low-level formatting can be done even if there are errors or bad sectors in the Hard Disk Drives.
- High-level formatting will not cause any physical damage to the internal or external hard drives, USB, or SD card. On the other hand, low-level formatting can cause physical damage to the hard disk drive, especially if it has bad sectors in it.
Conclusion
High-level formatting is the process of initializing portions of a hard drive to reinstall the data structures of the file system on it.
Through this article, you now have a fair idea about the process, how it works, and the ways in which you can perform high-level formatting on your hard drive for better file management.